Blood Glucose Levels
Need a Blood Glucose Levels Chart? Easily track blood sugar with the user-friendly chart. Manage diabetes with precision.


What Is A Blood Glucose Levels Chart?
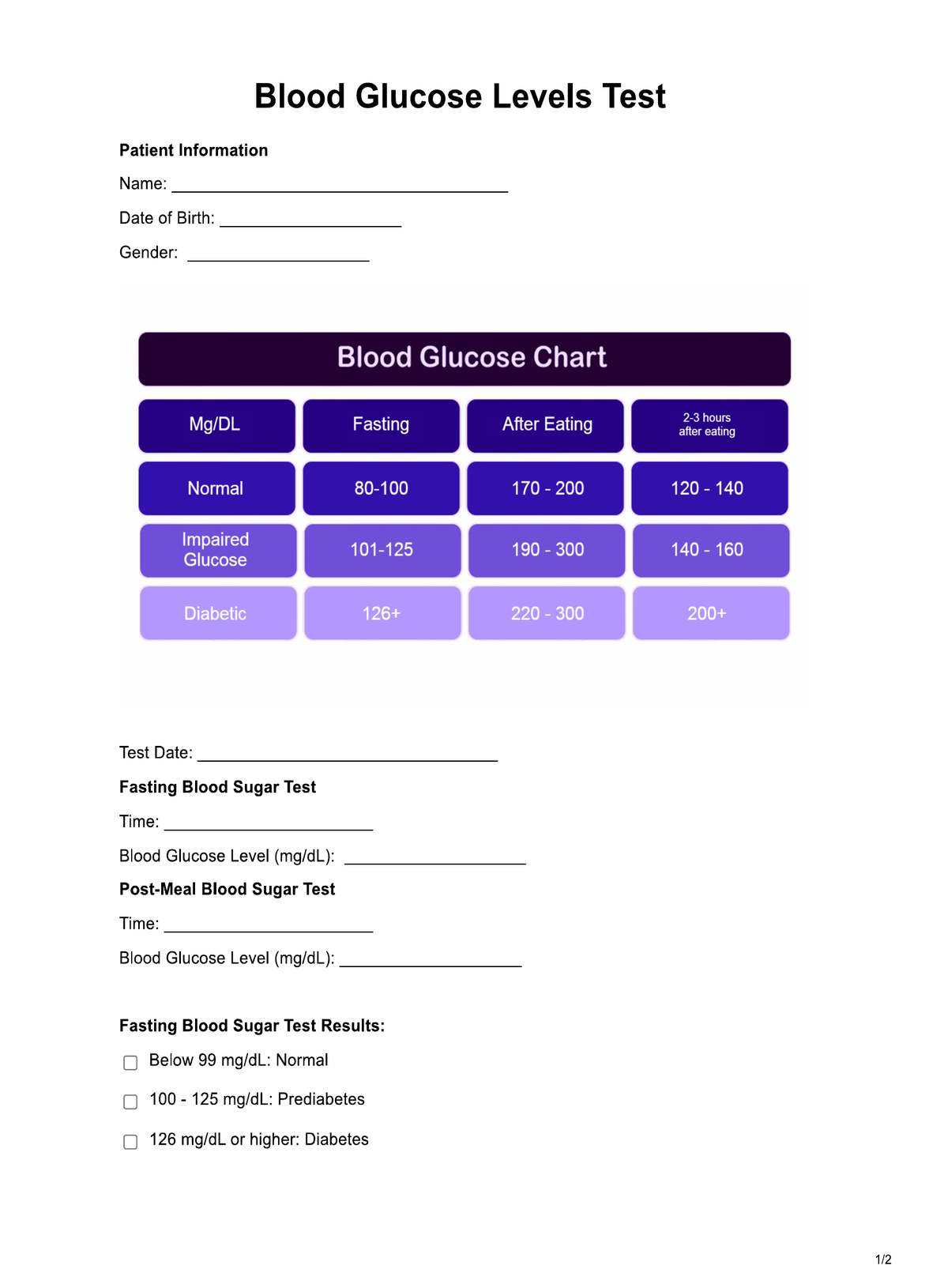
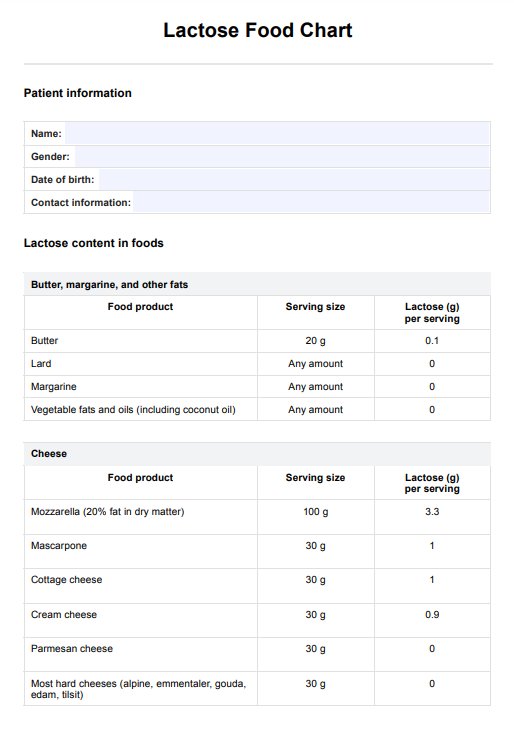
A Blood Glucose Levels Chart, commonly known as a blood sugar chart, is a visual reference tool used to track and interpret blood glucose levels over time. It is a vital resource for individuals managing diabetes or monitoring their prediabetic status. The chart typically displays blood sugar measurements in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) on one axis and time or specific intervals (e.g., before and after meals) on the other axis.
