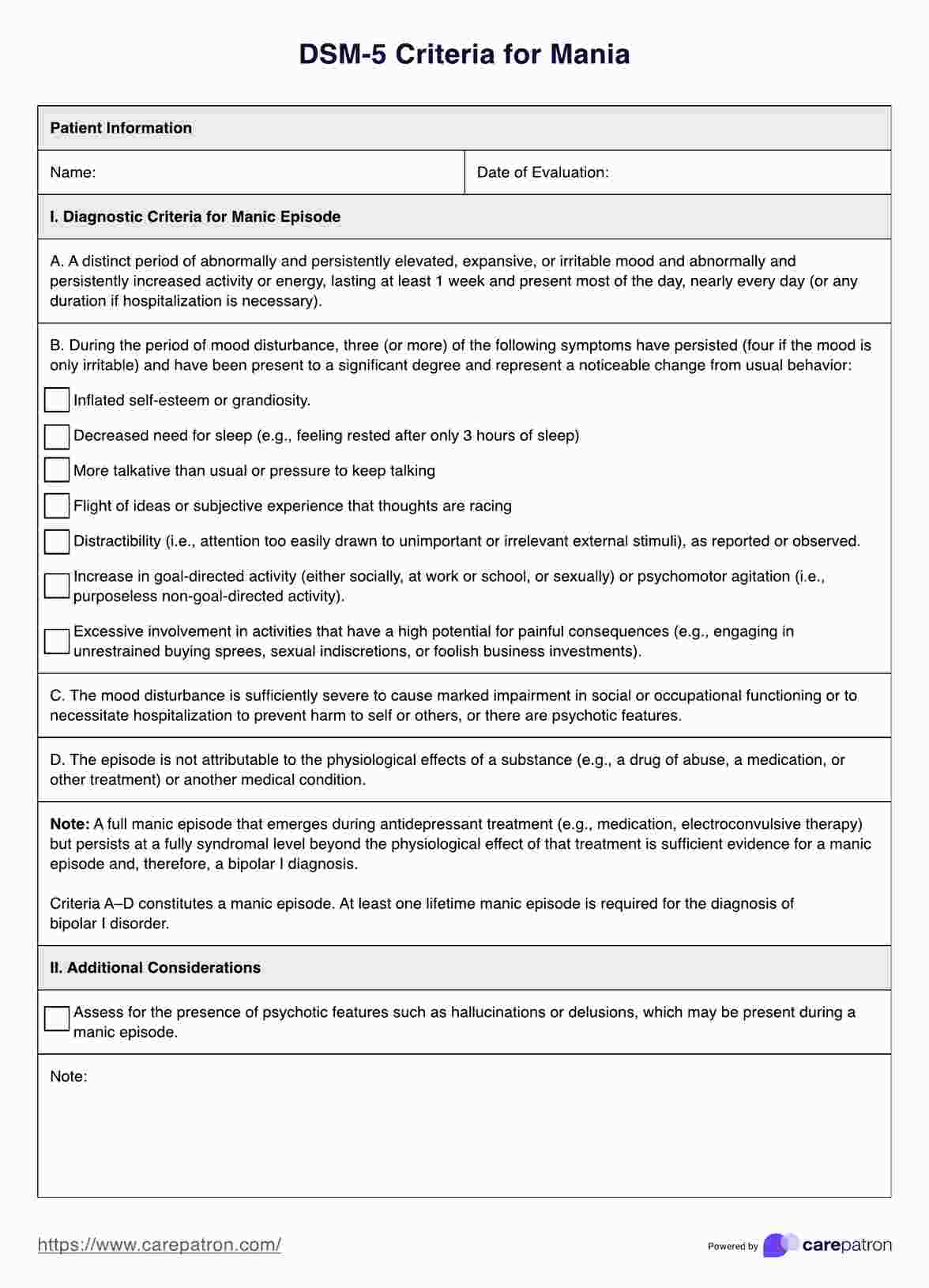
Substance Use Disorder DSM 5 Criteria
Understanding substance use disorder, its symptoms, withdrawal symptoms, causes, and diagnosis through DSM 5 criteria. Download our free Substance Use Disorder DSM 5 Criteria


What is substance use disorder?
Substance use disorder is a multifaceted condition marked by the problematic use of substances, encompassing either alcohol abuse, drugs (both illicit and prescription), or medications. This disorder, recognized within the realm of mental disorders, delineates itself from controlled usage through the manifestation of significant impairment or distress across various facets of an individual's life. Such distress impacts cognition, behavior, and emotional well-being, solidifying its status as a mental health condition.
