DSM 5 Generalized Anxiety Disorder Checklist
Here's a DSM 5 Generalized Anxiety Disorder Checklist to get clinical information and criteria, ICD-10 codes, and valuable resources for diagnosis support.


DSM 5 Checklist for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
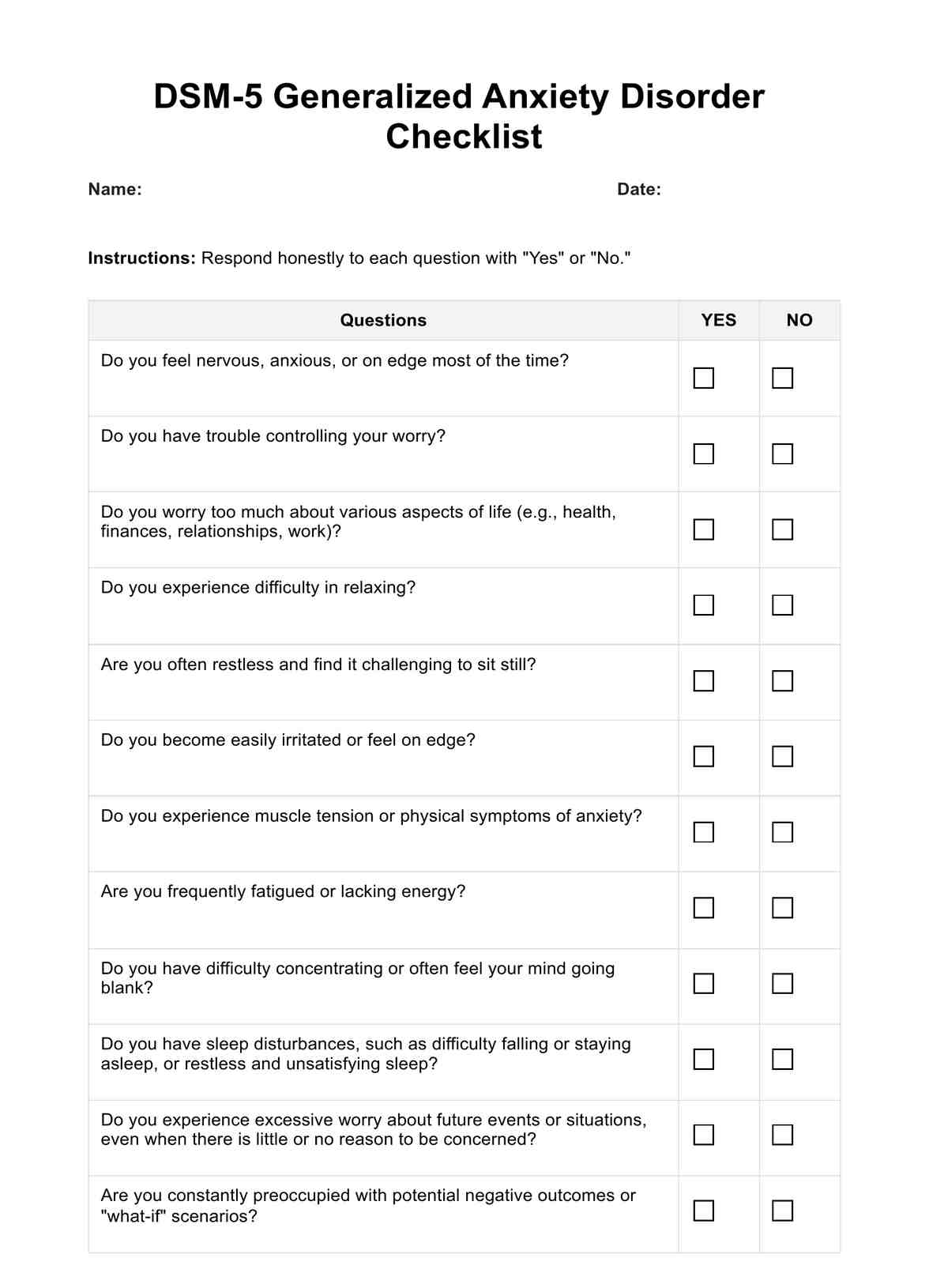
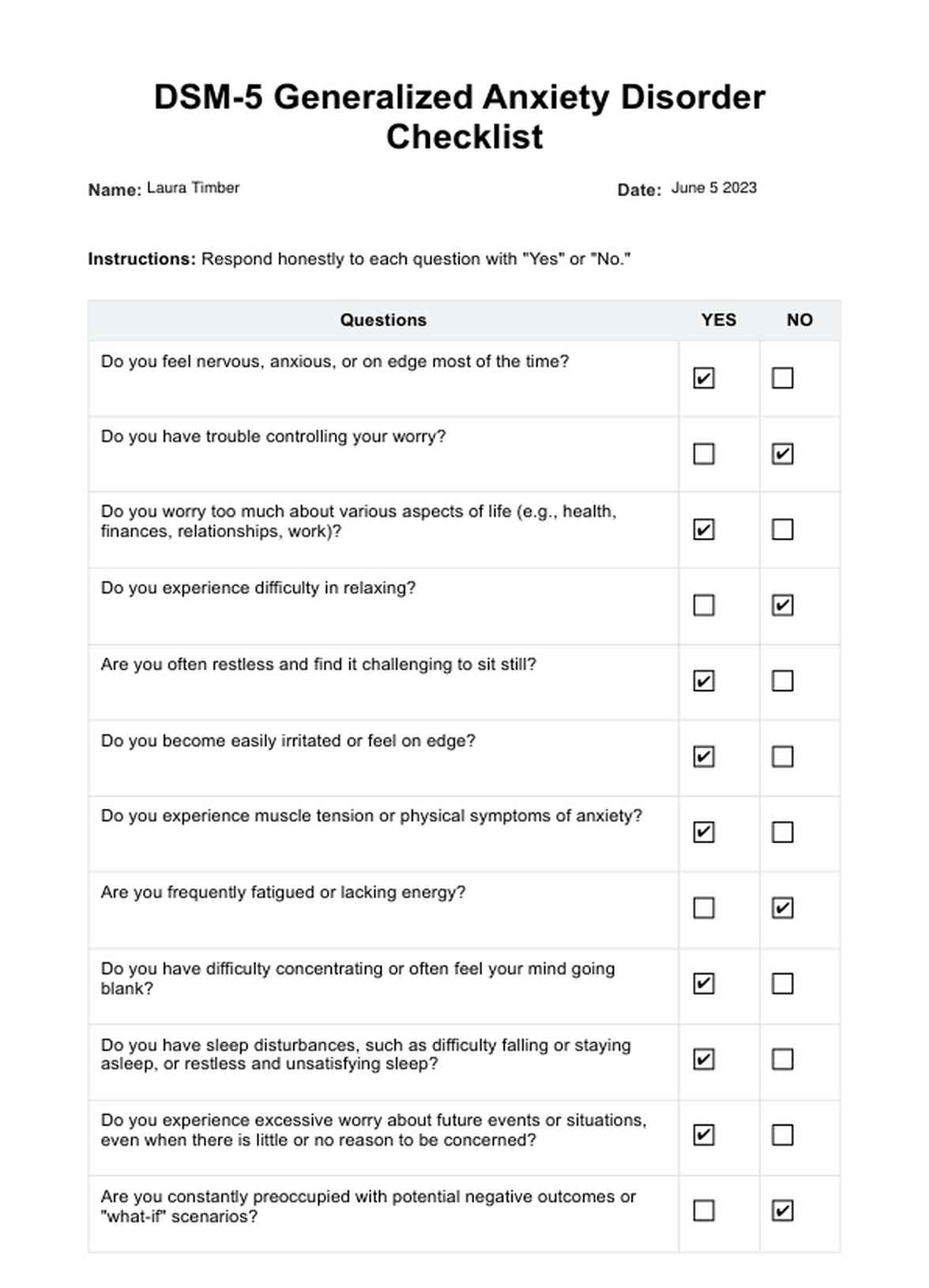
The DSM 5 Checklist for Generalized Anxiety Disorder is a tool used by mental healthcare practitioners to identify symptoms of Generalized Anxiety Disorder. It includes specific criteria and symptoms such as excessive worry, difficulty controlling it, restlessness, irritability, and more. However, it is not a standalone diagnostic resource and requires a qualified professional's evaluation.
If you suspect GAD, seek help from a mental health expert for a comprehensive assessment and appropriate treatment. Remember, support is available to manage GAD effectively.
DSM 5 Generalized Anxiety Disorder Checklist Template
DSM 5 Generalized Anxiety Disorder Checklist Example
Clinical Information and Criteria
Clinical Information
- GAD is characterized by excessive and uncontrollable worry about various aspects of life.
