PAINAD Scale
Learn about the Pain Assessment in Advanced Dementia Scale (PAINAD) and how to interpret results. Plus, get a free PDF template and example.


What is a Pain Assessment in Advanced Dementia (PAINAD) Scale?
Pain is a common symptom experienced by people with advanced dementia, and it can significantly negatively impact their quality of life. People with advanced dementia experience pain differently than those without it. They may be unable to express their pain verbally and may show signs such as changes in behavior, facial expressions, or body language when they are in distress.
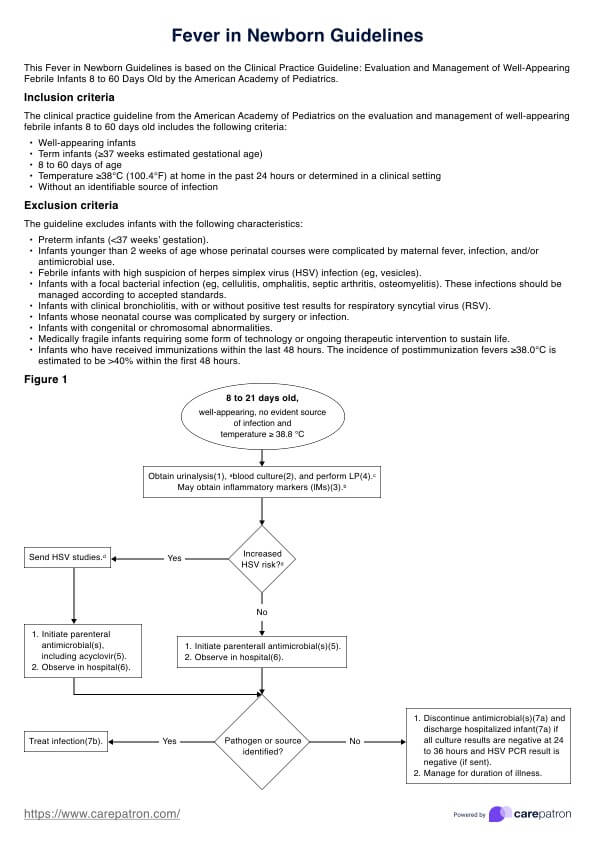
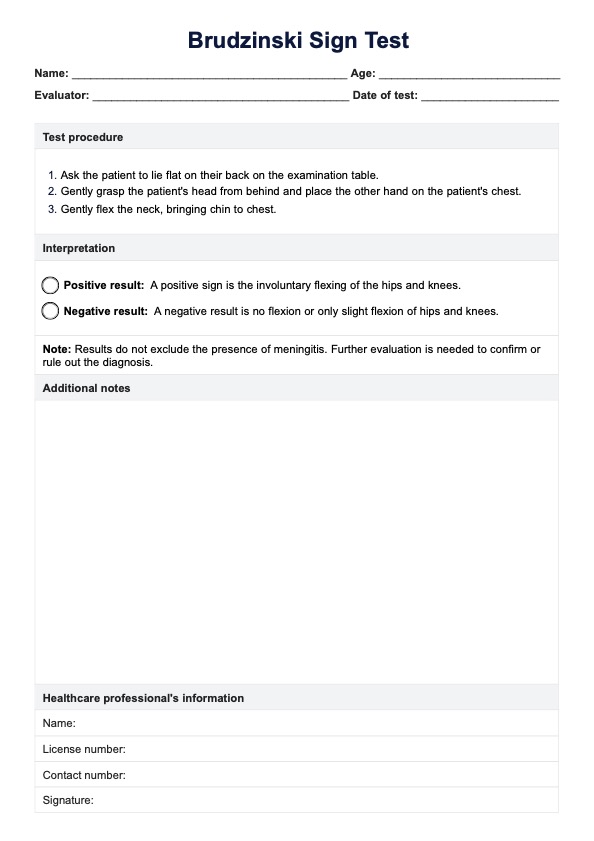
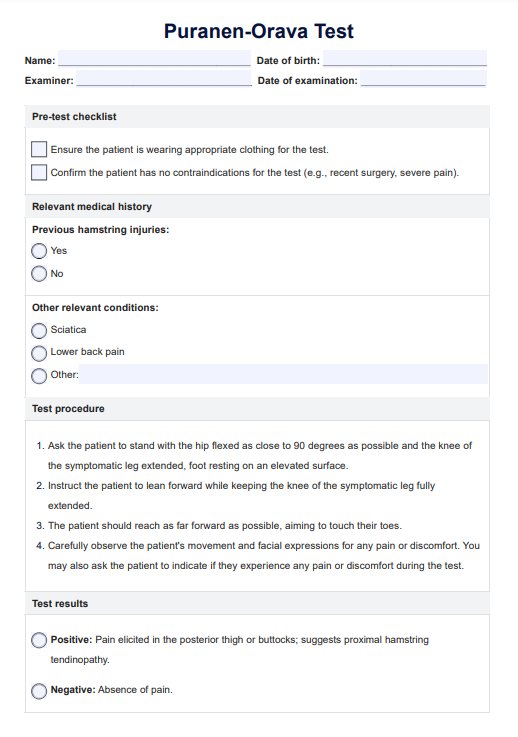
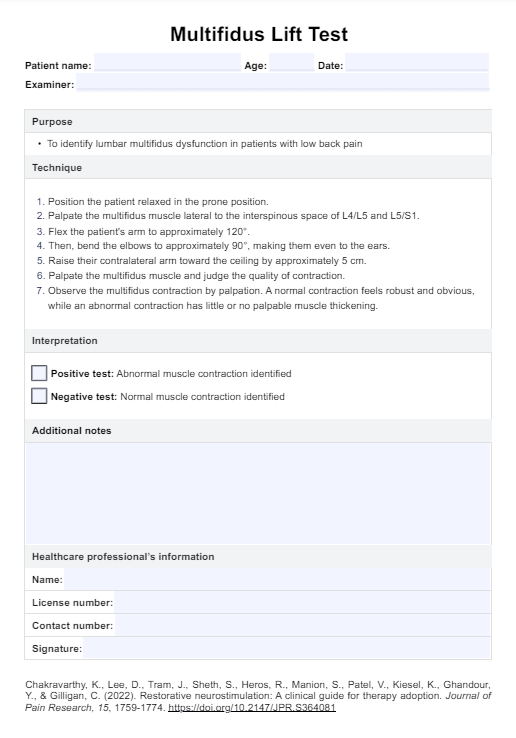
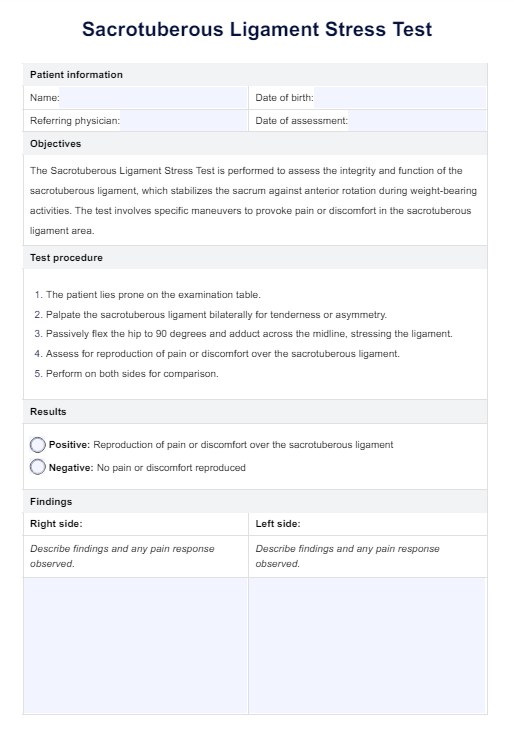
To properly assess and manage pain in people with advanced dementia, healthcare professionals use the PAINAD Scale. It helps healthcare providers to evaluate pain levels and determine the best course of action. The PAINAD Scale is a 2-point scale based on observing and assessing physical signs and non-verbal behavior associated with people with dementia in pain.
When assessing pain in older adults and people with advanced dementia, it is important to remember that there are no standard “cut-offs” for each symptom and that the scale should be used as a guide for observation and evaluation.
The PAINAD Scale is designed for a wide range of healthcare professionals, including physicians, nurses, caregivers, and specialists across various fields, to assess pain in individuals who may struggle to communicate. It can be applied in hospitals, nursing homes, and care facilities, but should not be used as a diagnostic pain assessment tool alone.
PAINAD Scale Template
PAINAD Scale Example
How does this PAINAD Scale work?
