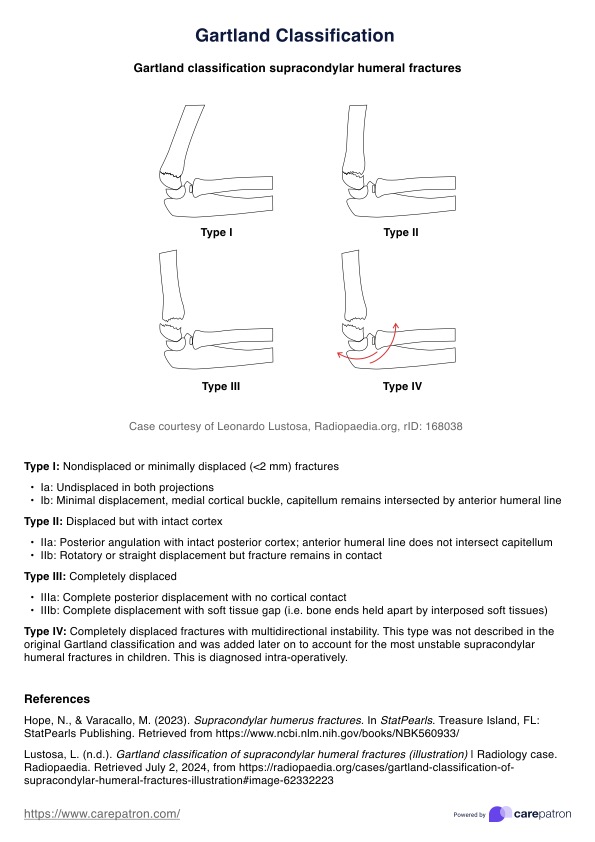
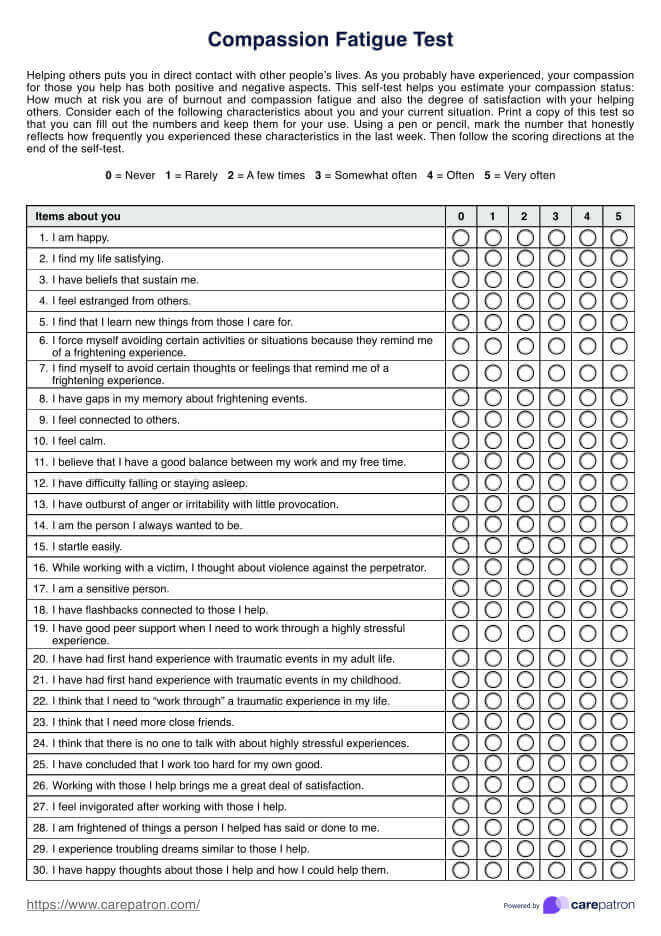
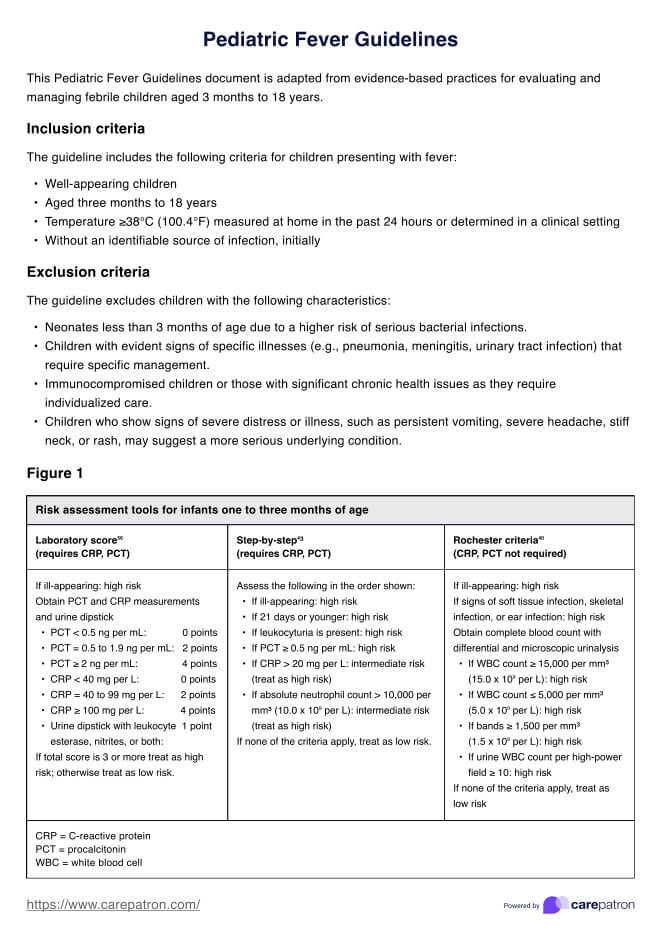
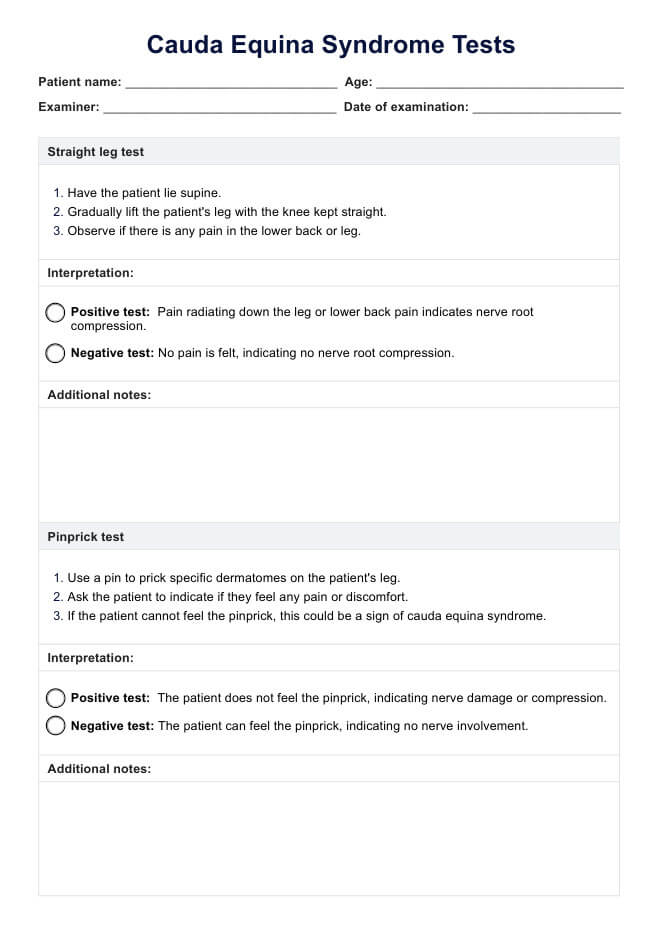
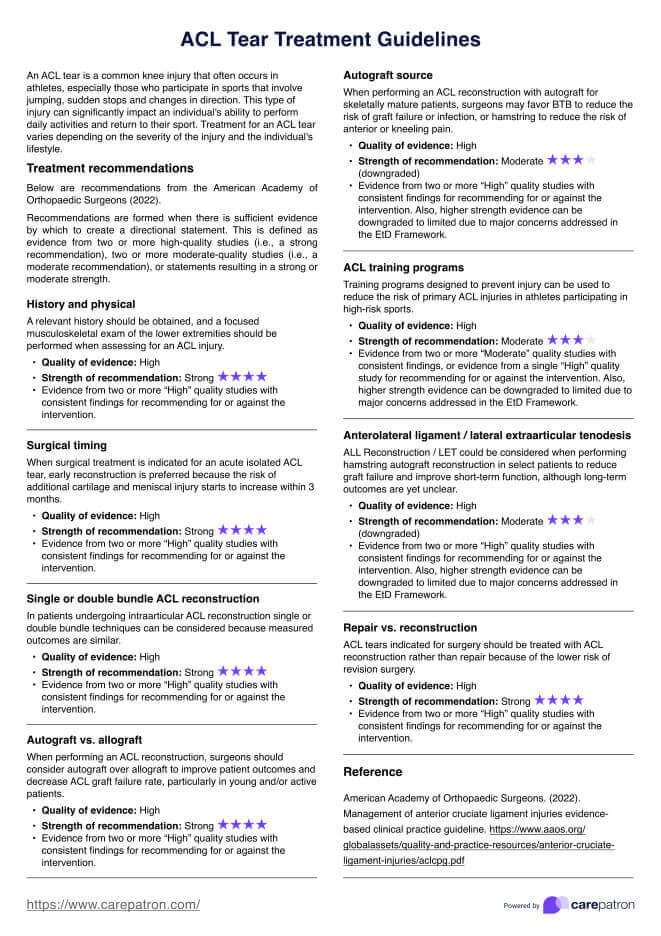
Printable Blood Pressure Log
Use this free, editable, downloadable, and Printable Blood Pressure Log to monitor your patient's blood pressure.


How do you measure blood pressure?
Measuring blood pressure levels is a critical skill for healthcare providers. It allows for the monitoring and managing patient health regarding cardiovascular risks and conditions. Accurate blood pressure measurements provide invaluable insights into a patient's heart health and are vital in diagnosing hypertension, assessing the risk of heart disease, and tailoring treatment plans.
A healthcare professional needs a properly calibrated sphygmomanometer (blood pressure monitor) and a stethoscope to measure blood pressure. An automatic digital monitor is also widely used as