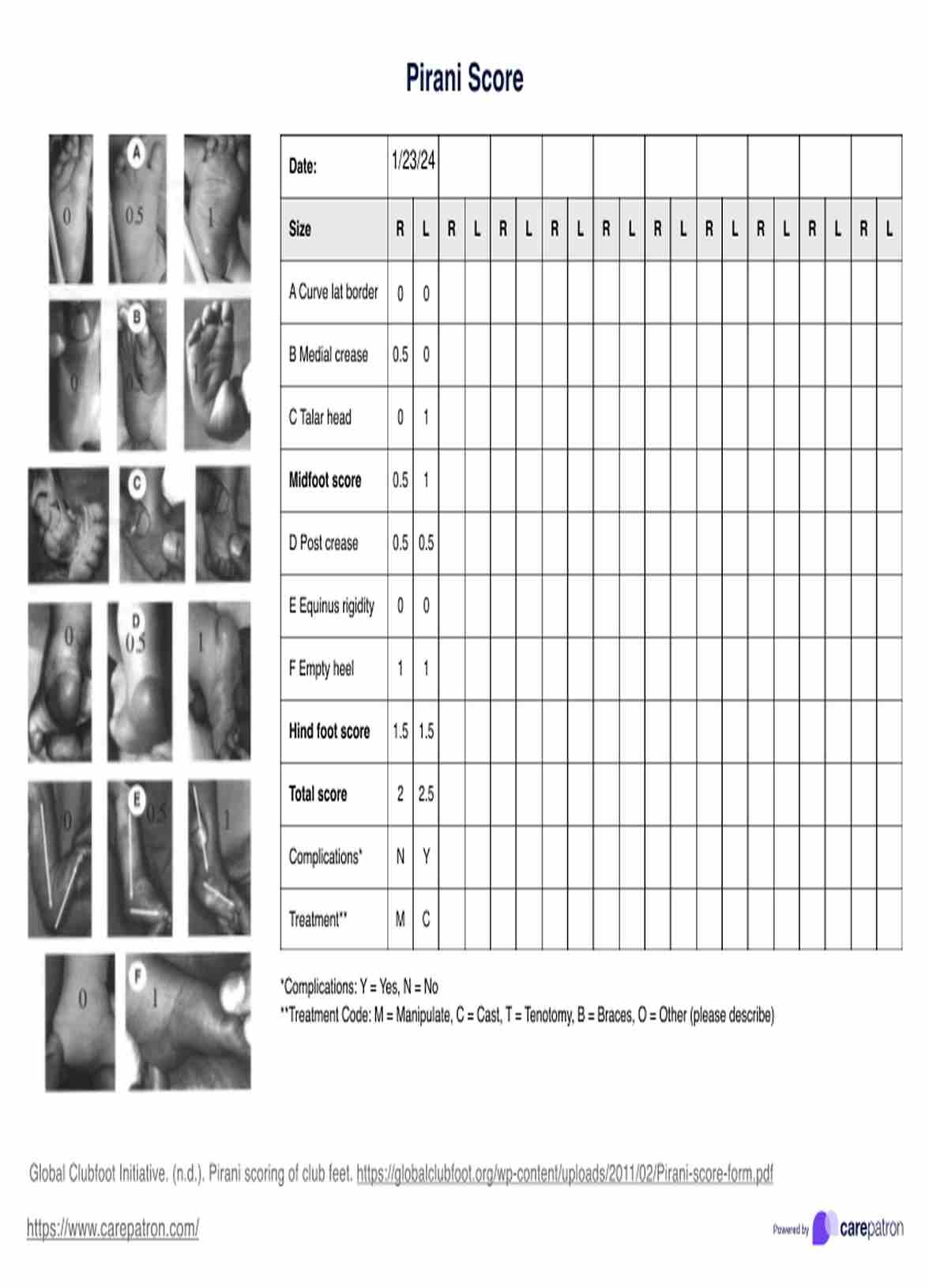
Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan
Confidently manage and monitor pneumonia and its risks through this comprehensive nursing care plan and guide for the delivery of effective and preventive care!



