BMI Chart Men
Use Carepatron's free PDF BMI Chart for Men to support clinical assessments, patient weight management, and evaluation.


What is body mass index?
Body mass index (BMI) is a numerical value derived from a person's weight and height, used to estimate body fat, check low body fat levels, and assess health risks (Khanna et. al., 2022). The BMI formula is weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared. Healthcare professionals use BMI to quickly categorize individuals into weight classifications—underweight, normal, overweight, or obese—helping determine if they fall within a healthy weight range.
While BMI is a convenient tool, it has limitations. It does not differentiate between muscle mass, fat, or bone, which can underestimate body fat in some cases. A high BMI may not always indicate excess fat, especially in muscular individuals (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institutem 2019). Despite these limitations, elevated BMI values are associated with increased risks of high blood pressure, heart disease, severe obesity, and chronic health conditions.
Practitioners should consider body composition, waist circumference, and lifestyle factors when interpreting BMI results. Using a BMI calculator provides a fast way to calculate BMI, but it should be part of a comprehensive health assessment for determining healthy body weight and reducing potential health risks.
BMI Chart Men Template
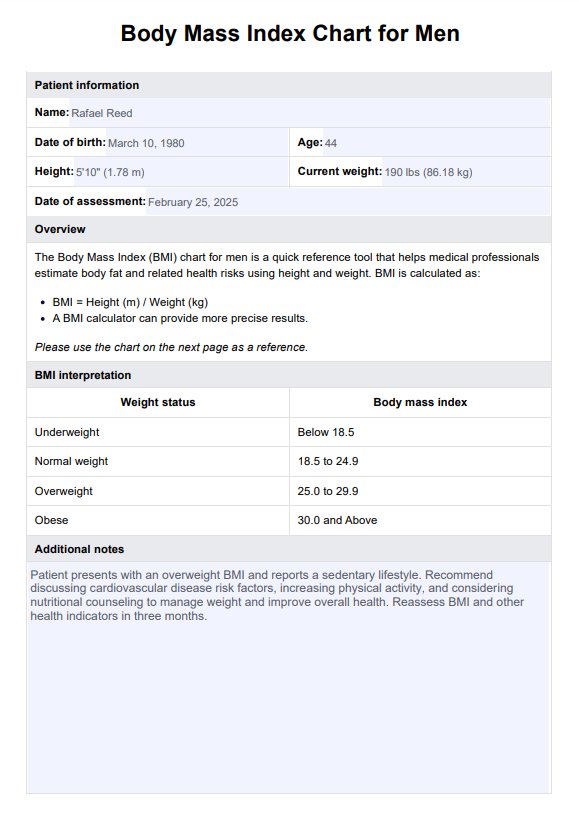
BMI Chart Men Example
What is the BMI Chart Men version?
The Body Mass Index (BMI) chart for men is a practical tool that helps healthcare providers assess weight status by using a combination of height and weight to estimate total body fat. By referencing the chart, practitioners can determine if a patient falls within the normal weight, underweight, overweight, or obese BMI categories. This classification plays a vital role in identifying potential risk factors associated with adult obesity, cardiovascular disease, and other chronic conditions that can affect overall health.
While the BMI calculation is the same for both men and women, men typically have more muscle mass, which can influence BMI readings. Two individuals with the same BMI may have different body compositions, making it essential to use BMI as part of a broader health assessment.
The BMI chart serves as a quick reference, guiding decisions about lifestyle changes, further diagnostic testing, and disease prevention strategies. However, it’s important to note that BMI doesn’t differentiate between fat and muscle. As a result, athletes or muscular individuals may appear to have excess weight when their body fat is low. Healthcare professionals should consider additional measures, such as waist circumference, to more accurately assess risk factors and improve disease control outcomes.
How to read BMI for men
To interpret the BMI chart men, start by locating the patient’s height and weight on the chart to find the corresponding BMI value. The BMI calculation is determined by dividing weight in kilograms by height in meters squared. The resulting value categorizes weight status into four main BMI ranges (American Heart Association, 2024):
- Underweight: below 18.5
- Normal weight:18.5–24.9
- Overweight: 25.0–29.9
- Obese: 30.0 and above
These categories help assess risk factors for conditions like cardiovascular disease and guide appropriate care.
It’s important to note that more body weight doesn’t always indicate unhealthy fat levels. Men with more muscle mass may have elevated BMIs without excess body fat, while others may have a normal weight but higher total body fat, increasing their health risks. A healthcare provider should interpret BMI results within the context of overall health, body composition, and other metrics to ensure accurate risk assessment and disease control planning.
How does it work?
The Body Mass Index Chart for Men on Carepatron is designed to streamline patient assessments by providing healthcare professionals with a quick, reliable tool to evaluate weight status and related health risks. Using the chart is simple, allowing practitioners to integrate BMI assessments seamlessly into their clinical workflows.
Step 1: Access the chart
Click the "Use template" button to access the Body Mass Index Chart for Men directly. This will lead you to the Carepatron app download, allowing immediate use of the template.
Step 2: Introduce the chart to the patient
When discussing the BMI chart with patients, provide a concise explanation of how it helps assess weight status and potential health risks. Emphasize that BMI is one of several tools used to evaluate overall health and that further assessments may be necessary to gain a complete picture of their health profile.
Step 3: Use chart in patient assessment
Enter the patient’s height and weight into the chart. Use the results to identify their BMI range and discuss potential risk factors for conditions like cardiovascular disease or adult obesity. Consider additional measurements, such as waist circumference, to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of body composition.
Step 4: Provide additional patient education and next steps
Explain the BMI findings in context, highlighting the importance of lifestyle changes when appropriate. Offer guidance on nutrition, exercise, or further diagnostic evaluations. If needed, schedule follow-ups to monitor progress or refer the patient to specialists for targeted interventions aimed at improving overall health outcomes.
Benefits of using this chart
The Body Mass Index Chart for Men offers medical professionals a practical tool to streamline patient assessments and enhance clinical decision-making. It enables practitioners to identify potential risk factors for conditions like cardiovascular disease and adult obesity without requiring complex equipment or lengthy calculations. Integrating the chart into patient evaluations promotes consistent use of standardized BMI ranges, supporting evidence-based care.
Additionally, the template facilitates clear communication when discussing health risks with patients, improving patient understanding and engagement. Using this chart also assists in documentation and compliance with clinical guidelines, making it easier to track patient progress over time.
Overall, the chart improves workflow efficiency by allowing healthcare providers to quickly assess body composition and overall health while focusing on patient-centered interventions and preventive care strategies.
References
American Heart Association. (2024). Body mass index (BMI) in adults. Www.heart.org. https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/losing-weight/bmi-in-adults
Khanna, D., Peltzer, C., Kahar, P., & Parmar, M. S. (2022). Body mass index (BMI): A screening tool analysis. Cureus, 14(2). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.22119
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2019). Assessing your weight and health risk. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/educational/lose_wt/risk.htm
Commonly asked questions
A healthy BMI for a man falls between 18.5 and 24.9, indicating a normal weight range associated with lower health risks. Values outside this range may signal potential risk factors for chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease or adult obesity.
For a 5'10" male, a healthy BMI should range from 18.5 to 24.9, which corresponds to a weight of approximately 129 to 174 pounds. Staying within this range helps minimize health risks related to excess weight or low body fat levels.
The BMI ranges for a 70-year-old man are the same as for younger adults, with a healthy BMI between 18.5 and 24.9. However, healthcare providers should also consider body composition and age-related muscle loss when interpreting results.