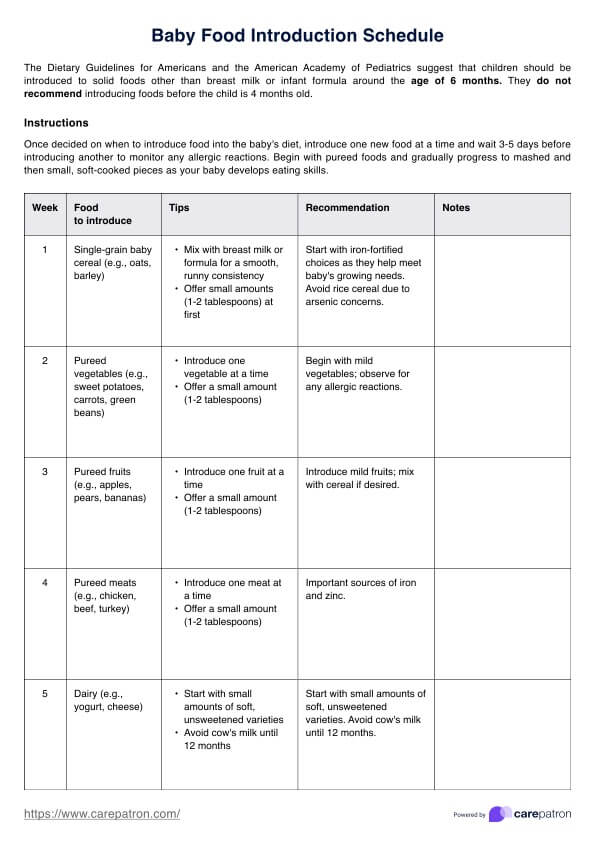
The PAINAD Scale is designed to assess pain levels in people with advanced dementia by observing and evaluating five key physical signs and non-verbal behaviors. Here's how to use this free template:
Step 1: Download the scale
In this guide, you have the option to select "Use template" to access it on the Carepatron platform, allowing you to customize it to suit your client's needs. Alternatively, you can choose "Download" to obtain a fillable PDF version of the template.
Step 2: Observe the patient
For each of the five categories, observe and rate the patient's physical signs and non-verbal behavior on a scale from 0 to 2.
Step 3: Calculate the score
Add up the ratings for each category and calculate the total score, ranging from 0 to 10. A higher score indicates increased levels of pain.
Step 4: Interpret results
Based on the total score, administer the appropriate comfort measures, pain relief medications, or additional medical care as needed. An "Additional Notes" section is also provided for you to record any further information or details about the patient.
