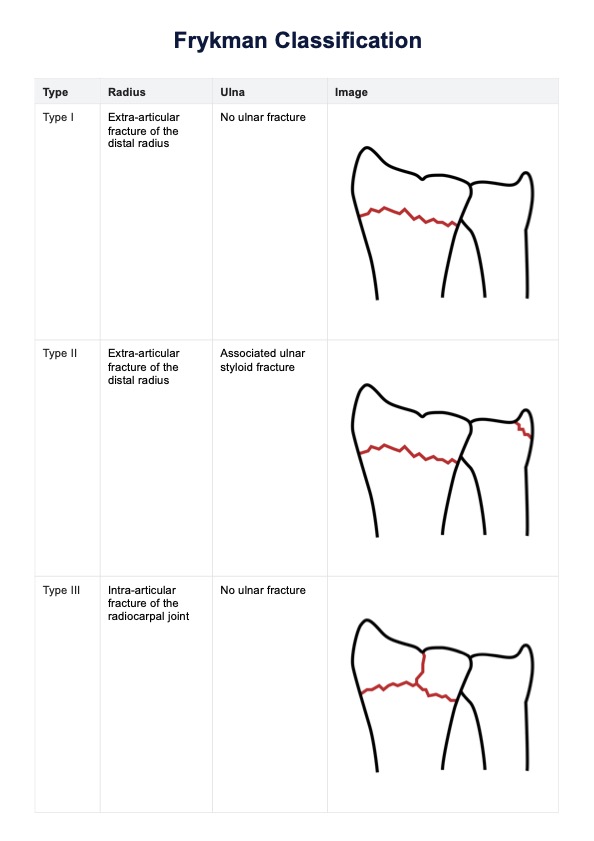
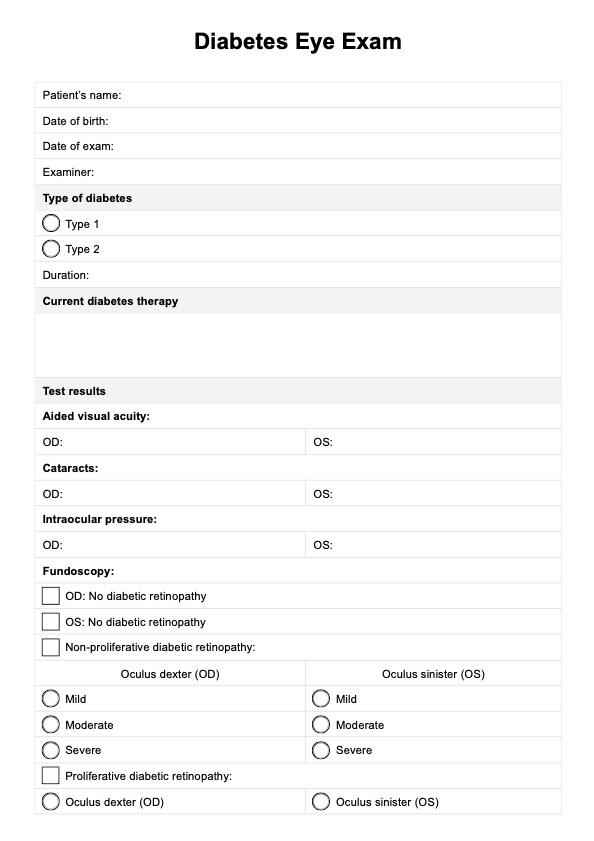
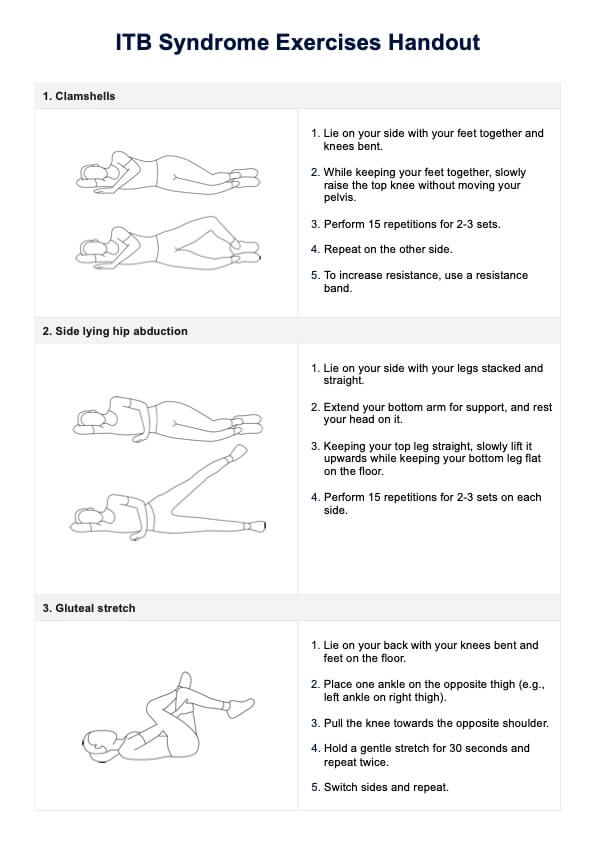
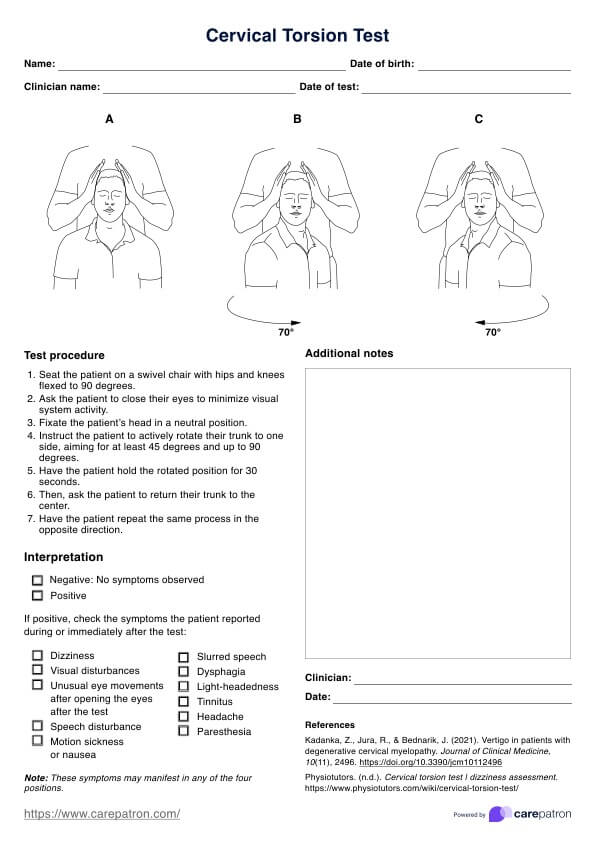
