Urinary Retention Nursing Care Plan
Effectively manage urinary retention with our Urinary Retention Nursing Care Plan template. Assess, plan, and implement personalized care to improve patient outcomes today.


What is urinary retention?
Urinary retention is a condition in which the bladder is unable to fully empty its contents. It can occur due to various underlying causes, such as nerve damage, prostate enlargement, or medication side effects.
There are two main types of urinary retention: acute and chronic.
- Acute urinary retention: Acute urinary retention occurs suddenly and requires immediate medical attention. It can be caused by physical obstructions in the urinary tract, such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate pressing on the urethra. Bladder muscle weakness or nerve damage can also contribute to acute urinary retention.
- Chronic urinary retention: Chronic urinary retention is a long-term condition in which the bladder does not fully empty with each urination. This can be caused by underlying conditions such as diabetes, multiple sclerosis, or spinal cord injuries. In some cases, there may be no identifiable cause for chronic urinary retention.
The treatment for urinary retention depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In acute cases, a catheter may need to be inserted to drain urine from the bladder until the obstruction is resolved. For chronic cases, treatment may involve medication to relax the bladder muscles or surgery to alleviate any physical obstructions.
Urinary retention vs. Urinary tract infection (UTI)
Urinary retention and urinary tract infections (UTIs) are two common urological conditions that can occur in both men and women. While they may share certain symptoms, these two conditions are different and require different treatment approaches.
As mentioned, urinary retention occurs when a person has difficulty emptying their bladder completely or at all. This condition can arise from a wide range of issues, such as an obstruction in the urinary tract or nerve damage that affects bladder function.
On the other hand, a UTI is caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract and multiplying, resulting in an infection. The most common cause of UTIs is bacteria from the digestive tract entering through the urethra and reaching the bladder or kidneys.
In cases of urinary retention, individuals may experience incomplete bladder emptying, leading to a sensation of an overfull bladder. Symptoms can also include lower abdominal discomfort and urinary urgency, as the bladder struggles to function correctly. A bladder scan can be a useful diagnostic tool in identifying the volume of urine retained after attempts to void, helping healthcare providers ascertain the extent of the retention.
Conversely, those suffering from a UTI often endure symptoms such as burning during urination and increased urgency to urinate, alongside frequent urination in small amounts. Effective management of both conditions can involve lifestyle adjustments. Adequate fluid intake is crucial, as it can help flush out the urinary tract in the case of a UTI, while pelvic floor exercises may alleviate symptoms from stress urinary incontinence or urge urinary incontinence.
Urinary Retention Nursing Care Plan Template
Urinary Retention Nursing Care Plan Example
What is a Urinary Retention Nursing Care Plan?
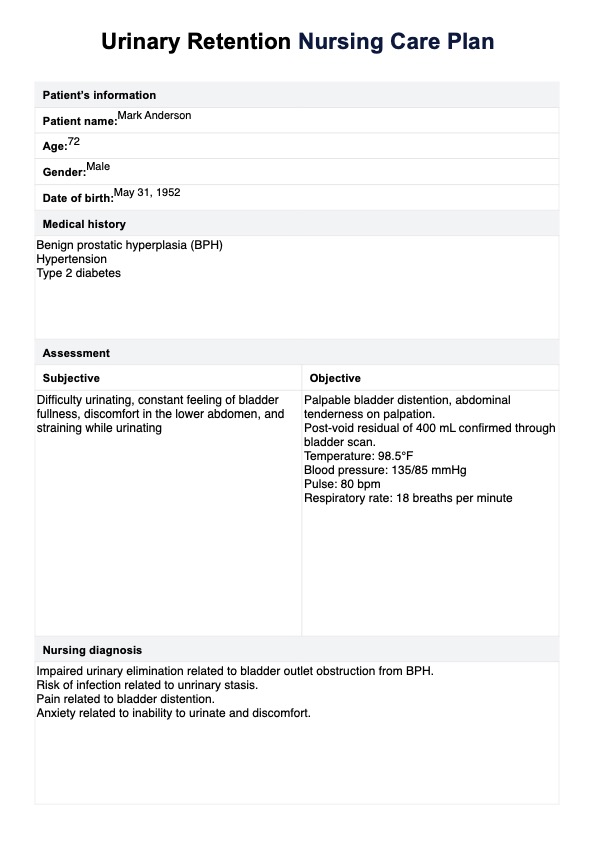
A Urinary Retention Nursing Care Plan is essential for nurses and healthcare professionals to manage and treat urinary retention effectively. It begins with an assessment and nursing diagnoses that identify the patient's specific needs and issues related to urinary retention, setting clear goals such as reducing retention, enhancing bladder function, and preventing complications.
The plan also outlines goals and targeted nursing interventions tailored to the patient's needs, including catheterization for immediate relief, bladder training to improve function, and fluid management to optimize urine output. Finally, it documents the rationale for each intervention and evaluates the patient's response to treatment, ensuring a cohesive and comprehensive approach to managing urinary retention.
