The most common neck problem is neck pain, often attributed to muscle strain, poor posture, or stress. It can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, affecting daily activities and quality of life.
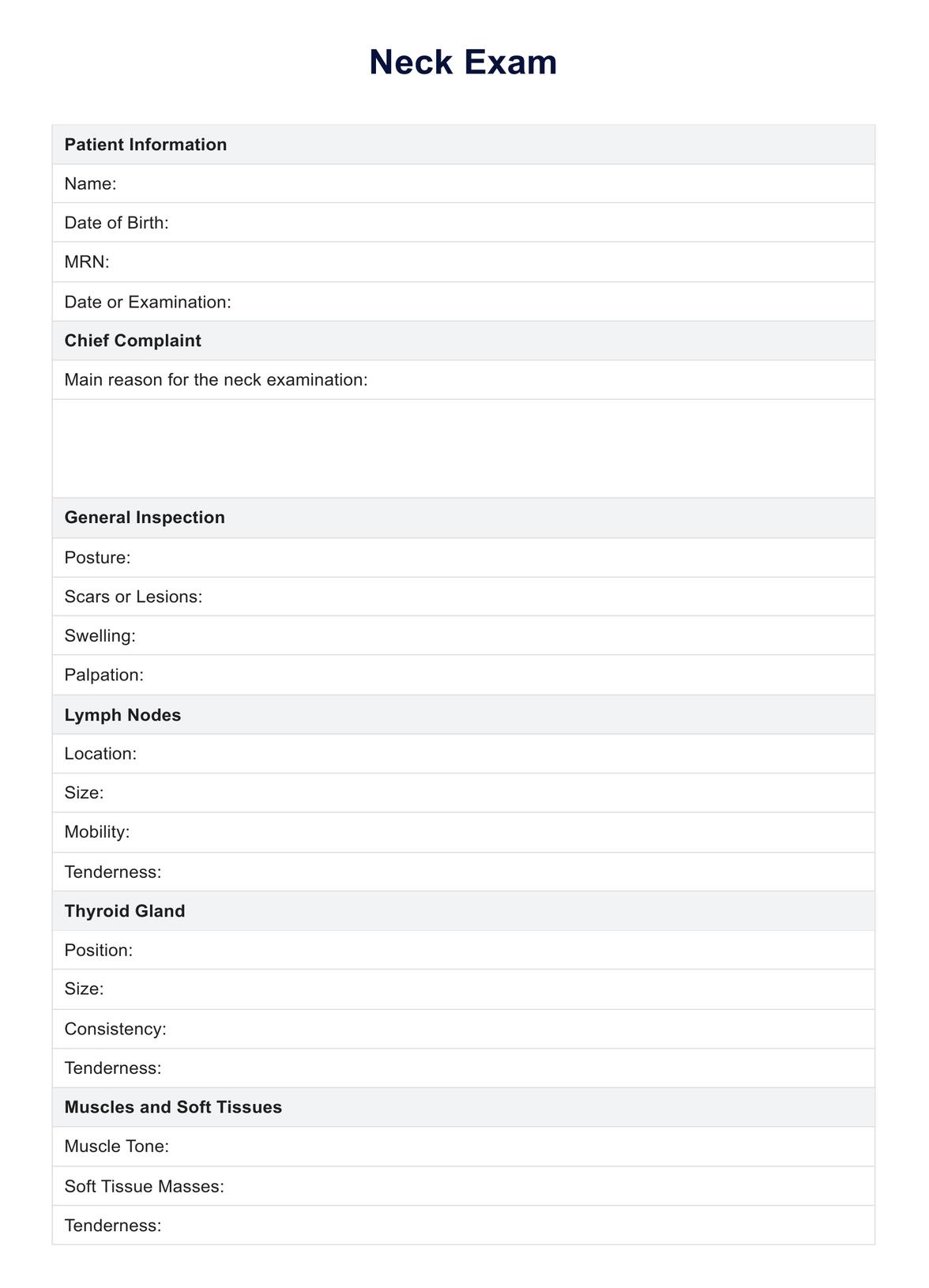
Neck exam
This comprehensive guide teaches you how to perform a thorough neck examination. Download Carepatron's PDF and get step-by-step instructions for conducting a neck exam.
Neck exam Template
Commonly asked questions
Assessing the neck is crucial to identify underlying issues, ranging from musculoskeletal conditions to neurological problems. Early detection allows timely intervention, preventing potential complications and improving patient outcomes.
Palpating the neck helps identify abnormalities in lymph nodes, thyroid, and blood vessels. It aids in detecting inflammation, masses, or tenderness, providing valuable information for diagnosis and treatment planning.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