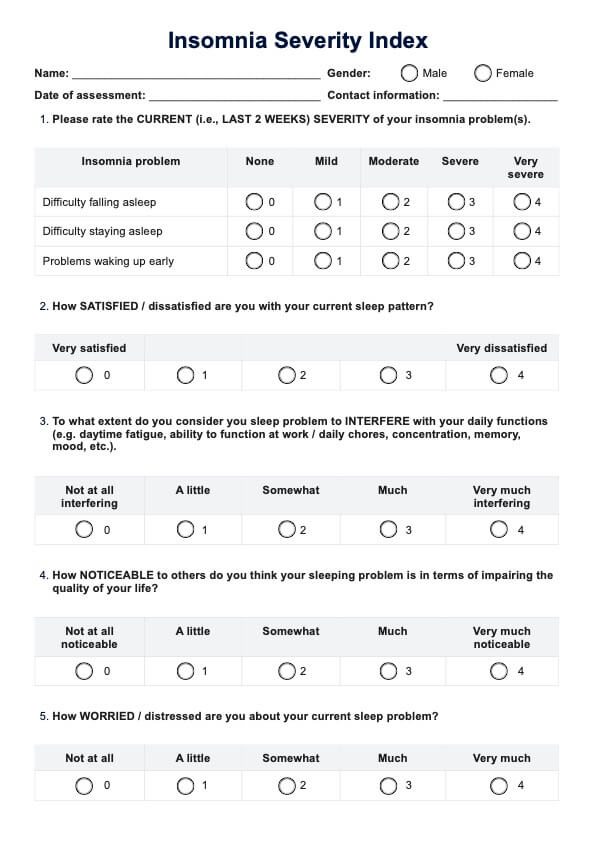
High uric acid foods chart
Provide a Diet Chart for patients with high uric acid to guide them with their meal planning. Click here for a free template copy!


