Squish Test
Discover how to assess and manage sacroiliac joint issues effectively with our comprehensive Squish Test guide. Download your free PDF today.


What does it mean for the sacroiliac joint to have impaired mobility?
Impaired mobility in the sacroiliac joint refers to reduced normal movement. This joint, located at the connection between the sacrum (the base of the spine) and the iliac bones (the pelvis), typically has a very limited range of motion. When its mobility is impaired, either through decreased or excessive movement, it can affect the joint's function.
What can impair a sacroiliac joint's mobility?
Several factors can lead to impaired mobility in the sacroiliac joint:
- Inflammation: Conditions such as sacroiliitis can cause inflammation in the sacroiliac joints, leading to pain and reduced mobility.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause the ligaments in the sacroiliac joint to relax and stretch, potentially leading to instability and altered mobility.
- Trauma: An injury from impact or sudden force can damage the ligaments and joint surfaces, affecting movement.
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis or other forms of arthritis can degrade the cartilage in the joint, leading to stiffness and mobility issues.
- Muscular imbalance: Imbalances or weakness in the muscles supporting the pelvis and spine can lead to abnormal stress on the sacroiliac joints, impacting their mobility.
What problems can this cause?
Impaired mobility in the sacroiliac joint can lead to several issues:
- Pain: The most common symptom is pain in the lower back, buttocks, or legs, which can be exacerbated by prolonged standing or sitting.
- Instability: Excessive movement can lead to a feeling of instability in the pelvis, making it difficult to stand or walk comfortably.
- Limited mobility: Stiffness or reduced movement can affect the overall mobility, impacting daily activities and quality of life.
- Radiating symptoms: Pain may radiate to the lower extremities, resembling sciatica, due to irritation of adjacent nerves.
- Postural changes: Chronic issues with the sacroiliac joint can lead to compensatory changes in posture, potentially causing secondary pain in other areas like the hips or lower spine.
Squish Test Template
Squish Test Example
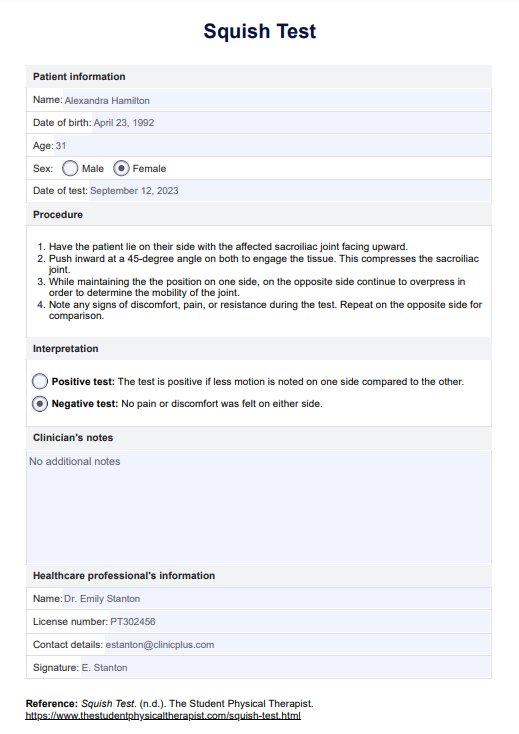
What is the Squish Test?
The Squish Test, also known as the pelvic compression test, is a diagnostic technique used to assess the integrity and function of the sacroiliac joint. It helps determine if pain or discomfort in the lower back, buttocks, or legs is due to sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
How is this test conducted?
Here are the steps involved in conducting the Squish Test:
- The patient lies on their side with the affected sacroiliac joint facing up.
- The examiner applies pressure at a 45-degree angle, effectively compressing the pelvis and 'squishing' the sacroiliac joint.
- The test is typically repeated on the opposite side for comparison.
How are the results interpreted?