Typical Blood Glucose Levels Charts include target or normal range values, often indicating fasting and post-meal levels. These values help individuals assess their blood sugar levels within healthy boundaries. Deviations from these norms can signify prediabetes or diabetes.
This chart aids in identifying trends, making informed decisions about diet, medication, or lifestyle adjustments, and helps healthcare providers tailor treatment plans. It empowers individuals to actively manage their blood sugar and minimize the risks associated with diabetes-related complications. Regularly using a Blood Glucose Levels Chart is essential for maintaining stable glucose control and overall well-being.
Blood Glucose Levels Template
Blood Glucose Levels Example
How Does it Work?
Using the Printable Blood Glucose Levels Chart is straightforward. Here are five essential steps to ensure its accurate completion:
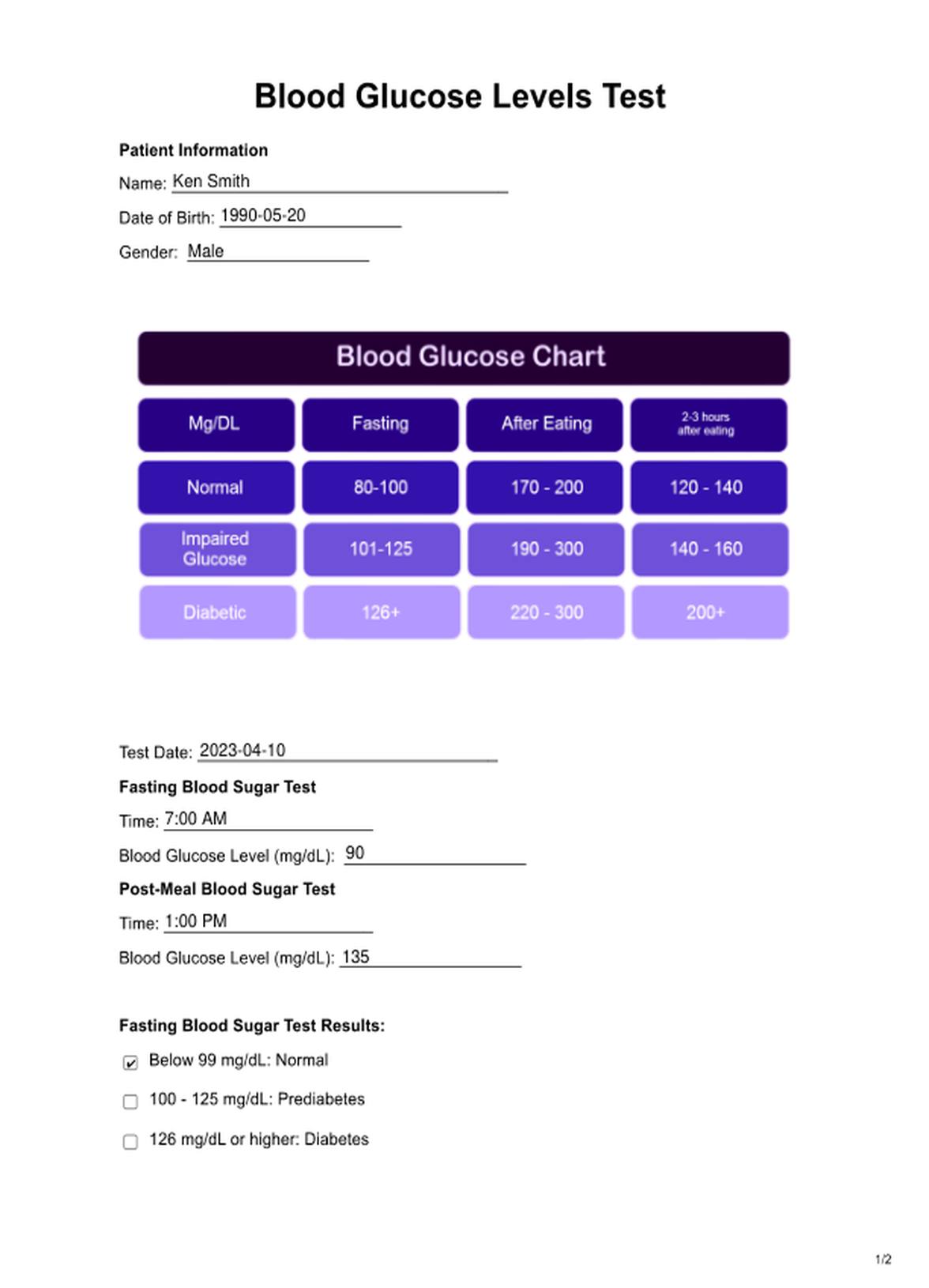
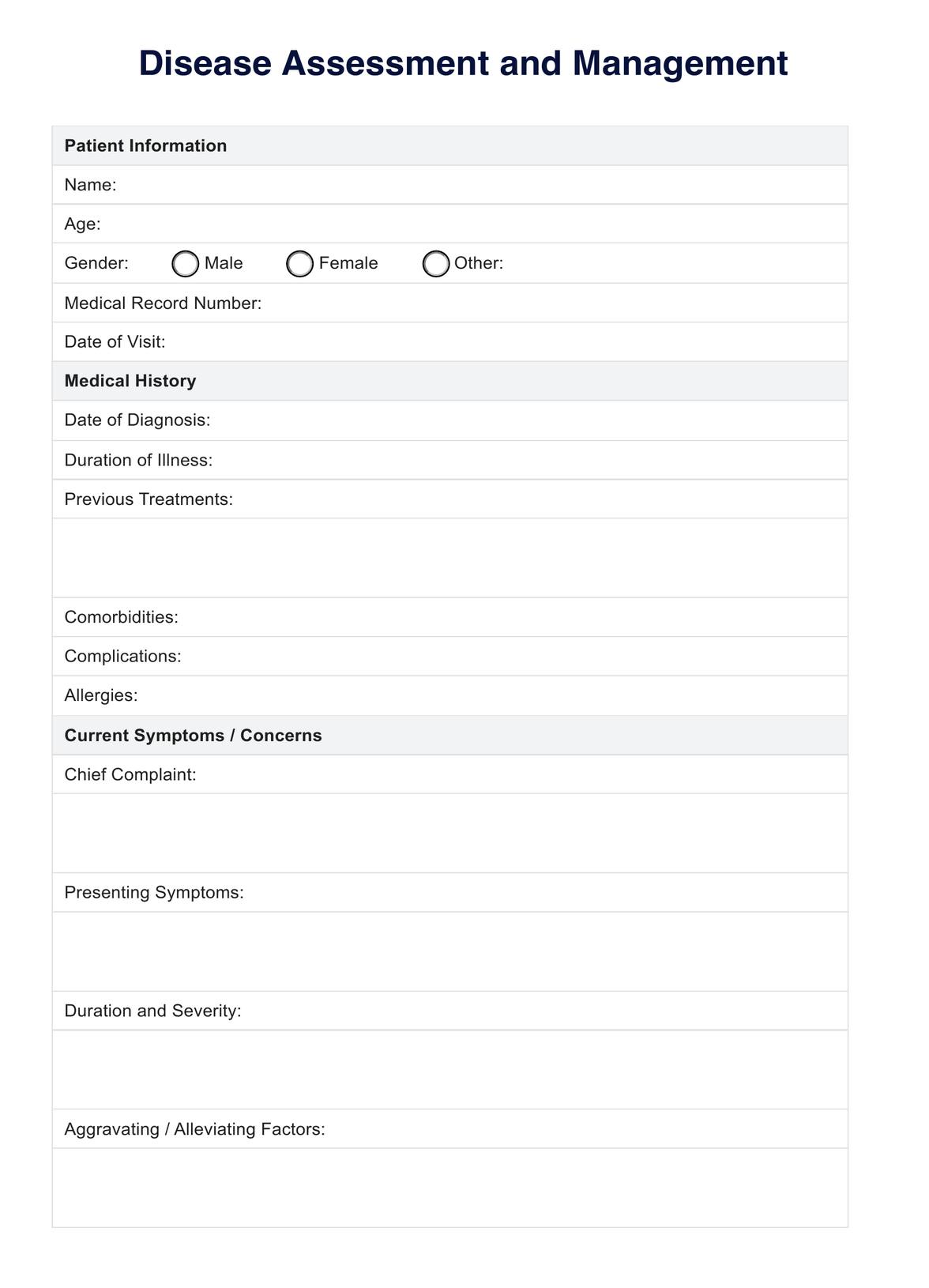
Step 1: Patient Information
Begin by entering the patient's personal details on the form, including their name, date of birth, and gender. This information is crucial for identification and record-keeping.
