Pediatric BMI Chart
Download our Pediatric BMI Chart for a resource that can assist you in assessing and documenting a child's weight status.


What is body mass index?
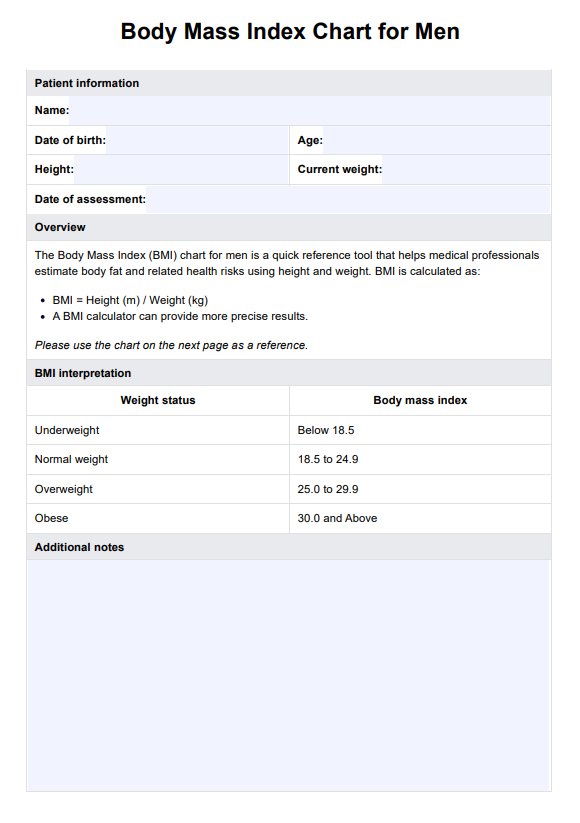
Body mass index (BMI) measures a person's weight based on their height to estimate body fat and determine whether their weight is healthy. For adults, a healthy BMI range is between 18.5 and 24.9, with underweight being below 18.5, overweight between 25 and 29.9, and obese at 30 or above. In children and teens aged 2 to 18, BMI is calculated based on age and gender, expressed as a percentile relative to peers.
