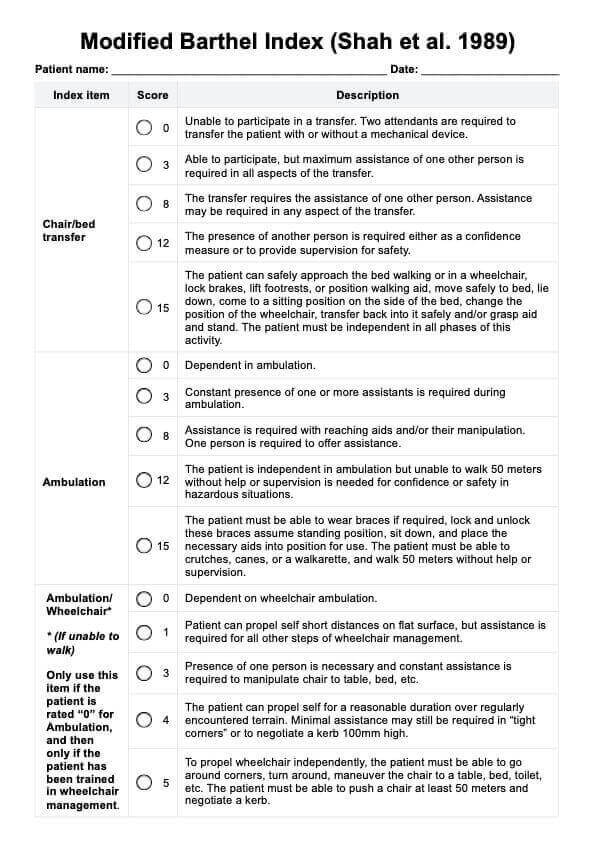
Hand Pain Diagrams
Efficiently diagnose and manage hand pain with our Hand Pain Diagram. Download it for free today!


Understanding hand pain
Hand pain refers to any discomfort, soreness, or ache that is experienced in the hand and/or fingers. It can range from a mild annoyance to a debilitating condition that affects daily activities. One significant contributor to hand pain is the condition of the blood vessels that supply the hand and fingers (Cleveland Clinic, n.d.; American Society for Surgery of the Hand, 2020). Poor circulation can lead to numbness and discomfort, often exacerbated by conditions such as diabetes or peripheral artery disease.
Additionally, the health of the joints in the hand plays a crucial role in overall hand function; inflammation or degeneration in the middle or end joints can lead to pain. Inflammation in these joints can restrict movement and make simple tasks increasingly challenging (Kılıc, 2018).
Musculoskeletal hand problems are particularly prevalent among those aged 50 and older, with an estimated monthly prevalence of 47% for hand issues and 31% specifically for hand pain. This condition can significantly impact daily life (Dziedzic et al., 2007). Patients with hand pain often experience difficulties with tasks that require fine motor skills, such as writing, typing, and grasping objects.
Symptoms of hand pain can also differ but may include sharp, shooting pain in the hands and/or fingers, dull ache or throbbing sensations, stiffness or difficulty moving the hand/fingers, swelling and inflammation in the affected area, numbness or tingling sensations, and weakness in the hand/fingers.