a home blood pressure monitor and can provide reliable readings with minimal training (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024).
Preparation involves ensuring the patient is relaxed and seated, with their arm supported at heart level. Within 30 minutes of the measurement, the patient should not have consumed caffeine, medicine, or alcohol, engaged in vigorous exercise, or smoked. They must also stay quiet before and during their blood pressure measurement to ensure accurate results.
The following steps are usually followed when measuring blood pressure.
- Cuff placement: Place the blood pressure cuff snugly on the upper arm, with the cuff bladder center above the brachial artery. Ensure the cuff size fits properly to avoid inaccurate readings.
- Finding the pulse: Palpate the brachial artery with your fingertips to locate the strongest pulse point.
- Inflation and deflation: When using a manual sphygmomanometer, inflate the cuff 20-30 mmHg beyond the point where the radial pulse disappears. This ensures you don't miss the systolic pressure. Begin deflating the cuff slowly. If using an automatic monitor, simply start the machine as directed.
- Listening for the Korotkoff sounds: Place the diaphragm of your stethoscope over the brachial artery. As you deflate the cuff, listen for the first sound (the systolic pressure) and the moment the sound disappears (this marks the diastolic pressure).
The healthcare provider records both the systolic and diastolic pressures, typically expressed as a fraction, with the systolic number above the diastolic (e.g., 120/80 mmHg, the normal blood pressure level). This measurement provides valuable information about the patient's cardiovascular status and guides appropriate treatment or management strategies using antihypertensive medication (Muntner et al., 2018).
Blood Pressure Log Template
Blood Pressure Log Example
What is a blood pressure log?