What is high uric acid?
High uric acid, referred to as hyperuricemia, is a medical condition characterized by elevated uric acid levels in the bloodstream. Uric acid is a metabolic byproduct generated by the body during the digestion of purine-containing foods.
Purines are natural substances in various foods, including organic meats, seafood, and certain vegetables. When the body produces more uric acid than it can efficiently eliminate, the excess accumulates in the blood, leading to hyperuricemia.
Elevated uric acid levels can result in crystals forming in joints and surrounding tissues, which may cause gout attacks. Furthermore, persistent hyperuricemia may contribute to the development of kidney stones. Monitoring and managing high uric acid levels are essential to prevent associated complications and maintain overall health.
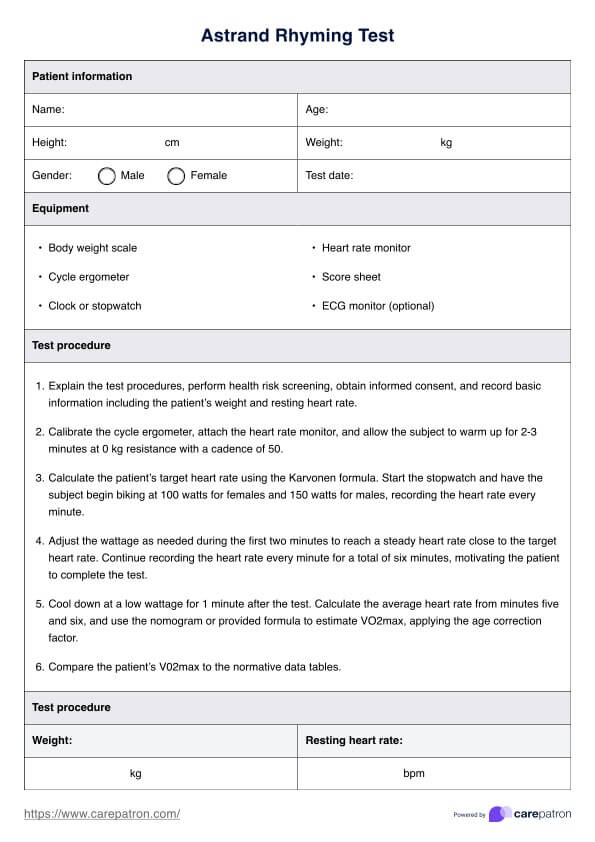
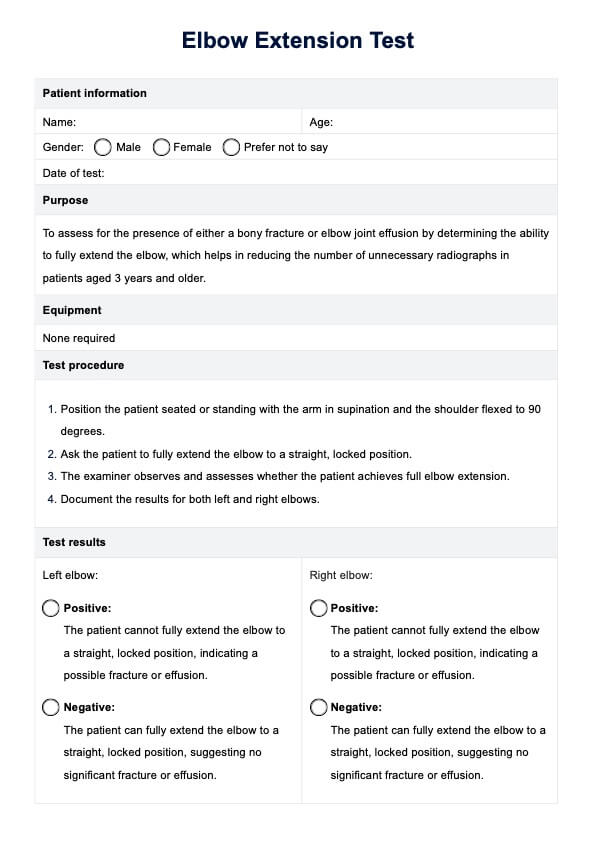
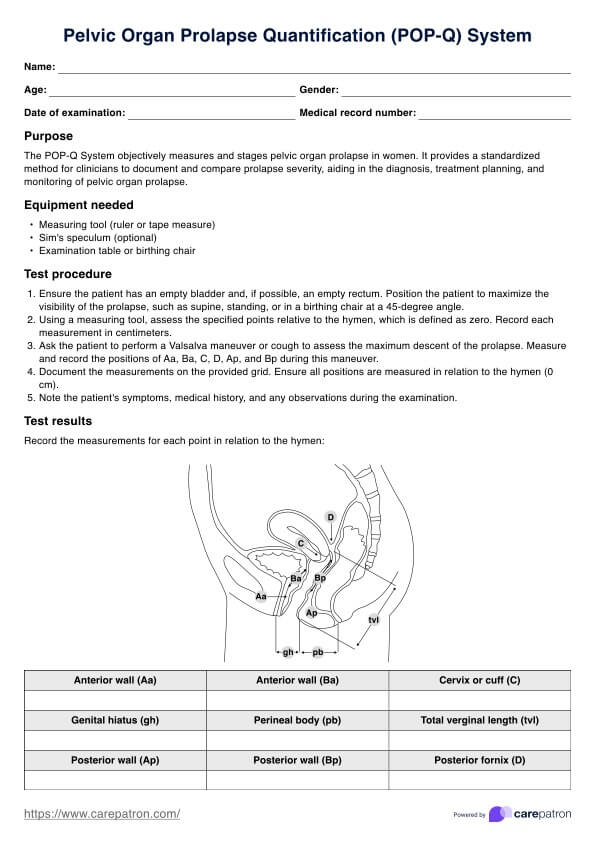
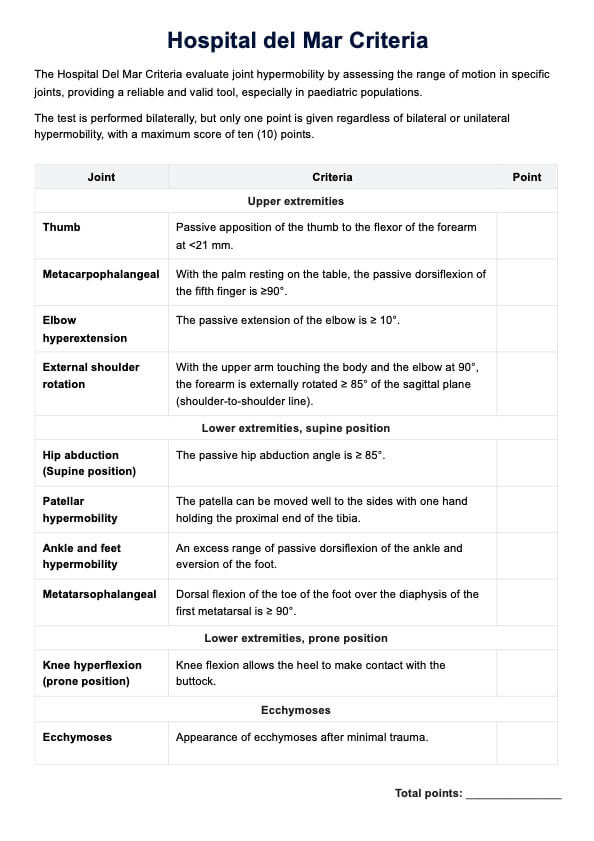
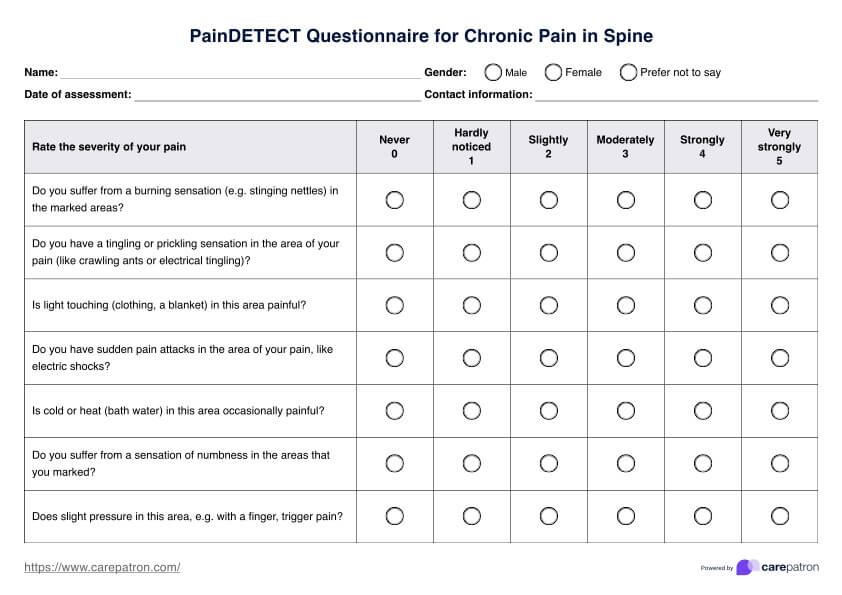
High uric acid foods chart Template
High uric acid foods chart Sample
