Palliative Performance Scale
Learn about the Palliative Performance Scale (PPS) and its application in hospice care. Download a free PDF template to use the PPS effectively.


What is a Palliative Performance Scale (PPS)?
The Palliative Performance Scale (PPS) is a reliable and valid tool based on and derived from the Karnofsky Performance Scale (KPS). Healthcare professionals use it to assess the functional status of palliative care patients, commonly advanced cancer patients or those with a significant disease like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Anderson et al., 1996).
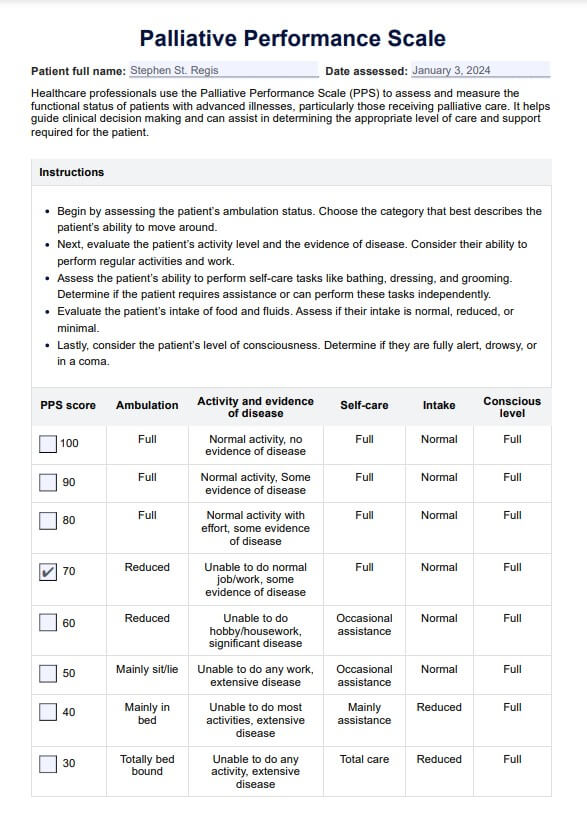
The PPS comprehensively evaluates a patient's ability to perform daily activities and addresses physical decline, level of consciousness, and the need for assistance. This is an 11-point scale ranging from 0% to 100%, with 10% increments. Each score represents a specific level of functional ability and describes the extent of assistance required for self-care activities, such as ambulation, activity level, evidence of disease, intake, and consciousness level (Ho et al., 2008). This makes it an essential tool to those who provide a palliative medicine consultation service because it can help determine disease trajectory, and a clear disease trajectory predicts survival estimates.
At the higher end of the scale, a score of 100% indicates a fully ambulatory patient with normal activity levels and self-care abilities with minimal or no help. As the score decreases, the patient's functional status declines, indicating a greater need for assistance and a higher level of palliative care interventions.
The PPS scale is widely used in palliative care settings, including hospice care and a palliative care unit, to assess a patient's eligibility for services and to guide care planning. Patients with a PPS score of 70% or lower are generally considered appropriate candidates for hospice care, as they typically require considerable assistance with self-care activities and have limited life expectancy.
Palliative Performance Scale Template
Palliative Performance Scale Example
How does this PPS Scale work?
The PPS uses a 100-point scale, with 100% representing a patient's normal activity level and 0% indicating death. By evaluating five critical areas of a patient's daily life, the PPS offers a snapshot of their functional ability (Ho et al., 2008):
- Ambulation: Ranging from fully ambulatory to completely bed-bound.
- Activity and evidence of disease: Considering normal activity, reduced ambulation, and extensive disease.
- Self-care: Assessing the assistance required for self-care activities, such as bathing, dressing, and eating.
- Intake: Evaluating the person's usual eating habits or oral intake and need for nutritional sustenance.
- Conscious level: Ranging from full alertness to coma or minimal responsiveness to verbal or physical stimuli.
The PPS score provides valuable information for health care professionals in palliative care settings, hospice care, and end-of-life care situations.
How does this Palliative Performance Scale work?
The PPS is a reliable tool used in palliative care to assess a patient's physical abilities, level of consciousness, and overall care needs. Below is a step-by-step guide on how the PPS works, making it a comprehensive resource for healthcare practitioners.
