Frykman Classification
Try our handout template about the Frykman Classification of Colles fractures. Learn about distral radius fracture types, symptoms, and treatment options here.


What is a distal radius fracture?
A distal radius fracture is a break near the wrist end of the radius, one of the two main bones in the forearm. It is one of the most common types of fractures, particularly affecting older adults due to osteoporosis, as well as in early age and children through high-impact activities or trauma, such as falls or sports injuries. These fractures can significantly impact wrist function and require precise diagnosis and treatment to ensure proper healing.
Symptoms
Distal radius fractures present with various symptoms that can impact daily activities and overall wrist function.
- Immediate pain at the fracture site, often accompanied by swelling and bruising.
- Visible deformity or an abnormal bend in the wrist.
- Difficulty or inability to move the wrist or fingers.
- Tenderness to touch near the site of the break.
Types of distal fractures
Understanding the different types of distal radius fractures helps in accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
- Colles' fracture: A fracture of the distal radius with dorsal displacement of the wrist and hand, typically caused by falling onto an outstretched hand.
- Smith's fracture: Also known as a reverse Colles' fracture, it involves a volar displacement of the distal fragment, usually resulting from a fall onto a flexed wrist.
- Barton's fracture: An intra-articular fracture of the distal radius with dislocation of the radiocarpal joint, often due to a direct blow to the wrist or a high-energy impact.
- Hutchinson's fracture: Also known as a chauffeur's fracture, this is a fracture of the radial styloid process, commonly caused by a direct blow to the wrist or a twisting injury.
Other types include:
- Intra-articular fractures: These extend into the wrist joint, complicating treatment and recovery.
- Extra-articular fractures: Fractures that do not involve the joint surface.
- Comminuted fractures: The bone is broken into multiple pieces.
- Open fractures: The bone breaks through the skin, requiring urgent medical attention due to infection risk
How to classify fractures
Classifying fractures involves assessing the specific location and nature of the break. Various classification systems exist to categorize fractures based on these criteria. Healthcare professionals use radiographic imaging to determine the exact type and severity of the fracture, aiding in the selection of the appropriate treatment approach. Systems like the Frykman Classification are instrumental in providing a structured framework for these assessments.
Frykman Classification Template
Frykman Classification Example
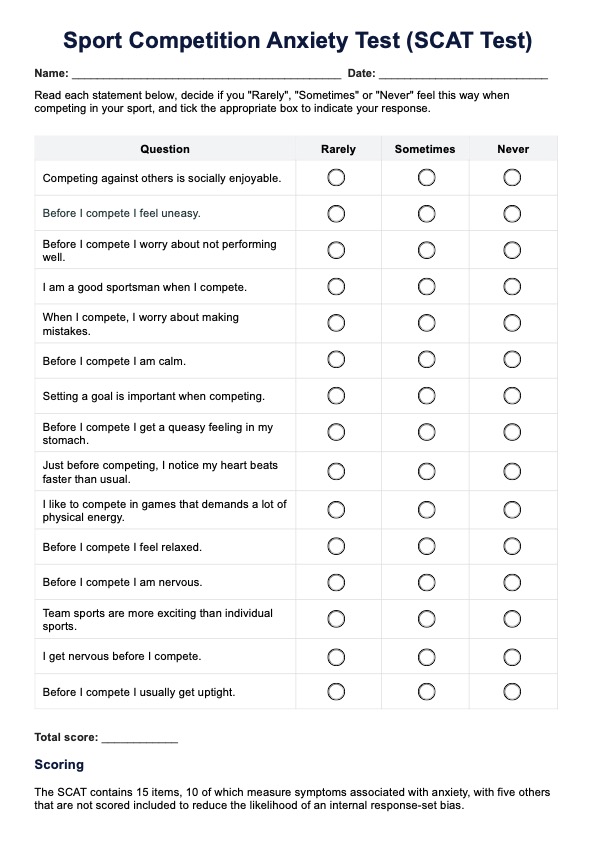
What is the Frykman Classification system?
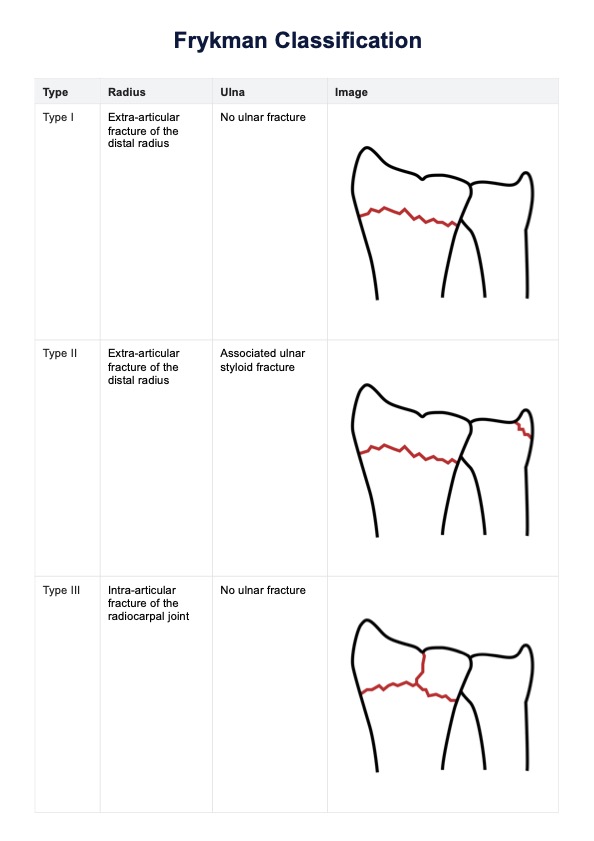
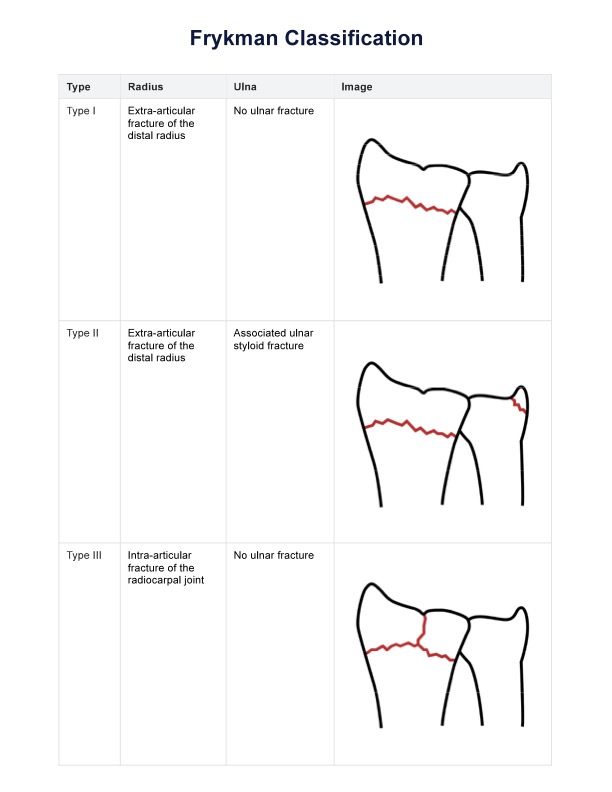
The Frykman Classification system is a widely used method for categorizing distal radius fractures, particularly focusing on the involvement of the distal radio ulnar joint. Developed by Gunnar Frykman, this classification focuses on the involvement of the radiocarpal and distal radioulnar joints and the presence of an ulnar styloid fracture (1967). The system's primary aim is to assist clinicians in diagnosing, treating, and predicting the prognosis of distal radius fractures.
The Frykman Classification assesses the extent of the fracture and any associated injuries to the ulna. This detailed evaluation helps healthcare professionals to determine the most appropriate treatment strategy, whether it be surgical or conservative management. The system divides the fractures into eight types, each with specific characteristics regarding the involvement of the joints and the presence of an ulnar fracture.
What are the classifications?
The Frykman Classification system consists of eight types, based on the involvement of the radiocarpal and distal radioulnar joints and the presence or absence of an associated ulnar styloid fracture:
- Type I: Fracture of the distal radius without involvement of the distal radioulnar or radiocarpal joints.
- Type II: Type I fracture with an associated ulnar styloid fracture.
- Type III: Fracture of the distal radius involving the radiocarpal joint, but not the distal radioulnar joint.
- Type IV: Type III fracture with an associated ulnar styloid fracture.
- Type V: Fracture of the distal radius involving the distal radioulnar joint, but not the radiocarpal joint.
- Type VI: Type V fracture with an associated ulnar styloid fracture.
- Type VII: Fracture of the distal radius involving both the radiocarpal and distal radioulnar joints.
- Type VIII: Type VII fracture with an associated ulnar styloid fracture.
These classifications help clinicians to understand the complexity of the fracture, predict possible complications, and achieve the best outcome in treament.
Limitations of the system
While the Frykman Classification system is valuable for categorizing distal radius fractures, it has several limitations. It primarily focuses on the involvement of the radiocarpal and distal radioulnar joints and the presence of an ulnar styloid fracture, which may not fully capture the complexity of some fractures. This can lead to oversimplification and potentially inadequate treatment plans for more complex cases. Additionally, it lacks consideration for the degree of displacement and comminution of the fracture, crucial factors in determining appropriate treatment and predicting outcomes.
Another limitation is the system's lack of attention to soft tissue damage accompanying these fractures, significantly impacting healing and recovery. The Frykman Classification may also be less effective for pediatric patients or those with osteoporotic bones, as these populations have unique considerations not adequately addressed by this system. Despite these limitations, the Frykman Classification remains useful for providing a general framework for diagnosing and managing distal radius fractures.
Treatments for distal radius fractures
Distal radius fractures, a common injury, often require a tailored treatment approach depending on the severity and type of fracture. Here are some common treatments:
- Casting and splinting: For non-displaced or minimally displaced fractures, immobilizing the wrist with a cast or splint can allow the bone to heal naturally.
- Closed reduction: If the fracture is displaced, a closed reduction may be performed to realign the bones without surgery, followed by casting.
- Surgical intervention: Severe fractures, such as dorsal comminution, may require surgery to properly align and stabilize the bones. This can involve the use of plates, screws, or pins.
- Physical therapy: Post-immobilization or surgery, physical therapy helps restore range of motion, strength, and function to the wrist and hand.
- Pain management: Medication and ice can help manage pain and reduce swelling during the healing process.
- Bone health optimization: Ensuring adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, and addressing any underlying conditions like osteoporosis, can support bone healing and prevent future fractures.
Reference
Frykman, G. (1967). Fracture of the distal radius including sequelae—shoulder-hand-finger syndrome, disturbance in the distal radio-ulnar joint and impairment of nerve function: A clinical and experimental study. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica, 38(sup108), 1–61. https://doi.org/10.3109/ort.1967.38.suppl-108.01
Commonly asked questions
The three eponymous classifications of distal radial fractures are Colles' fracture, Smith's fracture, and Barton's fracture.
Colles fractures are classified based on the degree of displacement, angulation, and comminution of the fracture fragments.
The Frykman Classification categorizes fractures of the distal radius into eight types based on the involvement of the radioulnar joint and the presence of an ulnar styloid fracture.