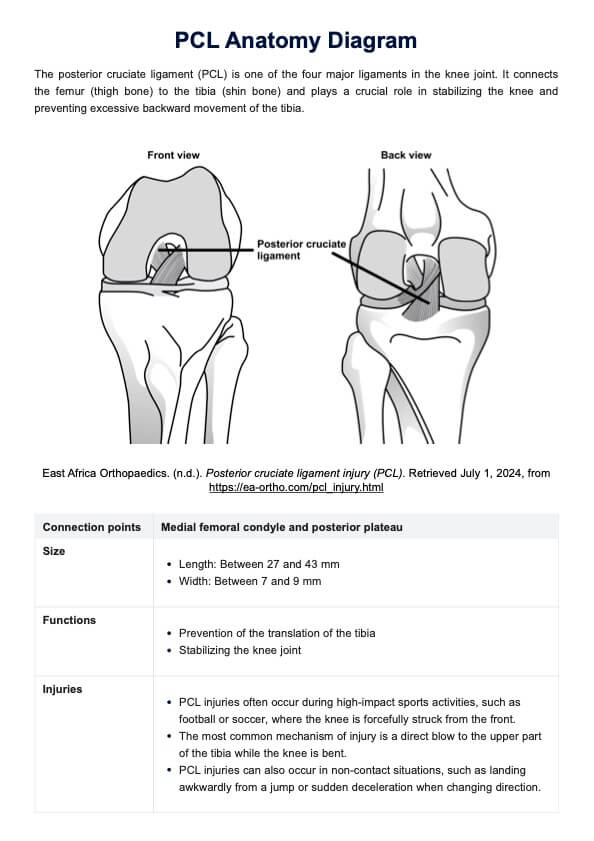
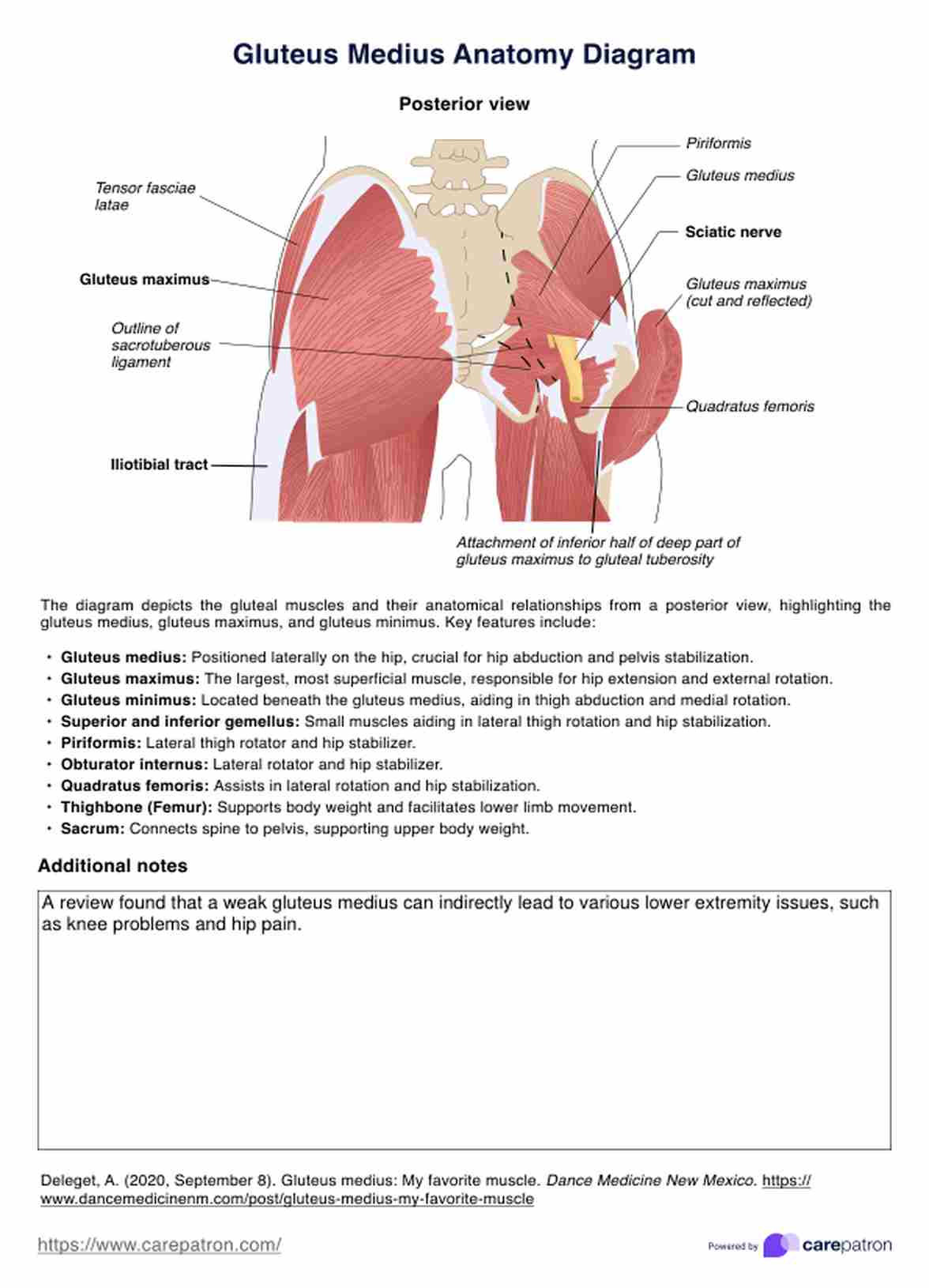
What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is a respiratory infection that affects the lungs, causing inflammation and fluid accumulation in the air sacs (alveoli). This condition can be caused by various microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. When the alveoli become filled with fluid or pus, or when pleural effusion occurs, it can lead to difficulty breathing, coughing, and decreased oxygen exchange in the lungs.
Pneumonia can range from mild to severe and can be particularly dangerous for certain high-risk groups, such as infants, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic health conditions (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, 2022). The severity of the infection depends on factors such as the type of pathogen causing the infection, the patient's age, and overall health status.
Common signs and symptoms of pneumonia include (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, 2022):
- Cough (may produce mucus)
- Fever and chills
- Shortness of breath or rapid breathing
- Chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing
- Fatigue
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea (more common in children)
- Confusion (more common in older adults)
Prompt recognition and appropriate treatment of pneumonia are crucial to prevent complications and promote recovery. When left unchecked, pneumonia can lead to complications such as secondary infection or even respiratory failure. Healthcare practitioners play an important role in assessing patients, initiating appropriate interventions, and educating patients and their families about the condition and its management.
