Heart Calcium Score
Have this Heart Calcium Score Chart on hand when analyzing and interpreting heart calcium scores. Download our free template.


What is a Heart Calcium Score Chart?
A Heart Calcium Score Chart is derived from a Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) test, a specialized heart CT scan. The coronary calcium scan utilizes multidetector CT (MDCT) technology that captures detailed images of the coronary arteries to identify and measure calcium deposits or blood flow (American Heart Association, Inc., 2023).
The CAC test provides a “calcium score,” indicating the quantity of calcium in the coronary arteries. This coronary artery calcium scoring reflects the level of plaque present, which can predict future heart disease risk, including heart attacks. High calcium scores correlate with a higher likelihood of significant coronary artery disease.
The results of the calcium score test is especially beneficial for patients at intermediate risk of heart disease. They assist healthcare professionals in making informed decisions regarding initiating preventive therapies such as statins or low-dose aspirin. It is particularly useful for individuals uncertain about starting or restarting statin therapy or those with intermediate risk factors.
However, it is important to note that CAC testing is not typically recommended for routine screening in low-risk individuals without symptoms, and it involves a radiation dose comparable to that of a mammogram (American Heart Association, Inc., 2023).
A Heart Calcium Score Chart is a valuable tool used to interpret and understand the results of a CAC test. This can help healthcare professionals assess an individual's risk of developing heart disease and determine a suitable treatment plan.
Heart Calcium Score Template
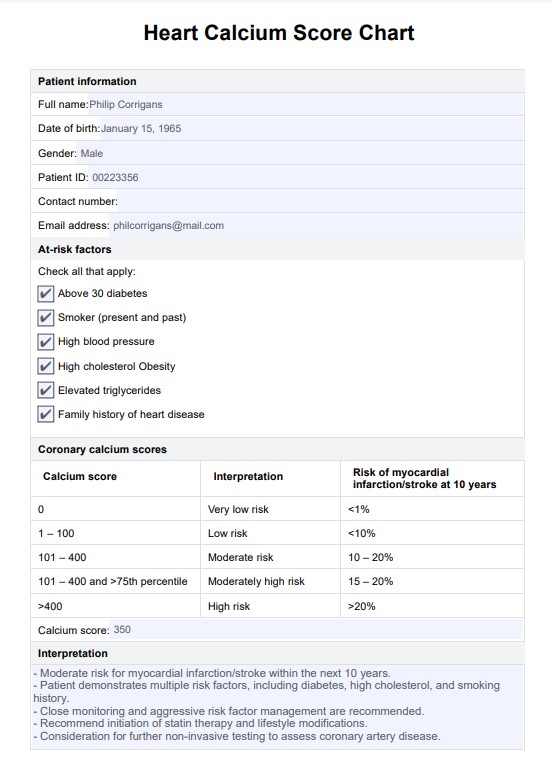
Heart Calcium Score Example
How to use the Heart Calcium Score Chart?
Using the Heart Calcium Score Chart effectively involves several key steps. The chart plays a pivotal role in evaluating coronary artery disease risk by translating the calcium score into actionable insights. Here is a concise guide on how to use the chart:
Step 1: Access the chart
Begin by downloading or accessing the Heart Calcium Score Chart template through Carepatron. Ensure you have the latest version for accurate and up-to-date information.
Step 2: Enter patient information
Input the patient's details, including full name, date of birth, gender, patient ID, contact number, and email address. Accurate demographic information is essential for proper record-keeping and future reference.
Step 3: Identify at-risk factors
Mark any relevant risk factors from the provided list, such as diabetes, smoking history, high blood pressure, or family history of heart disease. This helps contextualize the calcium score with the patient’s overall risk profile.
Step 4: Interpret the calcium score
Record the patient’s calcium score and interpret the results using the chart. The chart categorizes scores into risk levels, ranging from very low to high. Document the interpretation in the designated section.
Step 5: Provide recommendations
Based on the calcium score and interpretation, write down your clinical notes and recommendations. This may include advice on preventive measures or further diagnostic testing. Sign and date the form to complete the process.
When would you use this Heart Calcium Score Chart?
The Heart Calcium Score Chart is an invaluable tool in various clinical scenarios, providing crucial insights into coronary artery disease risk by measuring calcium deposits. Here are five key instances when using this chart is particularly beneficial:
Assessing intermediate-risk patients
For individuals with an intermediate risk of cardiovascular disease, the calcium score test helps refine risk assessments. It provides a more precise estimate of future heart attack risk and informs decisions about preventive treatments.