The interpretation of the Squish Test results is straightforward:
- Positive result: If the patient experiences pain or discomfort in the sacroiliac joint during the test, it is considered a positive result. It is also considered positive if less motion is noted on one side.
- Negative result: No pain or discomfort during the test, which suggests that the sacroiliac joint is likely not the source of the patient’s symptoms.
How to use our Squish Test template
Our Squish Test template is designed to streamline the assessment of sacroiliac joint mobility, helping healthcare professionals efficiently diagnose and manage related conditions. Here’s how to effectively use the template:
Step 1: Download the template
Start by downloading the Squish Test template from the provided link. Ensure you have the most current version for accurate assessment guidelines.
Step 2: Conduct the test
During the patient's visit, perform the test as instructed in the template. Carefully observe and note any signs of discomfort, pain, or resistance, as these are critical for accurate diagnosis.
Step 3: Analyze the results
After completing the test, analyze the findings using the criteria provided in the template. This step determines whether the test is positive or negative, influencing the subsequent treatment plan.
Download our free Squish Test template example here
Benefits of conducting this test
The Squish Test is a valuable diagnostic tool in the field of sports medicine and orthopedics, particularly for assessing the sacroiliac joint's functionality. Conducting this test offers several key benefits that contribute to more effective patient care and management:
- Early detection of dysfunction: The Squish Test allows healthcare professionals to identify sacroiliac joint dysfunction at an early stage. Early detection is crucial for preventing further complications and implementing timely interventions that can alleviate symptoms and improve patient outcomes.
- Non-invasive assessment: As a non-invasive procedure, the Squish Test poses minimal risk to patients. It does not require any special equipment or exposure to radiation, making it a safe choice for repeated assessments, which is particularly beneficial for monitoring the progression of treatment or recovery.
- Guided treatment decisions: The results from the Squish Test provide valuable insights into the nature of a patient’s sacroiliac joint issues. This information helps healthcare providers tailor treatment plans more effectively, choosing interventions that are most likely to offer relief and support recovery based on the specific dysfunction identified.
- Enhanced patient communication: Performing the test and discussing the results with patients can enhance communication and build trust. Patients gain a better understanding of their condition, which can motivate them to adhere more closely to prescribed treatment plans and actively participate in their recovery process.
How orthopedists address impaired sacroiliac joint mobility
Orthopedists use a variety of methods to address impaired mobility in the sacroiliac joint, tailored to the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here's how they typically manage these issues:
- Diagnosis and assessment: Accurate diagnosis is critical, involving clinical examinations and possibly imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs to determine the exact cause of the impaired mobility.
- Physical therapy: A cornerstone of treatment, physical therapy focuses on strengthening the muscles around the sacroiliac joint, improving flexibility, and reducing inflammation through techniques such as stretches and exercises.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs or muscle relaxants can be prescribed to reduce pain and swelling.
- Joint injections: For more severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered directly into the sacroiliac joint to provide relief from pain and inflammation.
- Support devices: Pelvic belts or braces may be recommended to stabilize the sacroiliac joint and reduce excessive movement, which can alleviate pain.
- Surgical interventions: In cases where conservative treatments fail, and the impairment significantly affects the quality of life, surgical options such as sacroiliac joint fusion might be considered to stabilize the joint permanently.
Commonly asked questions
To improve sacroiliac joint mobility, regular exercise that focuses on strengthening the core and pelvic muscles and stretching the lower back, hips, and pelvis can be effective. Physical therapy techniques such as manual manipulation or joint mobilization may also provide relief.
The Flexion, Abduction, and External Rotation (FABER) test is best for assessing sacroiliac joint mobility. This test evaluates pain and discomfort in the sacroiliac joint as the leg is positioned to stress the joint in various directions.
With SI joint dysfunction, it's advisable to avoid movements that involve excessive twisting of the hips or lower back, heavy lifting that strains the lower back, and prolonged sitting or standing in asymmetrical positions, as these can exacerbate pain and stiffness.