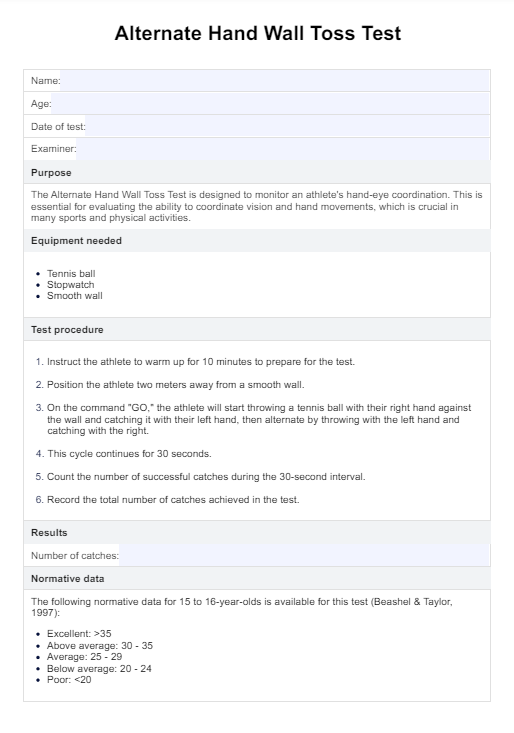
Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan Template
Download PDF TemplatePneumonia Nursing Care Plan Example
Download Example PDFTypes of pneumonia
Pneumonia can be classified into different types based on the infection's setting, the microorganism causing the infection, and the patient's underlying health status. The main types of pneumonia include the following:
The main types of pneumonia include:
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP)
This is the most common type of pneumonia in individuals who have not been hospitalized or residing in long-term care facilities (Mandell & Niederman, 2019). CAP can be caused by various pathogens, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and respiratory viruses, such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP)
Also known as nosocomial pneumonia, HAP develops 48 hours or more after hospital admission and is not present at the time of admission (Kalil et al., 2016). HAP is often caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP)