Guiding preventive therapy
In cases where patients are hesitant about starting statin therapy or other medications, the calcium score can clarify the potential benefits of such treatments. This is especially relevant for those who question whether they would benefit from preventive measures.
Evaluating risk in older adults
The chart is useful for older adults, such as men aged 55 to 80 and women aged 60 to 80, who have few risk factors but need to assess their risk of CAD. The calcium score provides additional data to guide treatment decisions.
Monitoring individuals with previous heart conditions
For patients with a history of coronary artery disease, the chart helps evaluate ongoing risk. Although not recommended for those who have had a heart attack or coronary bypass, it can be useful in assessing new or evolving risks in certain cases.
Addressing a strong family history
The calcium score test provides valuable information when there is a strong family history of premature coronary heart disease. Despite a low personal risk profile, it helps identify individuals who might benefit from early preventive strategies.
What do the results mean?
Interpreting the calcium scoring involves understanding how the calcium score reflects the presence and extent of blood clot or calcified plaque deposits in the coronary arteries. Here's a detailed guide to interpreting these results (Golub et al., 2023):
- Normal calcium score (0): A CAC score of 0 indicates no detectable calcified plaque deposits. This result generally suggests a very low risk of coronary artery disease and is associated with a reduced likelihood of future cardiovascular events. For patients with other risk factors, the absence of calcification can help decide to withhold statin therapy or other preventive measures. The healthcare team might consider less aggressive treatment or lifestyle modifications.
- CAC score 1–99: This score indicates some degree of calcified plaque. The risk of heart disease is considered relatively low but not negligible. Patients with scores in this range may be at moderate risk and should engage in further risk assessments or preventive strategies, particularly if they have other risk factors like a family history of cardiovascular disease or elevated cholesterol levels.
- CAC score 100–399: A score in this range suggests a moderate to high risk of coronary artery disease. This score indicates the presence of significant plaque buildup. It is often used to justify the initiation or intensification of preventive therapies, such as statins. A moderate calcium score can indicate a more proactive approach to risk management and lifestyle adjustments.
- CAC score 400 and above: A high score indicates advanced calcified plaque deposits, signifying a high risk of coronary artery disease and potential heart events. This score typically warrants immediate attention and often leads to the initiation of more aggressive therapeutic interventions, including statin therapy and possibly other medications, depending on the overall clinical picture and risk factors.
Clinical implications of CAC scoring
Here are some of the clinical implications that can be drawn from coronary artery calcium scoring:
- High-risk and very high-risk scores: In cases where the CAC score indicates high or very high risk, it is crucial to consider the patient's overall health context. The presence of a high calcium score may lead to recommendations for more frequent follow-ups, advanced diagnostic imaging, or additional tests to further evaluate heart health. It also helps personalize treatment plans to manage and mitigate risk factors effectively.
- Radiation exposure and imaging tests: While CT scanning is a valuable tool for assessing coronary artery calcium, it does involve radiation exposure. Healthcare providers must weigh the benefits of detailed imaging against the potential risks associated with radiation. The CAC test takes just a few seconds and provides multiple images to assess the extent of calcium buildup in the heart arteries (Golub et al., 2023).
- Integration with other risk factors: CAC scoring should be integrated with other risk assessment tools and clinical judgment. Family history, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other risk factors should be considered to provide a comprehensive view of a patient's cardiovascular health.
References
American Heart Association. (2023, April 13). Coronary artery calcium (CAC) test. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack/diagnosing-a-heart-attack/cac-test
Golub, I. S., Termeie, O. G., Kristo, S., Schroeder, L. P., Lakshmanan, S., Shafter, A. M., Hussein, L., Verghese, D., Aldana-Bitar, J., Manubolu, V. S., & Budoff, M. J. (2023). Major global coronary artery calcium guidelines. JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging, 16(1), 98–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2022.06.018
Commonly asked questions
Medical professionals will request a heart calcium score for patients who are part of at-risk populations yet present as asymptomatic. This score is invaluable for making predictions about the probability of heart-related events occurring in the future.
A Heart Calcium Score Chart is typically used to interpret the results of a CT scan and predict the probability of future cardiac injury. They are well-utilized for asymptomatic patients who have multiple risk factors, such as a family history of heart disease and high cholesterol.
Medical professionals use a Heart Calcium Score Chart to interpret the results from a CT scan and make predictions about the risk of future heart attacks or strokes. Collecting these results is painless and non-intrusive and provides fantastic preventive care.