Substance Use Disorder DSM 5 Criteria Template
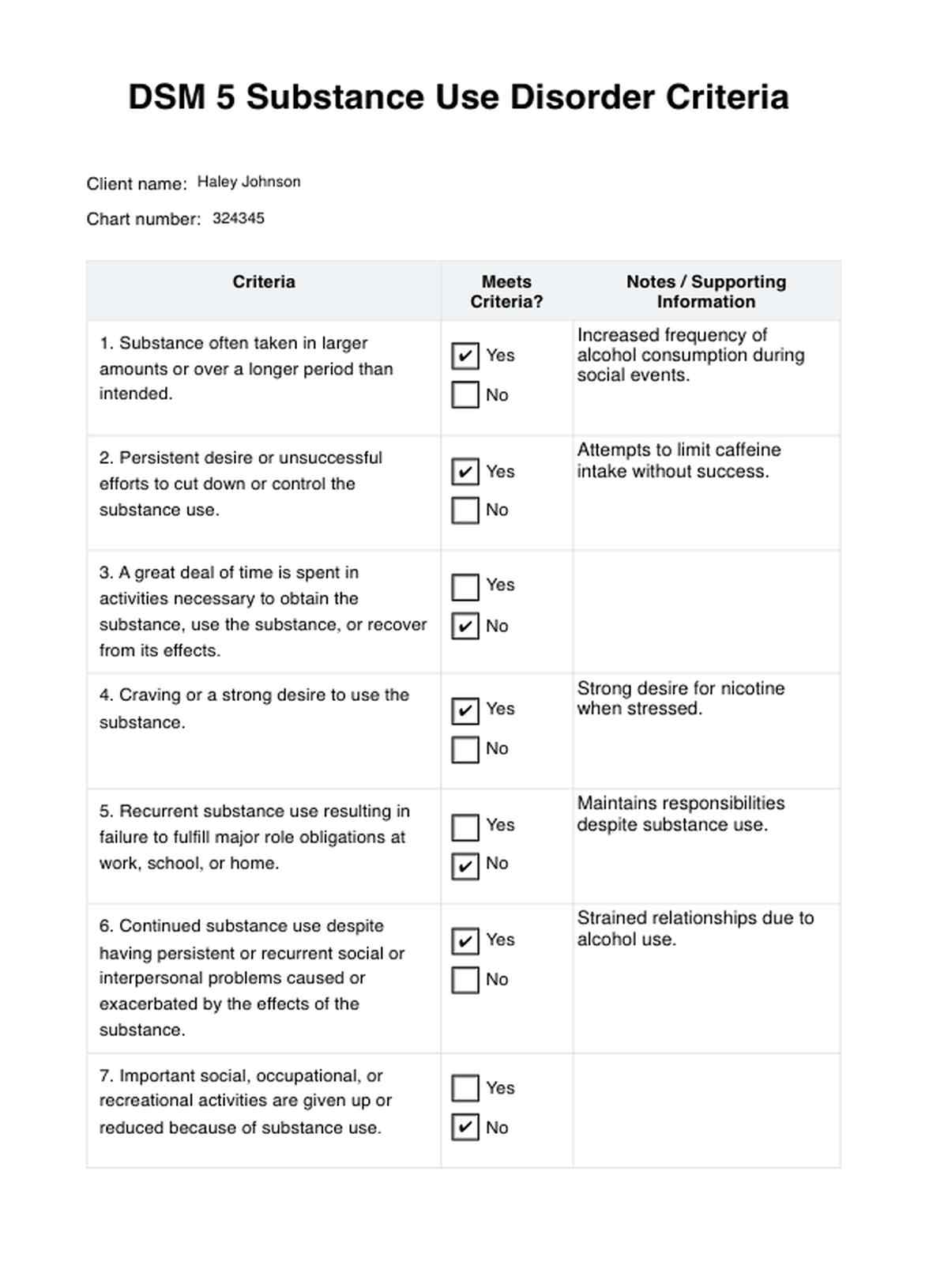
Substance Use Disorder DSM 5 Criteria Example
Symptoms of substance use disorder
The symptoms of substance use disorder collectively contribute to diagnostic criteria and exhibit varying severity levels based on individual contexts. Key symptoms include:
- Continued use despite negative consequences: Despite facing adverse outcomes such as health issues, relational strain, or legal entanglements, individuals persist in substance use.
- Cravings for the substance: Intense urges propel individuals towards compulsive behaviors aimed at acquiring and consuming substances.
- Tolerance to the substance: Over time, the body and mind adapt, necessitating increased substance quantities to achieve desired effects—a phenomenon known as tolerance.
- Withdrawal symptoms upon cessation: Abrupt cessation prompts a range of physical and psychological symptoms, collectively termed withdrawal, often driving continued substance use to mitigate discomfort.
- Inability to fulfill obligations: Substance use impairs individuals' capacity to meet responsibilities at work, school, or home, leading to absenteeism, decreased performance, or neglect of duties.
- Neglect of activities due to substance use: Substances usurp the focus of an individual's life, resulting in the abandonment of previously enjoyed activities, hobbies, or social engagements.
- Persistent use despite awareness of physical or psychological problems: Despite recognizing the detrimental impact of substance use on their physical and mental well-being, individuals persist in consumption, underscoring the compulsive nature of the disorder and the challenges inherent in cessation efforts.
