Neuro Exam Checklist
Streamline your neurology examinations with our comprehensive Neuro Exam Checklist Template, ensuring thorough assessments and efficient patient care.


What is a neurological examination?
A neurological examination is a structured series of tests and observations that healthcare providers use to assess the function of the nervous system. These exams are intended to detect problems within a patient's neurological system. Considering the nervous system's influence on our bodily functions and physical sensations, the insights drawn from a neurological exam also help provide a look into the overall status of a patient's health.
Conducting a neurological exam involves different sections that work to provide information that paints a more general picture of functioning. It begins with a mental status examination. Then, a detailed examination of the cranial nerves, motor function, sensory function, coordination, reflexes, and gait follows.
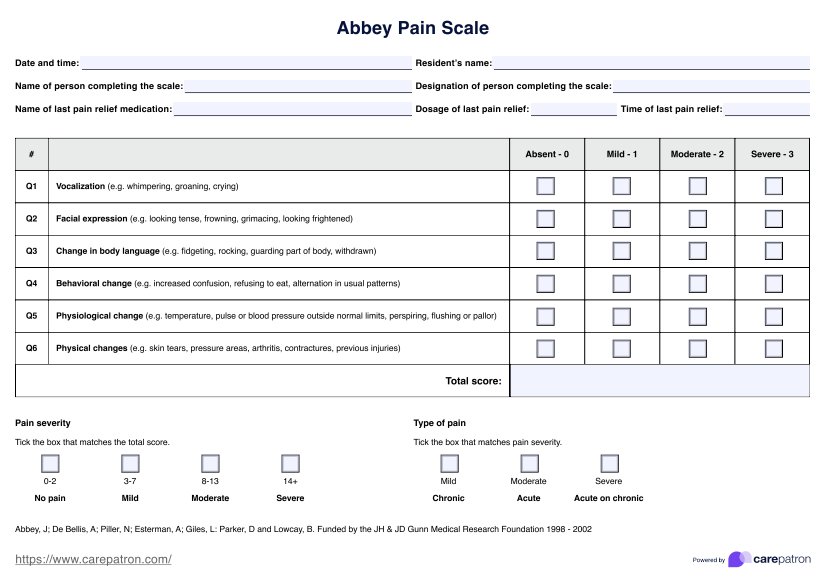
Neuro Exam Checklist Template
Neuro Exam Checklist Example
What is in our Neuro Exam Checklist Template?
A well-structured neurological exam checklist is a valuable tool for healthcare practitioners, ensuring a thorough and systematic evaluation of a patient's neurological function. Our template includes several key sections that cover various aspects of the nervous system:
Mental status examination
A critical component of the neurological exam, the mental status section typically includes evaluating one's:
- Alertness
- Orientation
- Attention
- Memory
- Language skills
Cranial nerve examination
This checklist should also include a comprehensive section for evaluating all twelve cranial nerves:
- Cranial nerve I (olfactory nerve): Results of smell testing
- Cranial nerve II (optic nerve): Visual acuity, visual fields, and fundoscopic exam findings
- Cranial nerve III, IV, VI (oculomotor, trochlear, abducens): Pupillary responses, eye movements, presence of ptosis
- Cranial nerve V (trigeminal nerve): Facial sensation, corneal reflex, jaw strength
- Cranial nerve VII (facial nerve): Facial symmetry, muscle strength, taste function
- Cranial nerve VIII (vestibulocochlear): Hearing acuity, balance testing
- Cranial nerve IX and X (glossopharyngeal, vagus nerve): Gag reflex, palatal movement, voice quality
- Cranial nerve XI (accessory): Shoulder shrug and neck rotation strength
- Cranial nerve XII (hypoglossal nerve): Tongue movement and strength
Motor function
This section allows for documentation of the following:
- Upper extremity strength
- Lower extremity strength
- Coordination
Sensory function
The template provides space to record findings during the sensory exam:
- Light touch
- Pain
- Temperature
- Vibration
- Proprioception
Reflexes
The reflex section of the neuro exam template typically includes the following:
- Deep tendon reflexes
- Plantar reflex
Gait and station
The final section of the template often includes space to document:
- Gait
- Balance
How to use this Neuro Exam Checklist Template
Our neurologic exam checklist is a valuable resource for healthcare practitioners to ensure a comprehensive neurological exam. Here's a concise guide on how to use this template in clinical practice effectively:
Step 1: Gather patient information and do a mental status exam
Ask the patient for their basic information, including name, age, date of birth, gender, and contact details. Next, proceed to the mental status section, evaluating and documenting the patient's alertness, orientation, attention, memory, and language skills. This initial evaluation provides crucial insights into the patient's cognitive function and level of consciousness.
Step 2: Conduct a cranial nerve examination
Systematically work through the cranial nerve assessment, checking each cranial nerve in order. For each nerve, perform the appropriate tests and mark whether the function is intact or if there are any abnormalities. This comprehensive evaluation helps identify potential neurological deficits related to specific cranial nerves.
Step 3: Evaluate motor and sensory function
Move on to assess motor function, including upper and lower extremity strength and coordination. Document your findings in the designated spaces. Then, conduct the sensory examination, testing and recording responses to light touch, pain, temperature, vibration, and proprioception. This step is crucial for identifying any motor weaknesses or sensory deficits.
Step 4: Test for reflex and gait
Complete the reflexes section by testing and documenting responses for deep tendon reflexes (biceps, triceps, patellar, and Achilles) and the plantar reflex. Finally, assess the patient's gait and balance. Note any abnormalities or concerns in the gait and station section.
Commonly asked questions
A comprehensive neurological assessment typically evaluates the following seven components: mental status, cranial nerves, motor function, sensory function, reflexes, coordination, and gait. This assessment helps identify any abnormalities or deficits in the patient's neurological functioning and guides further diagnostic testing and treatment planning.
When documenting a neurological exam, it is essential to use clear, concise language and provide specific details about the patient's performance on each assessment component. The documentation should include the patient's level of consciousness, orientation, speech, and any abnormalities in cranial nerve function, muscle tone, strength, reflexes, sensation, coordination, and gait.
A normal neurological exam indicates that the patient's brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves function within the expected parameters. The patient should be alert and oriented, with normal speech and language skills. Cranial nerves, motor function, deep tendon reflexes, and coordination should also be normal.