Hand Pain Diagrams Template
Hand Pain Diagrams Example
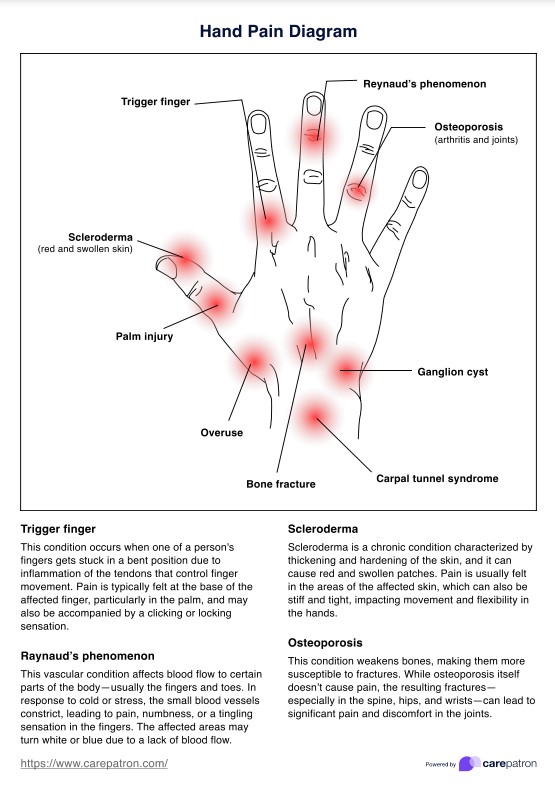
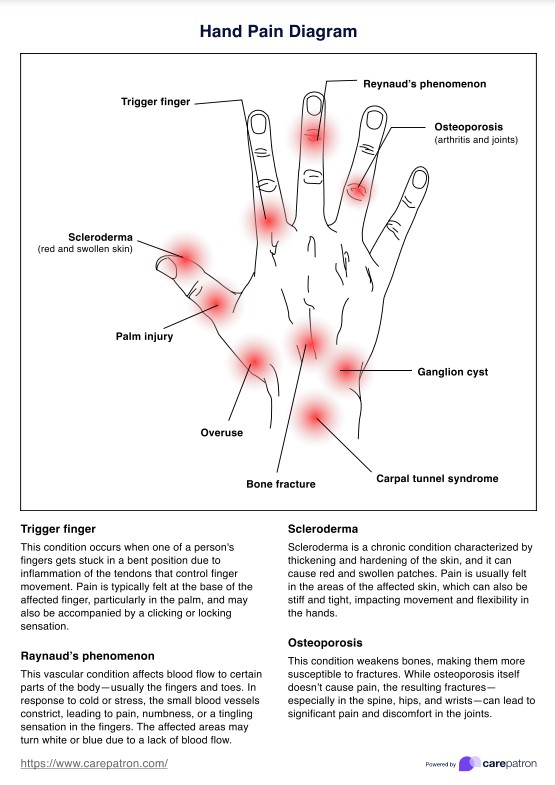
What is a Hand Pain Diagram?
A Hand Pain Diagram is a tool used by healthcare professionals to help identify the specific area and type of pain experienced by a patient. This diagram provides general guidelines on where a patient may experience pain in the hand or fingers and allows for more accurate diagnosis and treatment.
The diagram typically includes the location of pain with labels of conditions that commonly cause pain in those areas, such as carpal tunnel syndrome or arthritis. It may also include additional information, such as nerve pathways and common referral patterns for pain.
Carepatron has created a handy Hand Pain Diagram to help you easily identify the location of your patient's pain and potentially pinpoint the underlying cause. Our template also includes information about the conditions that may cause pain in that specific area, allowing you to better assess and manage your patient's pain.
How to use the Hand Pain Diagram
Here's a detailed breakdown of how to use the Printable Hand Pain Diagram effectively:
Step 1: Access the diagram
Start by obtaining the Hand Pain Diagram from the Carepatron website. This template should be readily available in a printable format, ensuring easy access for healthcare providers.
Step 2: Use the print or digital format
The Hand Pain Diagram can be used in either a print or digital format. It is recommended to have both options available for convenience and flexibility.
Step 3: Gather information from the patient
Before using the Hand Pain Diagram, gather information from the patient on their symptoms and pain levels. This will provide context for the diagram and aid in diagnosis.
Step 4: Use the handout as a reference
Instruct your patient to indicate the specific areas on their hand where they are experiencing pain or discomfort. Use the Hand Pain Diagram as a reference to help identify these regions and potential causes. Keep in mind that the pain locations depicted in the diagram serve as general guidelines and may differ from individual to individual. It is crucial to assess your patient's specific pain points using additional evaluation tools to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Step 6: Make notes and observations
While using the Hand Pain Diagram, make notes and observations about the location and severity of the patient's pain in your clinical documentation. This will help in creating a comprehensive assessment and treatment plan.
Step 7: Discuss findings with patient
Share your findings from using the Hand Pain Diagram with your patient. This will help them better understand their condition and how it may be treated.
When would you use this hand pain chart?
A Hand Pain Diagram can benefit many medical practitioners, including orthopedic surgeons, rheumatologists, physical therapists, and primary care physicians. Here are some scenarios where this template is especially useful:
Diagnosing hand injuries or conditions
When a patient presents with hand pain, discomfort, or dysfunction, a Hand Pain Diagram becomes essential for healthcare professionals. It assists in precisely pinpointing the location of the pain, which is crucial for diagnosis.
