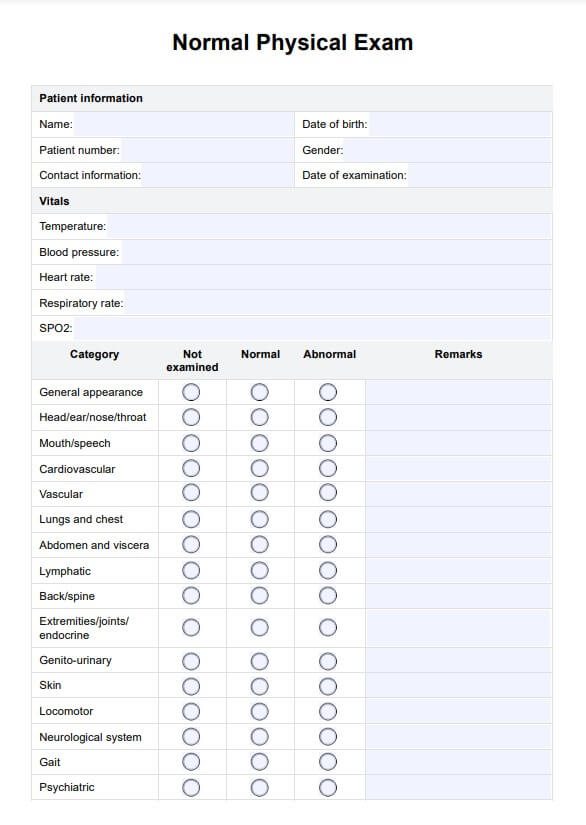
A full physical exam typically includes evaluating the patient's overall health, checking vital signs such as blood pressure, pulse, and temperature, and a head-to-toe examination. This comprehensive exam covers the head, neck, thorax, abdomen, extremities, and musculoskeletal system. A neurological assessment, including an evaluation of cranial nerves, reflexes, and motor and sensory functions, is performed.
Normal Physical Exam Template
Explore a comprehensive guide to a normal physical exam. Learn about key components, procedures, and documentation tips to enhance patient care and assessment.
Normal Physical Exam Template Template
Commonly asked questions
To document a normal physical exam, clearly and concisely describe the patient's appearance and note any findings. Include normal results for vital signs, such as heart rate and blood pressure, and document normal physical examination findings for each assessed body system. Ensure all observations are specific and objective to maintain accuracy.
In a musculoskeletal assessment, you can describe the patient's posture, gait, and movement abnormalities or limitations. Note muscle strength, tone, signs of atrophy, joint range of motion, tenderness, or swelling. Document any abnormal reflexes, muscle tone, and signs of weakness or paralysis.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