- Clinical presentation includes persistent worry and anxiety for at least six months.
- Symptoms include difficulty controlling worry, restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and sleep disturbances.
- Causes may involve brain chemistry, hormones, life events, substance abuse, pre-existing health conditions, and genetic factors.
- Diagnosis is made through a clinical interview and symptom assessment by a mental health professional.
- Treatment options include psychotherapy, medication, brain stimulation therapy, and lifestyle changes.
- Managing GAD involves adopting stress-reduction techniques, regular exercise, and healthy sleep habits.
- F41.1 is the DSM 5 generalized anxiety disorder code and it is characterized by excessive and uncontrollable worry about various aspects of life.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder DSM 5 Criteria
- One DSM 5 Generalized Anxiety Disorder criteria is excessive worry and anxiety. It must be present most days for at least six months.
- Another is difficulty controlling worry.
- At least three of the following: restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances.
- It is important to note that the DSM-5 criteria serve as a valuable tool, but a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional is necessary for an accurate diagnosis and to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for individuals with GAD.
What are the Generalized Anxiety Disorder ICD 10 Codes?
- F41.1: Unspecified generalized anxiety disorder DSM 5 code.
- F41.2: Persistent anxiety and worry for at least 6 months, exceeding normal expectations.
- F41.3: Anxiety and worry for at least 6 months, accompanied by at least 3 symptoms (e.g., restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating).
- F43.23: Difficulty coping with stress, leading to a blend of anxiety and depressive symptoms (Adjustment disorder with mixed anxiety and depressed mood).
- F43.11: Difficulty coping with stress, primarily presenting as anxiety (Adjustment disorder with anxiety).
- F41.9: Unspecified anxiety disorder without specific details.
- F43.20: Difficulty coping with stress without specific manifestations (Adjustment disorder, unspecified).
- F43.10: Unspecified PTSD without further details (Post-traumatic stress disorder, unspecified).
- F43.12: Long-term PTSD resulting from past traumatic experiences (Post-traumatic stress disorder, chronic).
- F43.21: Difficulty coping with stress leading to a predominant sense of depression (Adjustment disorder with depressed mood).
Other common anxiety codes:
- F40.1: Fear and discomfort in social situations (ICD-10 social anxiety disorder - social phobia).
- F41.0: Recurrent panic attacks and fear of future attacks (ICD-10 panic disorder).
- F42: Intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors (ICD-10 obsessive-compulsive disorder - OCD).
What resources can you use for patients diagnosed with Generalized Anxiety Disorder?
Carepatron provides a range of valuable resources for patients exhibiting symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder DSM-5. If your patient is diagnosed with GAD, you will find the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Resources particularly beneficial:
Generalized Anxiety Disorder Treatment Plan:
- Utilize a patient-centered approach to outline specific goals and interventions for treating GAD.
- Include sections such as diagnostic criteria, treatment goals, interventions, recommended medication, and progress notes.
- Implement the DSM 5 generalized anxiety disorder Checklist to assess and identify the presence of symptoms like excessive worry, difficulty controlling it, restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances.
Carepatron also offers other features and tools to assist in treating patients with Generalized Anxiety Disorder. Utilize schedule automation, note creation, and integrated telehealth consultations to enhance patient care and support those who may have difficulty physically visiting your clinic.
For future reference, Carepatron's template library continues to grow, and you can expect more resources related to generalized anxiety disorder DSM 5 and other mental health conditions. Stay updated to access additional tools to improve patient care and treatment planning.
.png)
Commonly asked questions
Yes, the checklist can assist in diagnosing GAD, but it's no substitute for a professional evaluation. It includes symptoms like excessive worry, difficulty controlling worry, physical signs of anxiety, restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and sleep problems. For an accurate diagnosis and proper management, consult a mental health professional.
Unspecified anxiety and GAD both involve excessive worry, but they differ in their diagnostic criteria. Unspecified anxiety lacks the full GAD criteria due to milder or shorter-lasting symptoms. GAD requires at least 6 months of hard-to-control worry about various issues and is often accompanied by physical symptoms like muscle tension and headaches.
Yes, GAD is recognized as a mental health disorder. It is a persistent condition that can considerably disrupt an individual's life. If you are encountering GAD symptoms, it is crucial to seek professional assistance, as there are effective treatments accessible to help you cope with anxiety and enhance your overall well-being.


































-template.jpg)