Monitoring the progress of treatment
The Hand Pain Diagram serves as a dynamic record for patients undergoing treatment for hand-related issues. It allows healthcare providers to track pain location and intensity changes over time. Physical therapists can use it to assess the effectiveness of rehabilitation programs.
Communicating hand pain information between healthcare providers
In cases where patients are receiving care from multiple specialists, effective communication is key. Hand Pain Diagrams enable seamless sharing of information among different healthcare providers.
Educating patients about their hand pain
Patient education is an integral aspect of healthcare. Hand Pain Diagrams help healthcare professionals explain complex hand conditions to patients in a visually accessible manner. By using the diagram, practitioners empower patients to better understand the location and nature of their hand pain, fostering informed decision-making and treatment plan compliance.
Benefits
Using our free Hand Pain Diagram offers numerous advantages for healthcare professionals, patients, and the overall healthcare process:
Pinpoint the location of hand pain
The primary advantage of a Hand Pain Diagram is its ability to identify the hand pain's location. This precision is invaluable for healthcare professionals, allowing them to target their assessment and treatment to the affected area directly.
Facilitate clear communication
Visual aids like the Hand Pain Diagram bridge the gap in communication between healthcare providers and patients. Patients can often find it challenging to describe their pain verbally, but with a visual representation, they can point to the exact location of their discomfort.
Assist in designing treatment plans
Healthcare providers can use the information gathered from the Hand Pain Diagram to tailor treatment plans to the patient's specific needs. For instance, physical therapists can design exercises targeting the identified pain location, while surgeons can plan surgeries with precision.
Treatment options for hand pain
Treatment options for hand pain can vary based on the underlying cause and severity of the discomfort. Here are some options to treat hand pain:
- Physical therapy: Focusing on both sensory and motor functions is essential for issues related to the median nerve, such as pain in the middle fingers. Physical therapy can significantly enhance the strength and flexibility of the affected hand through targeted exercises that promote healthy movement of the carpal and metacarpal bones.
- Splints: When joint pain is intensified by inflammation in the collateral ligaments, wearing splints can provide the necessary support for healing while minimizing strain on affected joints.
- Corticosteroid injections: If conservative treatments fail to alleviate pain, corticosteroid injections may be considered. This option can offer temporary relief by reducing inflammation in the affected area.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be required to address underlying conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome, trigger finger, or other causes of hand pain. This option is typically reserved for instances where conservative treatments have proven ineffective.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen and naproxen can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain in the affected hand.
- Minimizing stress: Lifestyle modifications are often recommended for hand pain stemming from repetitive strain injuries like carpal tunnel syndrome or tendinitis. These may include taking frequent breaks during repetitive activities, using ergonomic tools and equipment, and practicing proper hand and wrist positioning to minimize stress.
References
American Society for Surgery of the Hand. (2020). Vascular disease: Symptoms & treatment | the hand society. https://www.assh.org/handcare/condition/vascular-disease
Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Vascular pain: Causes, signs, & treatment. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12102-vascular-pain
Dziedzic, K., Thomas, E., Hill, S., Wilkie, R., Peat, G., & Croft, P. R. (2007). The impact of musculoskeletal hand problems in older adults: Findings from the North Staffordshire Osteoarthritis Project (NorStOP). Rheumatology, 46(6), 963–967. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kem005
Kılıc, M. C. (2018). The relationship between hand function and activity participation performance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eurasian Journal of Medical Investigation. https://doi.org/10.14744/ejmi.2018.07279
Commonly asked questions
Hand Pain Diagrams are used by a range of medical professionals, including orthopedic surgeons, rheumatologists, physical therapists, and primary care physicians.
Hand Pain Diagrams are used to diagnose hand injuries or conditions, monitor treatment progress, communicate pain information, and educate patients about their hand conditions.
They are filled out with patient details and used to pinpoint the location of hand pain and document its characteristics.
The Hand Pain Diagram helps patients and healthcare providers by providing a clear visual representation of hand pain, aiding in diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient engagement.
Hand or wrist pain can occur for a variety of reasons, such as repetitive strain injuries, arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, or tendonitis. However, hand and wrist anatomy are different, and pain in these areas may require different treatment approaches. It is important to accurately identify the source of pain before starting any treatment.