Step 2: Test Date and Times
Specify the date of the blood glucose test and record the exact times for both the fasting and post-meal blood sugar tests. Accurate timing is essential for interpretation.
Step 3: Blood Glucose Levels
For each test, input the corresponding blood glucose level in mg/dL. This data is the basis for evaluation and diagnosis, so precision is critical.
Step 4: Test Result Interpretation
Refer to the provided reference ranges to determine the patient's blood sugar status based on their test results. The firm offers clear categories, such as "Normal," "Prediabetes," or "Diabetes," to help with interpretation.
Step 5: Comments and Recommendations
If you're a healthcare provider, use the designated space to provide relevant comments or recommendations based on the test results. This is an opportunity to offer guidance and advice to the patient.
When Would You Use This Chart?
The Blood Glucose Levels Chart is an indispensable resource for many healthcare practitioners. Primary care physicians and endocrinologists frequently rely on this tool during initial patient assessments to gauge blood sugar control and diagnose potential diabetes or prediabetes.
It's a pivotal element for diabetologists in monitoring treatment effectiveness and making necessary adjustments. Certified diabetes educators can use the chart as an educational aid to explain blood glucose trends to patients, empowering them with knowledge for self-management.
Additionally, nutritionists and dietitians find it valuable when crafting personalized dietary plans, as they can correlate food intake with blood sugar fluctuations. In emergency care settings, the chart helps quickly evaluate patients' blood glucose levels, aiding in prompt decisions on intervention.
Thus, this resource finds utility across a spectrum of healthcare professionals, offering vital support in diagnosis, treatment, education, dietary guidance, and emergencies, ultimately enhancing patient care and well-being.
What do the Results Mean?
The Free Blood Glucose Levels Chart provides crucial insights into a patient's blood sugar status, with key implications for healthcare professionals. When fasting blood sugar levels fall below 99 mg/dL, this indicates normal blood glucose control, signifying no immediate cause for concern. The 100 to 125 mg/dL range suggests prediabetes, highlighting the need for lifestyle adjustments and closer monitoring. A fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or higher typically indicates diabetes, necessitating prompt medical attention.
In the post-meal blood sugar test, results below 140 mg/dL signify normal levels, while readings between 140 and 199 mg/dL generally indicate prediabetes. Results exceeding 200 mg/dL indicate diabetes, requiring immediate intervention to manage blood sugar effectively.
These interpretations guide healthcare professionals in providing tailored care, lifestyle recommendations, and treatment strategies for their patients, thereby supporting better blood sugar management and overall health.
Research & Evidence
In ancient times, the earliest reference to diabetes emerged in India, where it was known as "madhumeha" or "honey urine." Afflicted individuals displayed excessive thirst and urination, and their urine attracted ants, signifying a high sugar content. It wasn't until 1674 that English physician Thomas Willis coined the term "diabetes mellitus," meaning "honey urine." Fast forward to 1921, when Canadian scientists Frederick Banting and Charles Best achieved a groundbreaking milestone by successfully isolating insulin from canine pancreases, marking a pivotal moment in diabetes treatment.
Today, blood glucose monitoring is integral to diabetes management. The evolution of our understanding of blood glucose levels has led to crucial revelations, including the pivotal role of insulin in regulating glucose usage and the classification of diabetes into two main types: type 1, an autoimmune condition destroying insulin-producing cells, and type 2, a lifestyle-related resistance to insulin. High blood glucose levels can lead to severe complications like heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
As we look to the future, ongoing research seeks to develop innovative methods for diabetes prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Scientists aim to create artificial pancreas systems for automated blood glucose regulation, design more effective insulin-producing drugs, and explore gene therapy as a potential prevention or cure for diabetes. This research paves the way for improving the lives of individuals with diabetes and mitigating the disease's debilitating consequences.
References
- International Diabetes Federation (2023). IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation.
Commonly asked questions
It is usually requested by healthcare providers, such as doctors, nurses, or endocrinologists, to monitor and assess a patient's blood sugar levels.
The charts are used during routine check-ups, diabetes management, and for patients with blood sugar concerns, helping healthcare professionals make informed decisions about treatment and lifestyle changes.
These are used to record fasting and post-meal blood sugar readings over time. Patients can fill in the chart with their test results, which healthcare providers interpret to make recommendations.