Catherine Bergego Scale (CBS)
Learn the symptoms, causes, scoring, and benefits of the Catherine Bergego Scale (CBS) using our professional template to assess unilateral neglect.


What is unilateral neglect?
Unilateral neglect, also known as hemispatial neglect, is a neurological condition that typically occurs after damage to one hemisphere of the brain, most commonly the right. This damage leads to an inability to attend to or respond to stimuli on the opposite side of the body. For example, a person with right hemisphere damage might ignore everything on their left side. Unilateral neglect is often associated with stroke but can also result from traumatic brain injury, brain tumors, or other neurological conditions. The severity and impact of unilateral neglect can vary widely among individuals.
Although closely related, it’s essential to distinguish unilateral neglect from unilateral spatial neglect. Spatial neglect specifically refers to a failure to acknowledge or respond to objects or stimuli within the spatial environment on the affected side. Additionally, acute-stage spatial neglect is often observed in the early phases following a stroke and is critical for determining the initial rehabilitation approach.
In contrast, unilateral neglect can encompass a broader range of deficits, including personal neglect (ignoring one side of the body), peripersonal neglect (ignoring the space within arm’s reach), and unilateral spatial orientation neglect. Both conditions significantly impact daily living activities and quality of life. The severity of behavioral neglect, ranging from mild to severe, is also associated with patients' self-awareness of neglect (anosognosia).
Symptoms
The symptoms of unilateral neglect can vary but generally include:
- Difficulty paying attention to one side of the environment.
- Ignoring food on one side of the plate.
- Forgetting to dress or groom one side of the body.
- Bumping into objects or walls on the neglected side.
- Difficulty reading or writing, as the patient may neglect parts of words or sentences.
- In severe cases, complete unawareness of the affected side.
- Abnormal gaze orientation, where the patient may consistently turn their head or eyes away from the neglected side.
Causes
Unilateral neglect can be caused by various neurological conditions, with the most common being:
- Stroke, particularly affecting the right hemisphere.
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Brain tumors.
- Neurodegenerative diseases.
- Infections affecting the brain, such as encephalitis.
- Any condition leading to significant damage to one hemisphere of the brain.
Complications
Unilateral neglect can lead to several complications, impacting both safety and quality of life:
- Increased risk of injury from falls or accidents due to unawareness of the neglected side.
- Difficulties in performing daily activities, leading to decreased independence.
- Social isolation due to challenges in communication and mobility.
- Emotional and psychological distress, including frustration and depression.
- Reduced effectiveness of rehabilitation efforts if the condition is not managed correctly.
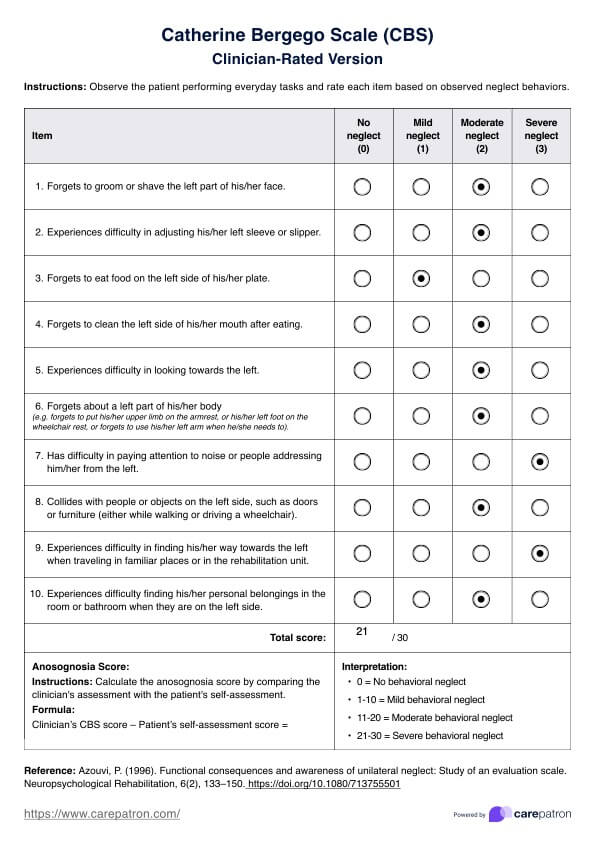
Catherine Bergego Scale (CBS) Template
Catherine Bergego Scale (CBS) Example
What is the Catherine Bergego Scale (CBS)?
