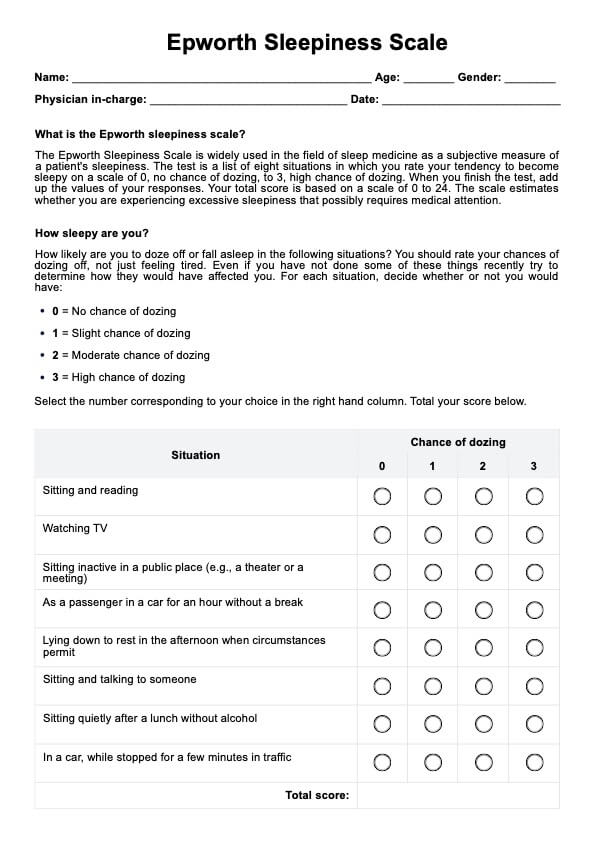
A normal Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) score typically ranges from 0 to 10, indicating minimal to moderate daytime sleepiness.
Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS)
Learn how to use and download the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) as a questionnaire to measure daytime sleepiness.
Use Template
Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) Template
Commonly asked questions
A total score greater than 10 suggests significant daytime sleepiness, warranting further evaluation for potential sleep disorders.
The Epworth Sleepiness Scale is graded based on total scores: 0-5 indicates lower daytime sleepiness, 6-10 suggests moderate sleepiness, and scores above 10 indicate excessive daytime sleepiness.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