Substance use disorder causes
The etiology of substance use disorders is multifaceted and encompasses a complex interplay of various factors, including genetic predisposition, environmental influences, psychological factors, and potentially associated biological factors. Genetic predisposition may render certain individuals more vulnerable to developing substance use disorders, with hereditary factors influencing susceptibility to addictive behaviors.
Environmental influences, such as peer pressure, societal norms, and access to substances, play a significant role in shaping patterns of substance use. Additionally, psychological factors, including stress, trauma, and co-occurring mental disorders, can contribute to the development and maintenance of substance use disorders.
Moreover, potentially associated biological factors, such as alterations in brain chemistry and neurobiology, further contribute to the neuroadaptive changes observed in individuals with substance use disorders. By comprehensively examining these multifaceted factors, healthcare professionals can gain insight into the underlying mechanisms driving substance-related behaviors, inform treatment approaches, and address substance use disorder criteria and risk factors to promote recovery and well-being.
Diagnosing substance use disorder DSM-5
Healthcare professionals use diagnostic criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-5) to diagnose substance use disorders and other mental disorders. The DSM-5 is a widely used classification system for mental disorders published by the American Psychiatric Association.
The DSM-5 outlines specific criteria for diagnosing substance use disorders, including criteria related to the presence and severity of symptoms, impairment or distress caused by substance use, and the duration of the disorder. It also includes specifiers to indicate the severity of substance use disorder, such as mild, moderate, or severe.
By adhering to the DSM-5 criteria, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose substance use disorders, guide treatment planning, monitor progress, and facilitate communication among healthcare providers. The DSM-5 serves as a valuable resource in the assessment and management of both substance use disorders criteria other-related problems, ensuring consistency and reliability in clinical practice.
How does our Substance Use Disorder DSM 5 Criteria template work?
Here's a 5-step guide to ensure accurate and reliable diagnosis, leading to effective treatment planning and support for individuals struggling with severe substance use disorder.
Step 1: Familiarize yourself with the DSM-5 criteria
Before using the template, familiarize yourself with the DSM-5 criteria for substance use disorder diagnosis. Understand the specific symptoms, severity levels, and duration required for diagnosis.
Step 2: Access the Substance Use Disorder DSM-5 Criteria template
Access our Substance Use Disorder DSM-5 Criteria template, available for free download. You can find the template here.
Step 3: Review the checklist
Open the template and review the checklist provided. Ensure that each criterion outlined in the DSM-5 for diagnosing substance use disorder is included in the checklist.
Step 4: Assess the individual
Use the checklist to systematically assess the individual's symptoms and behaviors related to substance use. For each criterion, mark whether it is present or absent based on the information gathered during the assessment process.
Step 5: Determine diagnosis and severity
After completing the checklist, analyze the results to determine whether the individual meets the diagnostic criteria for substance use disorder according to the DSM-5. Consider the severity of the substance-induced mental disorder based on the number of criteria met and their impact on the individual's functioning.
What are the benefits of using the Substance Use Disorder DSM-5 Criteria
The utilization of the Substance Use Disorder DSM-5 Criteria offers several benefits in the assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of substance-related disorders:
Standardized assessment
The DSM-5 provides a standardized framework for assessing substance use disorders, ensuring consistency and reliability in diagnostic practices across healthcare settings. By adhering to established criteria, healthcare professionals can conduct thorough evaluations and accurately identify individuals experiencing substance-related problems.
Comprehensive evaluation
The DSM-5 criteria encompass a wide range of symptoms and behaviors associated with substance use disorders, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of the disorder's presentation. This holistic approach enables healthcare professionals to consider various aspects of an individual's substance use patterns, severity, and associated impairment, facilitating a thorough understanding of the clinical picture.
Diagnostic clarity
By delineating specific diagnostic criteria, the DSM-5 enhances diagnostic clarity and precision in identifying substance use disorders. Clear and explicit criteria aid healthcare professionals in making accurate diagnoses and distinguishing substance use disorders from other mental disorders or non-clinical patterns of substance use.
Severity specification
The DSM-5 introduced severity specifiers for substance use disorders, enabling clinicians to classify the severity of the disorder based on the number of diagnostic criteria met. This feature allows for nuanced assessment and facilitates individualized treatment planning tailored to the severity of the disorder.
Treatment planning and monitoring
Utilizing the DSM-5 criteria enables healthcare professionals to develop targeted treatment plans based on the specific symptoms and severity of the substance use disorder. Additionally, the standardized criteria facilitate ongoing monitoring of treatment progress and outcomes, allowing for adjustments to optimize therapeutic interventions.
You can adopt this prescription template to boost your practice and client outcomes. This tool enables clients to formulate actionable plans for their progress.
Commonly asked questions
Common signs include cravings, tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, neglect of responsibilities, and continued use despite negative consequences.
Yes, substance use disorder is treatable through various interventions including therapy, medication, support groups, and rehabilitation programs.
Yes, substance use disorder can co-occur with other mental disorders such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder, complicating treatment and management.








































-template.jpg)