PAINAD Scale scoring and interpretation
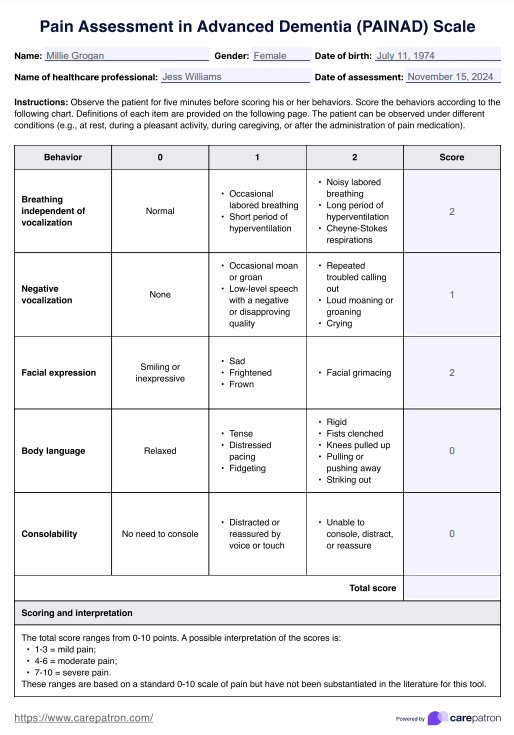
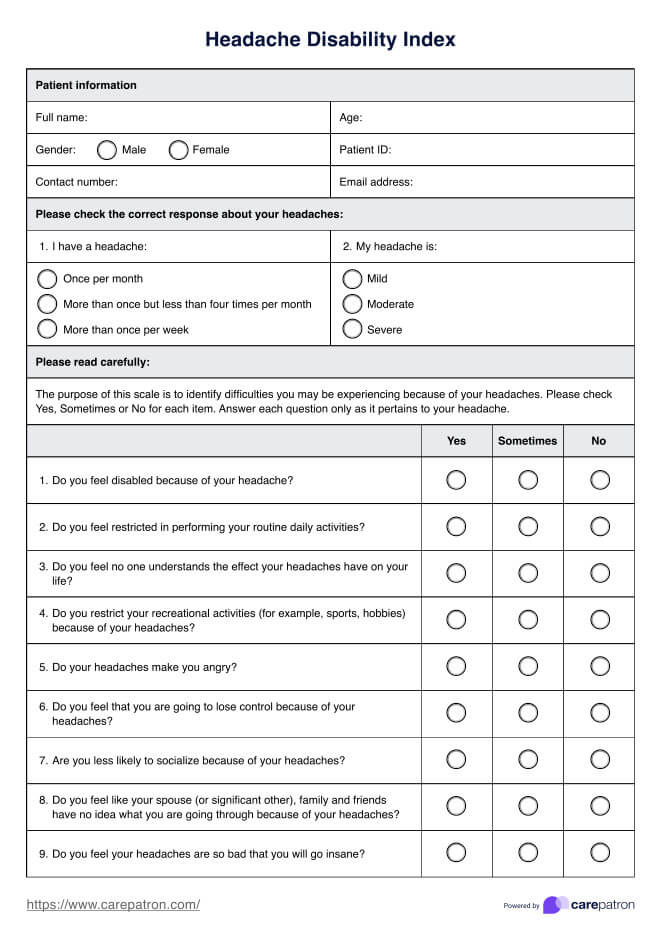
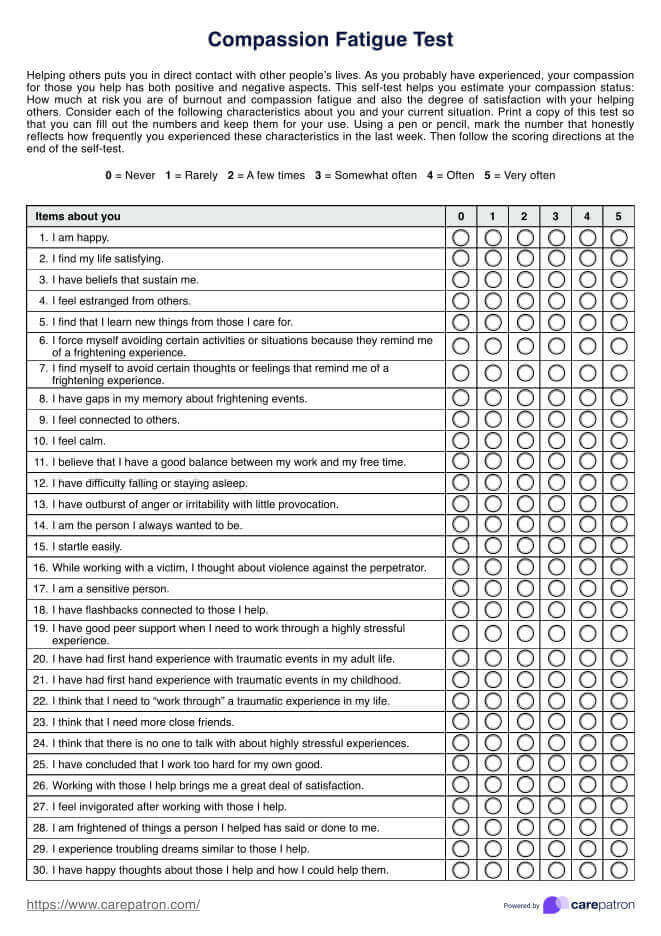
The PAINAD Scale measures five categories: breathing independent of vocalization, negative vocalization, facial expression, body language, and consolability. Each category is scored on a scale of 0-2 for a total score of 0-10.
Scores of 1-3 suggest mild pain, 4-6 indicate moderate pain, and 7-10 reflect severe pain. Although these ranges follow a standard 0-10 pain scale, they are not specifically substantiated in the literature for this tool.
When to use this PAINAD test?
The PAINAD Scale assesses pain levels in people with advanced or severe dementia only. You should use it when you suspect your patient is experiencing either acute pain or ongoing pain, and you need to determine the severity of their discomfort. You can also administer this test if or when:
You want to monitor the patient's pain over time.