Although BMI is a helpful screening tool, it is not a perfect measure of body fat, as muscle mass, age, sex, and ethnicity can affect its accuracy. Healthcare providers use BMI along with other assessments to evaluate health risks, and a high BMI may suggest excess body fat, potentially leading to issues like heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
BMI is a quick, easy method for estimating body fat, but it should be part of a broader health evaluation.
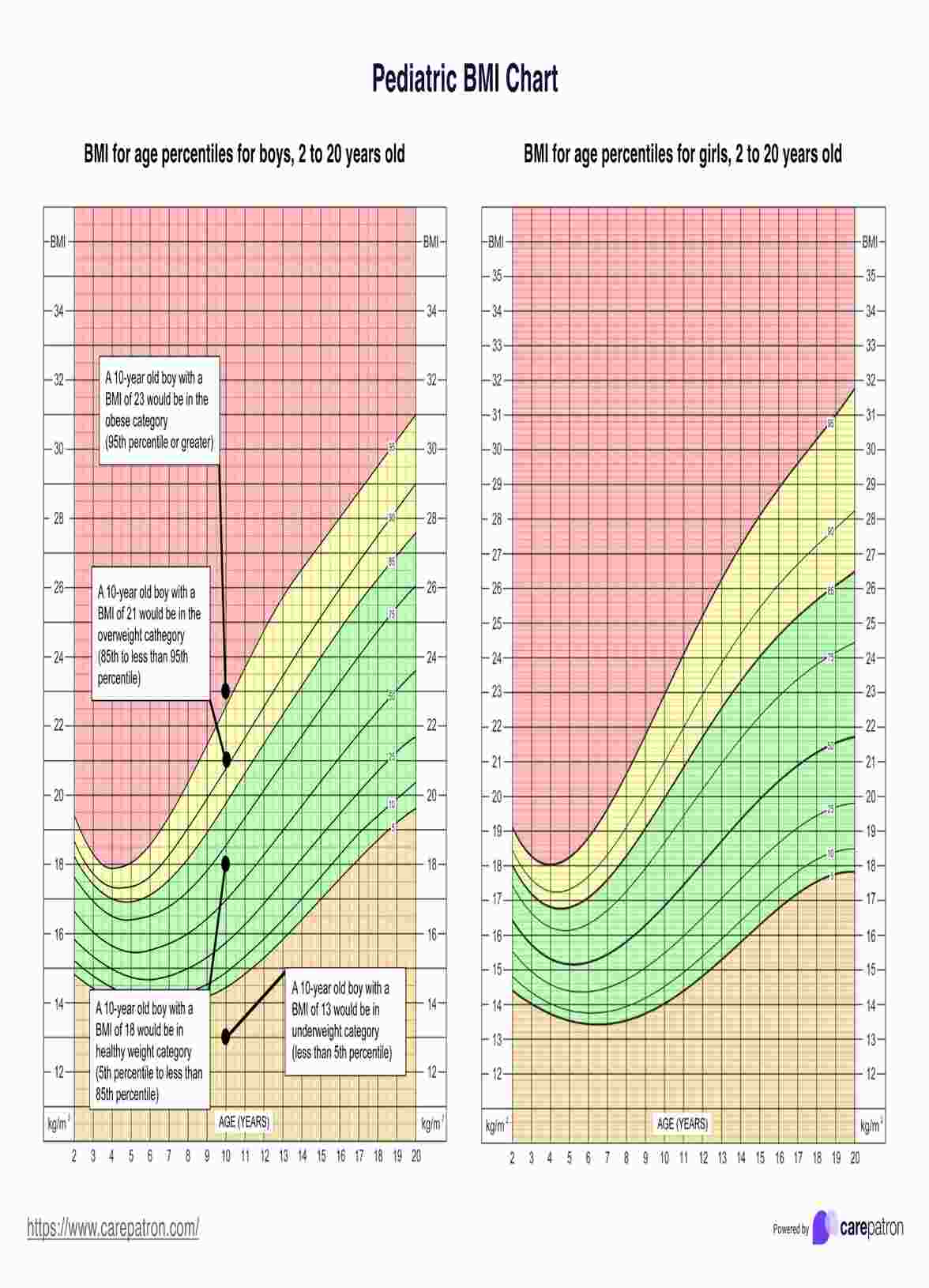
Pediatric BMI Chart Template
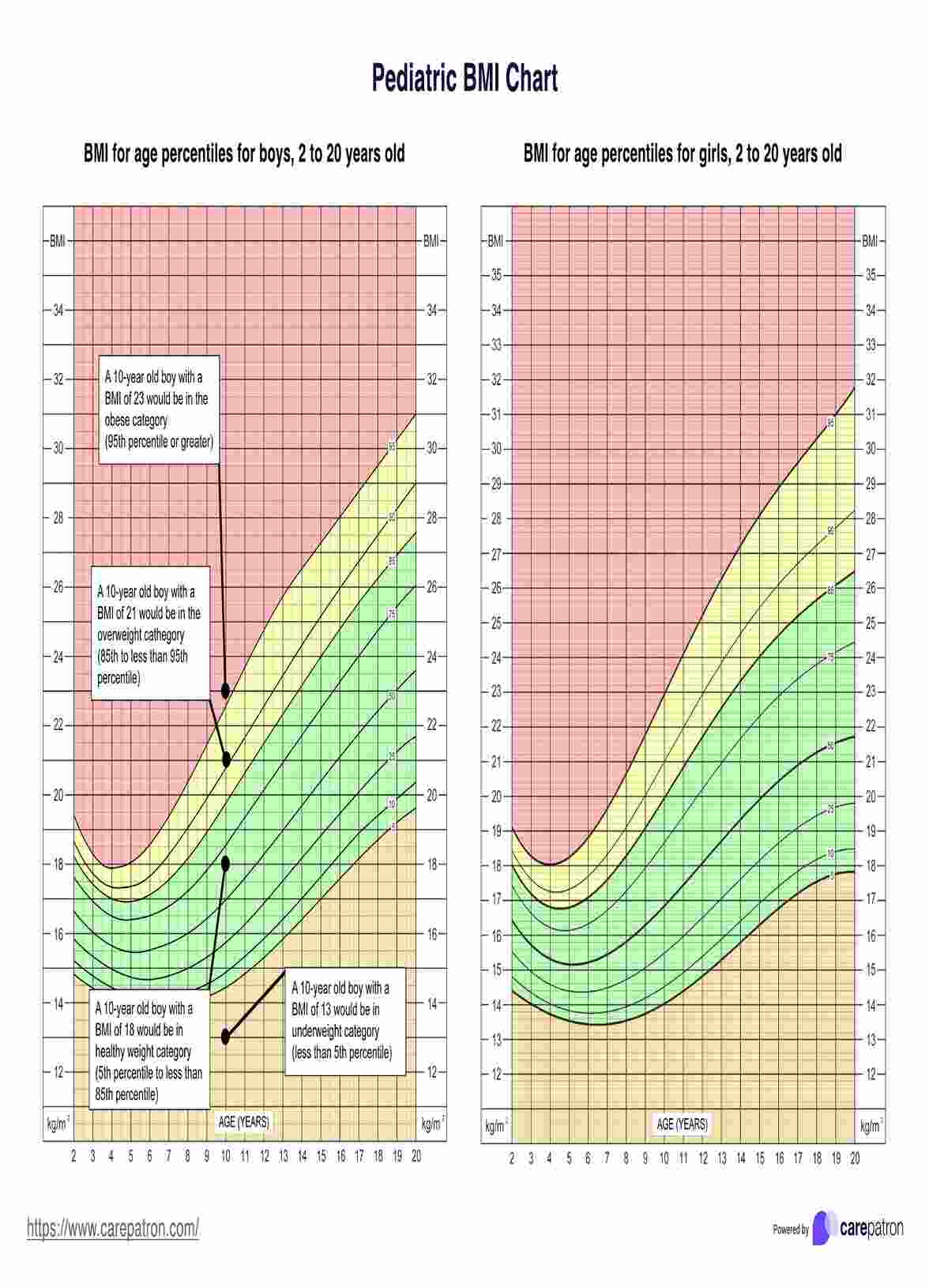
Pediatric BMI Chart Example
How is a pediatric BMI different from adult BMI?