The Catherine Bergego Scale (CBS) is a standardized checklist designed to detect the presence and degree of unilateral neglect while observing everyday life situations. Developed by Catherine Bergego and her colleagues, this scale is a valuable tool for clinicians to evaluate the impact of neglect on a patient’s daily functioning and to measure self-awareness of neglect. The CBS provides a comprehensive assessment involving the clinician’s observations and the patient’s self-report. Additionally, the many psychometric properties of the CBS, including its reliability and validity, make it a robust tool for clinical use in physical medicine.
The CBS can be used alongside the more general National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), which measures the severity of stroke symptoms. CBS's detailed behavioral assessment allows clinicians to tailor rehabilitation strategies to address each patient’s needs. Being a functional independence measure, it provides insights into the practical implications of neglect in daily activities. The CBS is widely used in rehabilitation medicine to tailor treatment plans for patients with unilateral neglect.
The CBS is also useful for measuring self-awareness of neglect. Patients are asked to rate their difficulties on the same tasks, and the difference between the clinician’s and the patient’s ratings provides an anosognosia score. By using the CBS, healthcare professionals can better understand the patient’s condition and monitor progress over time with appropriate treatment (Azouvi, 1996).
Scoring and interpretation
Scoring the Catherine Bergego Scale involves rating each of the ten items on a 4-point scale: 0 (no neglect), 1 (mild neglect), 2 (moderate neglect), and 3 (severe neglect). The total score is the sum of the individual item scores, with a maximum possible score of 30. Higher CBS scale scores indicate more severe neglect. For instance, a score between 0 and 10 suggests mild neglect, 11 to 20 indicates moderate neglect and 21 to 30 reflects severe neglect.
In addition to the clinician’s ratings, the CBS includes a patient self-assessment component to evaluate anosognosia or the patient’s awareness of their neglect. The CBS measures self-awareness of neglect by having patients rate their difficulties on the same tasks, and the anosognosia score is calculated as the difference between the clinician’s total score and the patient’s self-assessment score. This difference helps clinicians understand the extent of the patient’s awareness of their condition and tailor interventions accordingly (Azouvi, 1996).
How to use our Catherine Bergego Scale template
Our Catherine Bergego Scale template includes clinician-rated and patient-self-reported versions to assess unilateral neglect and anosognosia comprehensively.
Step 1: Download the template
Start by downloading our CBS template, which contains clinician-rated and patient-self-reported versions. This template is designed to be user-friendly and easy to administer.
Step 2: Prepare the patient
Ensure that the patient is comfortable and understands the purpose of the assessment. Explain that the clinician will observe them performing everyday tasks and that they will also answer some questions about their experiences.
Step 3: Administer the clinician-rated version
The clinician should use the first page of the template to observe and rate the patient on the 10 items listed. This involves watching the patient perform self-care activities, such as handling personal belongings and noting signs of unilateral neglect.
Step 4: Administer the patient-self-reported version
On the second page, ask the patient to answer the 10 questions about neglect assessment and their experiences with everyday tasks. This will help assess their self-awareness of neglect.
Step 5: Calculate the anosognosia score
After both versions are completed, the clinician should calculate the anosognosia score by subtracting the patient's self-assessment score from the clinician's CBS score. This final score helps determine the patient's awareness of their neglect.
Benefits of using our template
Using our Catherine Bergego Scale template offers several advantages for healthcare professionals:
Comprehensive assessment
Our template thoroughly evaluates unilateral neglect by combining clinician observations with patient self-reports, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the patient's condition.
Standardized measure
By using a standardized checklist, our template ensures consistency in assessments, making it easier to track patient progress over time and compare results across different cases.
Reference
Azouvi, P. (1996). Functional consequences and awareness of unilateral neglect: Study of an evaluation scale. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation, 6(2), 133–150. https://doi.org/10.1080/713755501
Commonly asked questions
The CBS is designed to detect the presence and degree of unilateral neglect in patients by observing their performance in everyday tasks. It also measures the patient's self-awareness of their neglect.
The CBS is administered by a clinician who observes the patient performing specific tasks. The clinician rates the patient's performance from 0 to 3. There is also a self-reported version where the patient assesses their difficulties.
A high CBS score indicates more severe unilateral neglect. The total score can range from 0 to 30, with higher scores reflecting greater impairment.