How does it work?
Our free Urinary Retention Nursing Care Plan is easy to use. Here's how:
Step 1: Download the template
Get a copy of the Urinary Retention Nursing Care Plan template by clicking on the download button. The template is in a printable PDF format, making it easy to use and share with your healthcare team.
Step 2: Assess the patient
The first step involves comprehensively evaluating the patient’s urinary retention symptoms. Begin by taking a detailed health history, including any previous urinary tract infections or surgeries. It is also important to assess the patient’s current medications and any factors that may contribute to urinary retention, such as prostate enlargement or spinal cord injury.
Step 3: Conduct a nursing diagnosis
Based on the assessment data, nurses can identify a relevant urinary retention nursing diagnosis. Common diagnoses include impaired urinary elimination, risk of urinary tract infection, or risk of skin breakdown.
Step 4: Set goals and outcomes
Goals and outcomes are also established to meet the specific needs highlighted in the nursing diagnosis. Nurses should make sure they are personalized for each patient, emphasizing the improvement of bladder emptying, the prevention of complications, and the enhancement of comfort.
Step 5: Plan for intervention
Interventions are designed with specific goals in mind. Bladder retraining exercises typically aim to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, enhancing urinary control and preventing incontinence. These interventions may encompass catheterization for immediate relief, medication management to improve bladder tone, bladder retraining exercises, and lifestyle modifications.
Step 6: Document rationale
Use the template to document your rationale for the chosen interventions. This helps evaluate the care plan's effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
Step 7: Evaluate outcomes
Regular assessment and documentation of progress toward goals and outcomes are essential to evaluate the effectiveness of the care plan. Any deviations or setbacks should be addressed promptly, and modifications should be made if needed.
Nursing interventions for urinary retention
Nursing interventions for urinary retention focus on relieving the patient's discomfort and assisting in eliminating urine from the body. Some common nursing interventions for urinary retention include:
- Management of underlying issues: Attention must be paid to factors that may contribute to urinary retention, such as an enlarged prostate, which can obstruct urine flow. In cases of recurrent urinary tract infections or kidney infections, appropriate medical intervention is necessary to address the underlying causes. Some underlying issues may also require ongoing management, such as neurological conditions that affect bladder control.
- Assessment of urinary stasis: Regular assessment for urinary stasis is vital in patients at risk for urinary retention. Nurses should observe for signs of bladder distention, which may be indicated by symptoms such as abdominal pain or discomfort, a visible or palpable bladder, and changes in bladder pattern. Prompt identification of urinary stasis can prevent further complications.
- Management of residual urine: Nurses should also evaluate the volume of residual urine post-voiding, as significant amounts can exacerbate urinary retention issues. Bladder scanning can be an effective non-invasive method to measure post-void residual volume. Following this assessment, appropriate interventions may include catheterization or further medical evaluation to effectively manage the underlying cause of the urinary stasis.
- Support for urination: For patients experiencing difficulty initiating urination or those with neurogenic bladder dysfunction, strategies may include timed voiding, manual stimulation of the bladder, or the use of a urinary catheter to facilitate urine drainage.
- Monitoring and education: Nurses should educate patients about signs and symptoms of potential complications, such as filling of the urinary bladder, that could lead to further issues. It's also essential to monitor urine flow rates and renal function to prevent transient or acute incontinence related to underlying bladder dysfunction.
When would you use this template?
The Urinary Retention Nursing Care Plan can be used in various settings and scenarios, such as the following:
During hospitalization
Nurses can use this template to develop a personalized care plan for patients with urinary retention admitted to the hospital. The template serves as a guide in formulating interventions and documenting progress toward goals.
In community settings
This template is also useful for nurses working in community settings, such as home health or long-term care facilities. It provides a structured approach to managing urinary retention and monitoring patient outcomes.
In specialized units
Nurses working in specialized units, such as urology or geriatric wards, can benefit from using this template to create individualized care plans for patients with urinary retention. It helps ensure that all pertinent interventions are considered and implemented.
In educational settings
This template can also be used in educational settings by nursing students to understand the principles and steps involved in developing a comprehensive nursing care plan for urinary retention. It provides a practical and standardized approach to planning patient care.
Commonly asked questions
Develop a Urinary Retention Nursing Care Plan Template by including sections for assessment, nursing diagnosis, goal setting, interventions, and evaluation specific to urinary retention management.
Urinary Retention Nursing Care Plan Templates are used to manage patients with acute or chronic urinary retention, particularly in postoperative care and long-term care settings, and individuals with underlying medical conditions.
Healthcare professionals use these Urinary Retention Nursing Care Plan Templates to assess, plan, implement, and evaluate care for patients with urinary retention, focusing on individualized patient needs.
A nursing care plan for urinary retention entails a structured approach to address bladder emptying challenges through comprehensive assessments and targeted interventions. It emphasizes the importance of patient education, evidence-based practices like bladder training, and a multidisciplinary team to optimize outcomes and enhance the quality of life for individuals experiencing urinary retention.

.jpg)