Pediatric BMI differs from adult BMI by accounting for age and gender, expressed as percentiles relative to peers of the same age and sex. Children's bodies change as they grow, affecting body fat levels and development rates. Pediatric BMI is plotted on age- and sex-specific charts, while adults use fixed BMI ranges.
For children, weight status categories are based on percentiles, such as overweight (85th to <95th percentile) and obesity (≥95th percentile), whereas adults use fixed BMI values (e.g., overweight 25.0-29.9 kg/m^2, obesity ≥30 kg/m^2).
The transition from pediatric to adult BMI typically occurs around age 20, shifting from age- and sex-specific percentiles to fixed BMI categories.
What is a healthy BMI for children?
Weight status categories for children and teens include:
- Underweight: Less than the 5th percentile
- Normal weight: 5th percentile to less than the 85th percentile
- Overweight: 85th to less than the 95th percentile
- Obesity: Equal to or greater than the 95th percentile
These vary by age, so it is important to consider that when looking at a child's BMI percentile.
What is a Pediatric BMI Chart?
A pediatric BMI chart is a resource that assists practitioners during physical evaluations in documenting and assessing a child's weight status based on their body mass index (BMI), age, and sex.
BMI for children and teens is calculated using the same formula as for adults (weight in kg divided by height in m squared), but its interpretation differs for younger age groups. Children's and teens' BMI levels are expressed as percentiles relative to others of the same age and sex, using CDC growth charts based on national survey data. A child's BMI percentile indicates how their BMI compares to that of peers; for example, a BMI in the 60th percentile means that 60% of children of the same gender and age have a lower BMI.
Pediatric BMI charts are valuable for monitoring a child's growth pattern over time and should be taken at least once a year, starting at age 2. Although BMI is a helpful screening tool, it is not a definitive measure of body fat, and further assessments may be necessary to evaluate whether a child's weight poses a health risk. These charts help healthcare providers to document and identify children at risk of weight-related health problems, facilitating early intervention and promoting healthy growth and development.
How does our Pediatric BMI Chart template work?
Our chart can help in the documentation and assessment process during physical evaluations. Here is a quick guide on how to use our Pediatric BMI Chart effectively:
Measure the child's height and weight
Begin by measuring the child's height in inches using a stadiometer and weight in pounds using a scale. Record the measurements accurately.
Locate the child's height and weight on the chart
Find the child's height in inches on the left column and their weight in pounds across the top row.
Determine the child's BMI
Trace the child's weight column down and height row across until they intersect. The value at this intersection is the child's BMI.
Interpret the child's BMI
Compare the child's BMI value to the color-coded categories at the bottom of the chart to determine their weight status. This will indicate if the child is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese.
Use the Body Mass Index Template to assess and monitor a patient's weight relative to their height. This template helps in evaluating nutritional status and guiding weight management strategies. By incorporating this tool, you can better understand and address issues related to weight and overall health in your practice.
Ways to maintain a healthy BMI for a child
Maintaining a healthy BMI for a child involves various strategies to help manage the child's weight and promote overall well-being. Here are some ways to support a healthy BMI for a child:
- Balanced diet: Encourage a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Monitor portion sizes and limit high-calorie, high-sugar foods to help manage body fat and maintain a healthy weight.
- Regular physical activity: Encourage children and teens to engage in regular physical exercise, such as playing sports, dancing, or simply being active outdoors. This helps manage their body weight and promotes healthy growth.
- Monitor BMI percentile: Keep track of your child's BMI percentile to ensure they stay within a healthy range. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor changes in the child's BMI for age.
- Family involvement: Set a positive example by adopting healthy eating habits and staying active as a family. This creates a supportive environment for the child to maintain a healthy BMI.
- Limit screen time: Encourage children and teens to reduce screen time, including watching TV, playing video games, or using electronic devices, as excessive screen time is associated with high BMI and excess fat.
Commonly asked questions
Pediatric BMI is calculated using the same formula as adult BMI: weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared (kg/m²). However, its interpretation for children and teens differs due to age and sex.
BMI percentiles rank a child's BMI relative to their peers' BMI (same age and sex). For example, a BMI in the 60th percentile means the child's BMI is higher than 60% of children of the same age and sex.
Pediatric BMI should typically be checked annually during well-child visits, starting at age 2. More frequent assessments may be needed if there are concerns about a child's growth or weight.