A blood pressure log is a record-keeping tool that allows individuals to track their blood pressure readings over time. It is a valuable resource for patients and healthcare practitioners in monitoring and managing hypertension (high blood pressure) or other cardiovascular conditions.
They typically consist of a table or a chart where individuals can document their systolic (top number) and diastolic (bottom number) blood pressure readings, along with the date, time, and relevant notes or observations. Some logs may be used alongside a blood pressure chart for more accurate interpretation.
How does this Printable Blood Pressure Log work?
This blood pressure tracker can help healthcare professionals guide their patients in effectively monitoring and tracking their blood pressure readings. Here's a step-by-step guide that healthcare professionals can follow when introducing this tool to their patients:
Step 1: Emphasize the importance of monitoring
Download the printable template from the link in this guide and explain to patients how regular blood pressure monitoring helps identify potential issues early and aids in managing hypertension or cardiovascular conditions.
Step 2: Check for proper equipment
Ensure patients have a reliable and properly calibrated blood pressure monitoring device, and demonstrate how to use it correctly.
Step 3: Introduce the printable log
Explain the purpose of the log and its sections to record the date, time, systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings, and any additional factors that may influence readings.
Step 4: Instruct on proper technique
Guide patients on taking readings at consistent times, ideally in the morning after resting, and accurately record the information in the log.
Step 5: Encourage consistent usage and review
Advise patients on the recommended frequency for monitoring and emphasize the importance of bringing the completed log to appointments for review and informed decision-making regarding treatment plans and lifestyle modifications.
Why are blood pressure readings important?
Blood pressure readings are vital indicators of cardiovascular health, providing essential information for diagnosing and managing various conditions. Here's why monitoring blood pressure is so important:
- Hypertension detection: Regular blood pressure checks can identify individuals with hypertension, a significant risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. Early detection of a high blood pressure reading allows timely intervention and management to prevent complications.
- Monitoring treatment efficacy: Regular blood pressure checks help evaluate the effectiveness of prescribed medications or lifestyle modifications for individuals diagnosed with hypertension or other cardiovascular conditions.
- Identifying potential health risks: Blood pressure readings can reveal underlying health issues beyond hypertension. For example, abnormally low blood pressure (hypotension) may indicate dehydration, shock, or other severe conditions.
- Tracking trends: When patients maintain a blood pressure journal even with their self-measured blood pressure, healthcare professionals can identify patterns and trends over time, which can aid in determining the most appropriate course of action.
- Tailoring treatment plans: Blood pressure readings, combined with other factors like age, medical history, and lifestyle, help healthcare professionals develop personalized treatment plans and preventive strategies for each individual.
Regular blood pressure monitoring is a simple yet powerful tool that helps medical professionals make informed decisions, promote early intervention, and ultimately improve cardiovascular health outcomes for their patients.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024). Self-measured blood pressure monitoring with clinical support. https://hdsbpc.cdc.gov/s/article/Self-Measured-Blood-Pressure-Monitoring-With-Clinical-Support
Muntner, P., Carey, R. M., Gidding, S., Jones, D. W., Taler, S. J., Wright, J. T., & Whelton, P. K. (2018). Potential US population impact of the 2017 ACC/AHA high blood pressure guideline. Circulation, 137(2), 109–118. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.117.032582
Commonly asked questions
To create a blood pressure log, obtain a notebook or use a printable template. Record the date, time, and location of each blood pressure reading. Note any symptoms you experienced before or after the reading, such as dizziness or headache. Maintain consistency by taking measurements simultaneously daily, ideally in the morning and evening. For more convenience, you may also use a blood pressure app.
To record blood pressure readings, write down the systolic (top number) and diastolic (bottom number) values precisely as they appear on your home monitor. For example, if your reading is 120/80 mmHg, record it as "120/80." Include the time and date of each reading.
Create a graph with the date on the x-axis and blood pressure values on the y-axis. Plot each reading as a point on the graph, using a different color or symbol for systolic and diastolic values. Connect the points to visualize trends and patterns in your blood pressure over time. Refer to the chart to identify significant changes or fluctuations in your readings.