How does this foods high in uric acid chart work?
Incorporating a High Uric Acid Foods Chart in your practice can help your clients decrease uric acid levels. Here's how to use this:
Step 1: Download the template
You will see a download button when you hover over the sample image of our High Uric Acid Foods Chart. Click on that one to secure a copy of the template. If you have a Carepatron account, you can find it in the templates library.
Step 2: Fill out patient information
Complete the patient information section, including their uric acid level. Be sure to include the name of the physician who conducted the blood test. If needed, contact the physician for additional information to ensure your client receives the appropriate guidance from you as their nutritionist or dietitian.
Step 3: Explain the chart
Review the chart, which highlights foods high in purines that should be avoided and those that are safe to consume. Discuss how these food choices impact uric acid levels and provide personalized dietary recommendations, considering the client's overall health and any specific needs.
How to detect uric acid in blood?
Urine levels in blood are detected through a urine blood test, also called a serum uric acid measurement. This diagnostic tool gauges the quantity of uric acid in the bloodstream, offering insights into the body's production and elimination of uric acid.
Before undergoing uric acid testing, adequate preparation is essential. This may involve a 4-hour fasting period, during which consumption of food and drink is restricted. One must also avoid ingesting certain substances, including alcohol, specific medications like aspirin and ibuprofen, high vitamin C levels, and dyes from X-ray tests since it can interfere with test accuracy. Patients must disclose all medications and supplements to the healthcare provider because it may also affect the uric acid test results. This Uric Acid Test Template is an excellent tool during the test.
The uric acid blood test involves a simple blood draw, usually from the inner elbow or back of the hand, with minimal risks, such as slight bruising or dizziness. Results help diagnose and monitor conditions like gout, kidney disorders, and the effects of chemotherapy or radiation.