The PAINAD Scale is excellent for monitoring and managing chronic pain in people with advanced dementia. Regular pain assessment can help you detect changes in the patient's overall health and respond appropriately to avoid leaving them with untreated pain.
You need to adjust the patient's pain relief medication.
Regular pain and symptom management and assessments can help you determine if the patient is responding well to their current pain relief regimen or if you need to make adjustments.
Your patient is unable to verbalize their pain accurately.
For those patients with dementia who cannot verbalize their pain, the PAINAD Scale can provide valuable insight into their discomfort. You can better understand their pain levels by observing and rating the patient's physical signs and non-verbal behavior.
Your patient is exhibiting signs of distress, physical discomfort, or agitation.
The PAINAD Scale can help you detect pain in patients who cannot express it verbally. If the patient exhibits signs of distress, physical discomfort, or agitation, this tool can be used as a guide for observation and evaluation.
Benefits of a free PAINAD assessment
The PAINAD Scale is an effective tool for assessing pain levels in people with advanced dementia. Here are some of its benefits:
It's easy to use and interpret.
The PAINAD Scale is simple to administer. Its scoring system is also clear and intuitive, making it easy to interpret.
It's accurate and reliable.
The PAINAD Scale is a valuable and accurate tool for assessing pain in people with advanced dementia. You can be confident that the results are reliable.
It's fully digital.
The PAINAD Scale is available in PDF format and can be used with any digital device. You can access it wherever you are and use it at any time.
It helps you provide better care.
Using this tool, you can provide better, more tailored patient care by accurately assessing pain levels and prescribing the correct pain medication. Regular assessments also help detect changes in the patient's overall health.
It helps improve patient outcomes.
Using the PAINAD Scale, you can make informed decisions about managing your patients' pain and improving their overall health outcomes.
Commonly asked questions
Victoria Warden, Ann C. Hurley, and Ladislav Volicer developed the PAINAD Scale to provide healthcare professionals with a tool to assess and monitor pain intensity levels in people with advanced dementia.
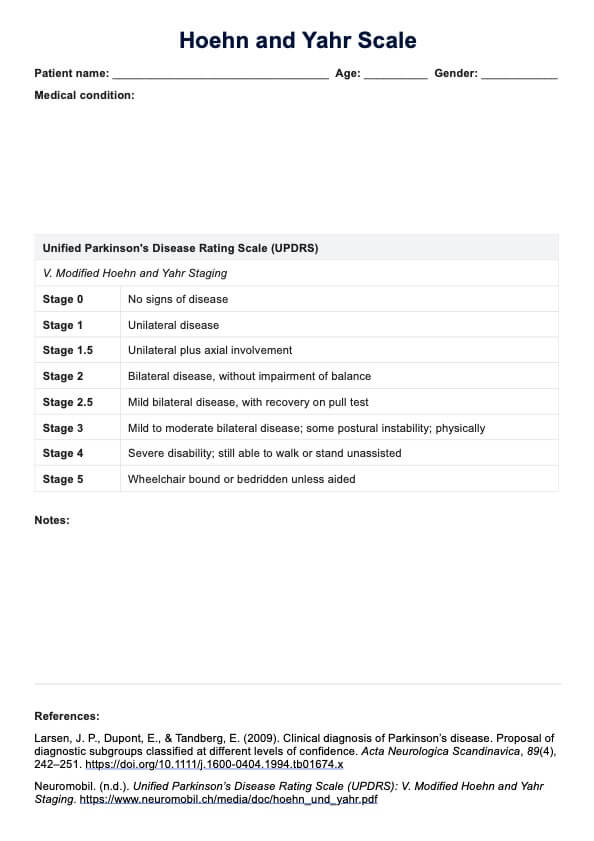
The PAINAD Scale is scored on a 2-point scale, ranging from 0 to 2. A score of 0 is assigned for behaviors or physical signs that are considered non-painful. Meanwhile, a score of 2 is given for those that indicate severe pain.
The PAINAD Scale is interpreted by assessing the patient's behavior and physical signs. It is important to remember that this is an objective pain assessment. A score of 0 indicates no pain, while a score of 1 or 2 suggests that the patient is experiencing some degree of pain. Depending on the severity of the pain, healthcare providers can adjust their treatment plans accordingly.