Step 1: Determine the level of ambulation and activity
Begin by assessing the patient's physical ability to perform daily activities and their level of ambulation. On the PPS, being fully ambulatory and able to carry on with normal job duties or hobbies like enjoying walking or backyard putting corresponds to higher scores, indicating minimal impact on the patient's lifestyle.
Step 2: Evaluate the ability to carry out self-care
The self-care column of the PPS measures a patient's ability to fulfill personal care tasks, ranging from fully independent to completely unable, showcasing degrees of physical decline. The goal is to pinpoint where patients require minor assistance for certain activities, significant help, or are totally bed-bound, guiding healthcare providers in adjusting care strategies accordingly.
Step 3: Assess oral intake and response to physical stimuli
A normal intake reflects a diet unaltered by disease, while new or challenging symptoms due to illnesses like cancer or extensive disease may affect this. Additionally, evaluating how the patient responds to external stimuli helps in understanding their conscious level and the presence of good cognitive abilities. This is crucial in planning active treatments or palliative measures.
Step 4: Refer to the PPS
The PPS's prognostic value lies in its ability to predict median survival time based on the patient's condition. This function is instrumental for clinicians in making informed clinical judgments regarding disease progression and potential significant complications.
Step 5: Calculate the PPS score and implementing care plans
The Palliative Performance Scale score is determined after evaluating the patient across different dimensions—activity, self-care, oral intake, and consciousness. This score ranges from 100% (full alertness and normal activity) to 0% (death). Using this score, healthcare professionals can communicate effectively about the patient's status, provide meaningful survival estimates, and tailor-fit care plans that address physical decline, provide appropriate support for maintaining quality of life, and help in decision-making for advanced care planning.
Since we mentioned the Karnofsky Performance Scale earlier, we'd like you to know that we have a Karnofsky performance scale template. It will provide valuable support to enhance your practice and client results. Use it alongside the PPS scale to cover more ground.
Benefits of free PPS template
The free Hospice PPS scale template offers several advantages to healthcare professionals in palliative and hospice care settings. This is a standardized and accessible way to assess a patient's functional status. The PPS can improve patient outcomes, facilitate communication among the care team, and streamline the decision-making process.
This section will explore the key benefits of using a free Hospice PPS scale template in greater detail.
Standardized assessment
The PPS provides a standardized method for assessing a patient's functional status, promoting consistency and clarity among healthcare professionals. This common language helps ensure that all care team members have a shared understanding of the patient's condition, which can lead to more informed decision-making and better patient outcomes.
Improved communication
Using the PPS can facilitate communication among the care team by concisely summarizing the patient's functional status. This can help prevent misunderstandings and promote more effective collaboration, ultimately improving the quality of care provided to the patient.
Guides clinical decision-making
The PPS can help inform decisions about treatment plans, resource allocation, and care transitions, leading to more personalized and appropriate care. By offering a snapshot of the patient's current functional status, the PPS can assist healthcare professionals in identifying areas where additional support or intervention may be needed.
Healthcare professionals can use our free Hospice PPS scale template to take advantage of these benefits and improve the quality of care provided to patients in palliative and hospice settings.
References
Anderson, F., Downing, G. M., Hill, J., Casorso, L., & Lerch, N. (1996). Palliative performance scale (PPS): a new tool. Journal of Palliative Care, 12(1), 5–11. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8857241/
Ho, F., Lau, F., Downing, M. G., & Lesperance, M. (2008). A reliability and validity study of the palliative performance scale. BMC Palliative Care, 7, 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-684X-7-10
Commonly asked questions
Healthcare professionals use the Palliative Performance Scale to assess the functional status and decline of palliative care patients, primarily those with advanced cancer or other significant illnesses. The PPS evaluates five key areas: ambulation, activity, evidence of disease, self-care, oral intake, and level of consciousness.
A PPS score of 30% indicates that the patient is entirely bed-bound, requiring extensive assistance for all self-care activities, and has a minimal intake, often only able to take sips of fluid. At this stage, the patient is likely experiencing profound weakness or paralysis, with a significantly reduced level of consciousness, potentially ranging from drowsiness to coma.
While both scales assess a patient's functional status and ability to perform daily activities, the PPS is specifically designed for palliative care settings and focuses on five key areas. In contrast, the KPS is a broader measure of general performance status. Additionally, the PPS scale is presented in 10% increments, while the KPS uses a 100-point scale with 10-point increments.