What are the symptoms of having too much uric acid?
Hyperuricemia can manifest with various symptoms, although it's noteworthy that only around one-third of individuals with elevated uric acid experience noticeable signs.
Gout flare-ups
Gout, a painful form of arthritis, can also affect individuals with hyperuricemia. While it can impact any joint, it often initiates in the large toe. Gout symptoms include intense joint pain, stiffness, difficulty in joint movement, redness and swelling, and potentially deformities in affected joints. Thus, it's essential to advise clients on a suitable gout diet.
Tophaceous gout
If one has excess uric acid, crystals may aggregate into clumps known as tophi. These firm lumps form beneath the skin, around joints, and in the curvature at the top of the ear. Tophi exacerbates joint pain, potentially causing long-term joint damage or nerve compression.
Kidney stones
Uric acid crystals can lead to the formation of kidney stones. These stones may be small and pass through urine, but they can also grow to a size that obstructs parts of the urinary tract. It is essential to control uric acid levels to prevent it from worsening.
Diet recommendations to lower uric acid levels
Managing high uric acid levels involves making informed dietary choices, especially if the client is at risk of developing gout. Here are some valuable tips to help your clients regulate uric acid:
1. Limit purine-rich foods and reduce sugar intake
Advise your clients to limit high-purine foods, which contribute to increased blood uric acid levels. Recommend reducing or avoiding organ meats like liver, seafood such as anchovies, herring, shellfish, shrimp, sardines, red meat, and fatty foods like bacon. Explain that purines are released when the body breaks down fructose, leading to elevated uric acid levels. Specifically, they must avoid alcohol, sweets —especially those with high fructose corn syrup—sweet drinks, and carbonated beverages.
2. Follow a low-purine diet
Encourage clients to consume nuts in moderation and include fruits rich in Vitamin C, such as citrus. Recommend vegetables like gourds, particularly bitter gourds, and whole grains in pasta, wheat bread, and specific unsweetened cereals. Suggest fat-free or low-fat options like low-fat milk and non-dairy alternatives for beverages.
3. Stay hydrated
Emphasize the importance of adequate fluid intake for faster kidney elimination of uric acid. Encourage clients to carry a water bottle to maintain consistent hydration.
4. Limit alcohol
Advise clients that alcohol consumption can trigger elevated uric acid levels and contribute to dehydration, both of which can exacerbate symptoms.
5. Manage weight
Inform clients that excess weight increases the risk of gout. If they have already been diagnosed with gout, maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
Treatments for high uric acid levels
Treating high uric acid levels, or hyperuricemia, encompasses a combination of lifestyle adjustments and, when necessary, pharmaceutical interventions. Here are common approaches to managing elevated uric acid levels:
Lifestyle changes
Initiating lifestyle alterations is a fundamental aspect of managing hyperuricemia. This involves dietary modifications, maintaining a healthy weight, and ensuring adequate hydration. Mitigating uric acid levels often consists of abstaining from alcohol and restricting the intake of purine-rich foods.
Medication
When lifestyle adjustments prove insufficient, healthcare providers may prescribe medications to lower uric acid production or enhance its elimination by the kidneys.
Pain relief
During gout flares, managing pain and inflammation becomes pivotal. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, or colchicine may be prescribed for effective control.
Self-care steps
In less severe cases, individuals can take self-care measures to alleviate symptoms. This involves abstaining from soft drinks and alcohol, using ice for pain relief, elevating the affected leg to mitigate gout symptoms, and maintaining adequate hydration.
Commonly asked questions
Foods high in purines, such as red meats, organ meats, and certain seafood, like sardines and mackerel, can increase uric acid production. Additionally, sugary foods and beverages, particularly those high in fructose, can elevate uric acid levels.
Eggs are low in purines and do not significantly contribute to high uric acid levels, making them a safe protein option for individuals managing their uric acid levels.
The timeline can vary based on individual factors and consistency with dietary modifications. Noticeable reductions typically take about weeks.