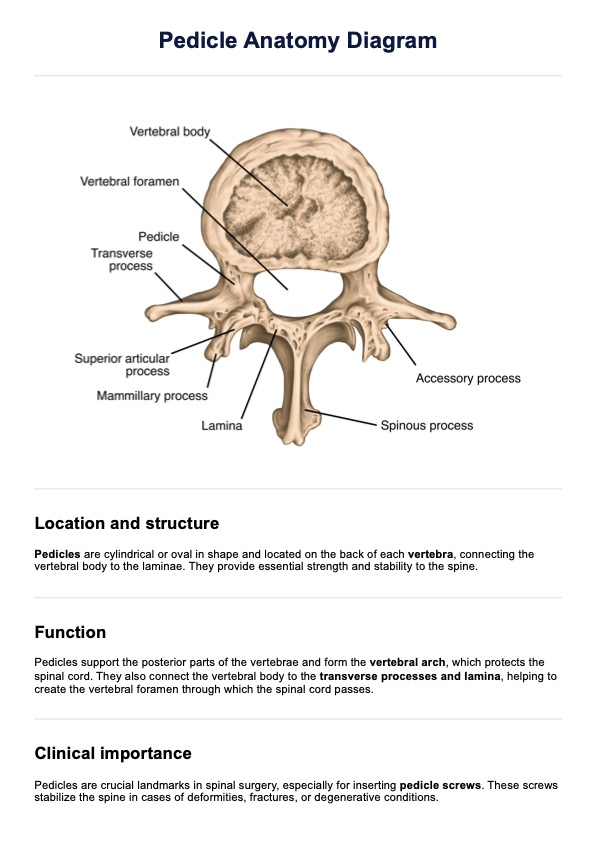
Pedicle Anatomy Diagram
Explore the anatomy of the vertebral pedicle with our detailed diagram. Learn key structures and the importance of pedicle anatomy for spinal procedures.


What is the pedicle?
The pedicle is a bony structure extending posteriorly from the vertebral body on each side of a vertebra. The pedicles are oriented from T1 to T12, but more medially from T1 to T10 and becoming nearly neutral at the T11 and T12 levels. It connects the vertebral body to the posterior parts of the vertebra, including the lamina and transverse processes. The pedicles help form the walls of the vertebral foramen, through which the spinal cord travels.
They also include the superior and inferior vertebral notches, which align with those of adjacent vertebrae to create the intervertebral foramina. These foramina allow spinal nerve roots and blood vessels to pass through. The pedicles' robust cortical bone provides a crucial link between the vertebra's anterior and posterior sections, making them essential for anchoring spinal instrumentation such as pedicle screws.
Pedicle Anatomy Diagram Template
Pedicle Anatomy Diagram Example
What is the importance of knowing pedicle anatomy?
A thorough understanding of pedicle anatomy is essential for spine surgeons, particularly when performing instrumented spinal fusion procedures involving pedicle screw fixation in the thoracic and lumbar spine. Pedicle screws provide rigid fixation by being inserted through the pedicles into the vertebral body. Accurate placement is crucial to avoid damaging nearby neural structures such as the spinal cord and nerve roots.
Pedicle anatomy varies between vertebral levels. For instance, thoracic pedicles typically have a more medial angulation compared to lumbar pedicles. Surgeons must recognize these differences to determine the optimal entry point and trajectory for screw placement.
Preoperative imaging is vital for assessing pedicle integrity and dimensions to choose the correct screw size and ensure secure bony purchase while minimizing the risk of pedicle breach or fracture.
How does our Pedicle Anatomy Diagram work?
Our Pedicle Anatomy Diagram template is designed to help you understand the function of the pedicles. Here’s how to use the template effectively:
Download and open the template
Download the Pedicle Anatomy Diagram template and open it on your device. Ensure you have the appropriate software that allows you to view, edit, or annotate the diagram as needed.
Understand the pedicles and surrounding structures
Carefully study the diagram to grasp the detailed anatomy of the pedicle and its surrounding parts. Observe how the pedicle connects to other vertebral components, providing a foundation for spinal stability. Recognizing the relationship between the pedicle and adjacent structures is crucial for accurate analysis or study using this template.
Annotate the diagram with relevant details
Use the template to add any necessary annotations or notes. This might involve marking specific areas of interest, recording measurements, or highlighting important relationships between different structures.
Use the annotated diagram as a reference tool
Keep the annotated Pedicle Anatomy Diagram on hand as a reference. Whether you are studying vertebral anatomy, planning a medical procedure, or educating others, this diagram will serve as a valuable visual guide to support your knowledge and work.
How will our diagram benefit healthcare professionals?
Our Pedicle Anatomy Diagram will benefit healthcare professionals, including surgeons, radiologists, and medical students, in several ways:
Preoperative planning
The Pedicle Anatomy Diagram is invaluable for planning spinal surgeries, especially for procedures involving pedicle screw fixation. It provides a detailed view of the lumbar spine, thoracic spine, and the associated vertebral bodies. Surgeons can use it to understand the anatomy of the thoracic and lumbar spine, ensuring accurate placement of pedicle screws in the lumbar vertebrae and thoracic pedicle screw placement. This clarity helps in avoiding complications and achieving optimal alignment of the spinal column.
Diagnostic interpretation
For radiologists, the diagram serves as a reference for interpreting imaging studies of the vertebral bodies and lumbar vertebrae. It aids in correlating pedicle screws with anatomical structures observed in MRI or CT scans. Understanding the anatomy of the pedicle and its relationship to the spinal cord and vertebral column enhances diagnostic accuracy, particularly in assessing the success of pedicle screw fixation or identifying issues in the mid thoracic spine.
Educational purposes
The diagram is an excellent educational tool for learning about the lumbar spine, thoracic spine, and the detailed anatomy of the pedicle. It helps students visualize the placement of pedicle screws and understand their role in stabilizing the vertebral bodies. By studying the anatomy of the spinal column and how pedicle screws interact with the vertebral body, students gain a comprehensive understanding of spinal mechanics and surgical interventions.
Commonly asked questions
The pedicle is a bony structure that extends from the vertebral body to the transverse process of each vertebra. It plays a crucial role in the stability of the spine and serves as an attachment point for pedicle screws used in spine surgery.
Accurate knowledge of pedicle anatomy is essential for spine surgery to ensure proper placement of pedicle screws. Misplacement can lead to complications, including damage to the nerve root or spinal cord. Understanding the pedicle height and its relationship to the vertebral body helps in avoiding such issues.
The spinous process is the bony projection that extends posteriorly from the vertebra. It is connected to the pedicle via the lamina. In spine