This type of pneumonia occurs in patients who are on mechanical ventilation and develops 48-72 hours after endotracheal intubation (Klompas et al., 2014). VAP is a serious complication that can lead to longer hospital stays, increased healthcare costs, and higher mortality rates.
Aspiration pneumonia
This type of pneumonia occurs when food, liquid, or other substances are inhaled into the lungs, causing infection (Mandell & Niederman, 2019). Aspiration pneumonia is more common in individuals with swallowing difficulties, impaired consciousness, or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
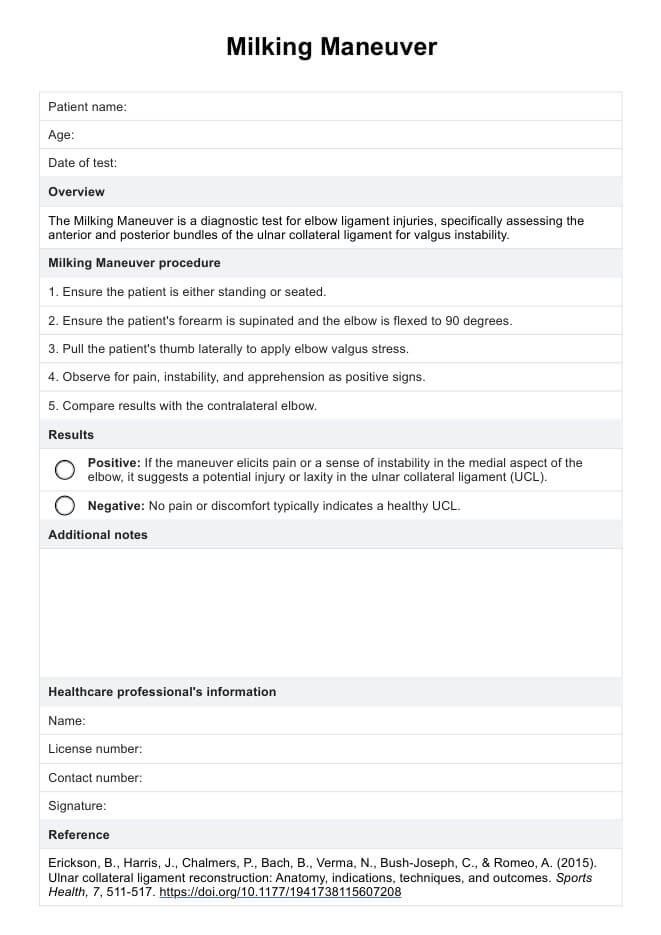
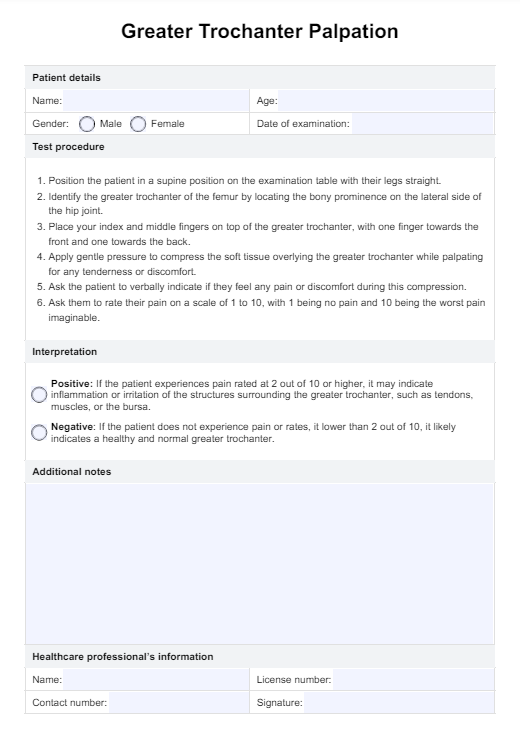
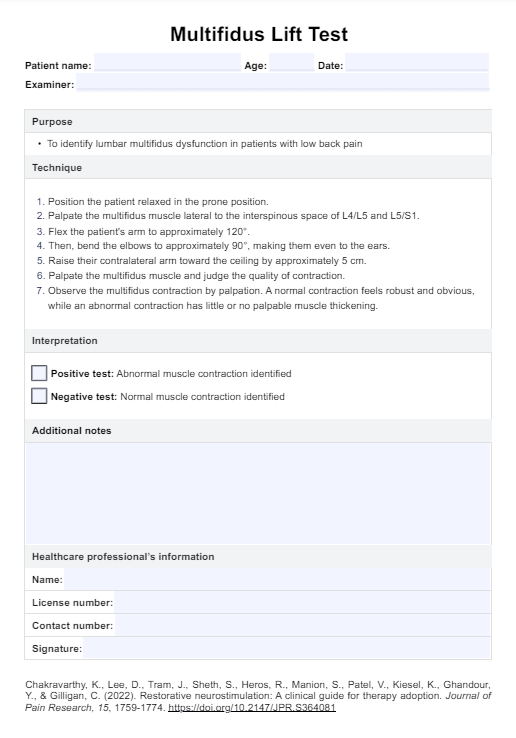
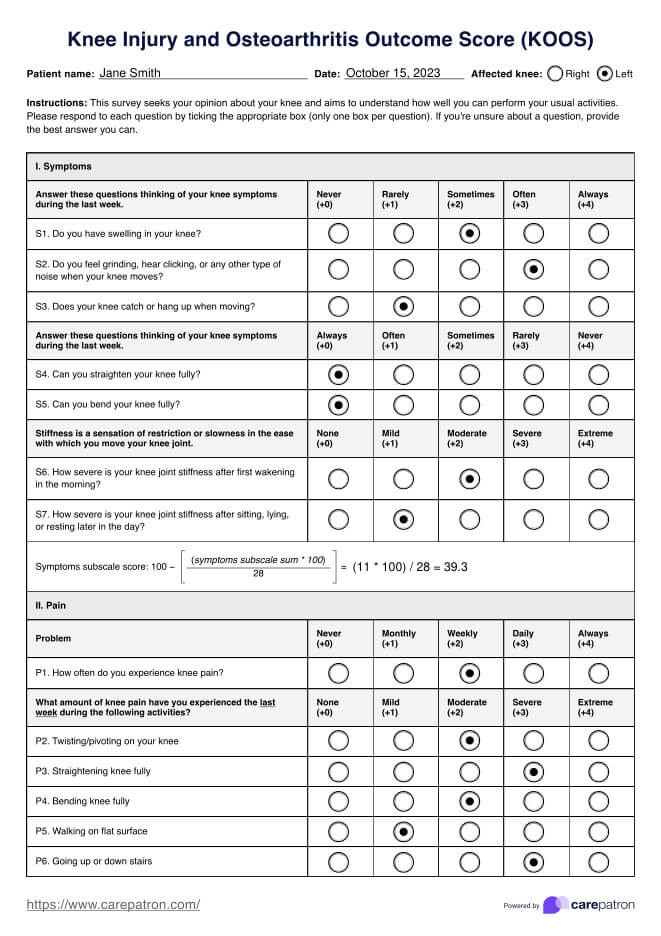
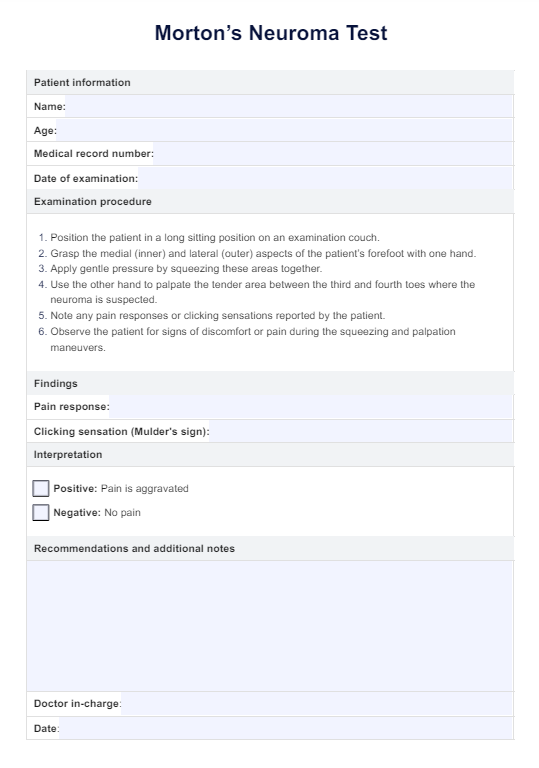
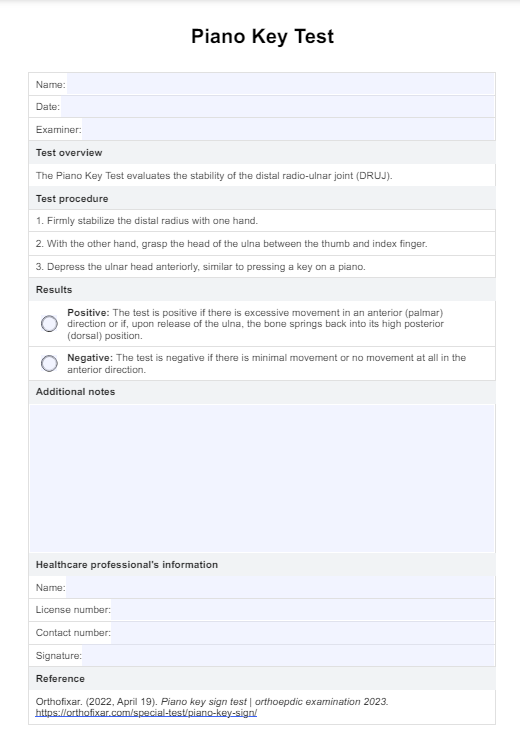
Pneumonia nursing diagnosis
When caring for patients with pneumonia, it is essential to develop a comprehensive nursing care plan that addresses the patient's specific needs and promotes optimal outcomes. This process is crucial to identifying appropriate nursing diagnoses that guide selecting interventions and desired outcomes.
Some common nursing diagnoses for patients with pneumonia include (Herdman & Kamitsuru, 2017):
- Ineffective airway clearance: This diagnosis is related to the patient's inability to clear secretions from the respiratory tract effectively, often due to respiratory distress, increased mucus production, inflammation, and weakened cough reflex. Patients with pneumonia may experience difficulty breathing, coughing, and increased sputum production, which can further compromise airway clearance.
- Impaired gas exchange: Pneumonia can lead to impaired gas exchange due to fluid accumulation and lung inflammation, resulting in decreased oxygen diffusion and carbon dioxide removal. Patients may exhibit signs of hypoxemia, such as shortness of breath, tachypnea, and decreased oxygen saturation levels.
- Acute pain: Patients with pneumonia may experience acute pain related to inflammation, coughing, and pleuritic chest pain. The pain can be described as sharp, stabbing, or aching and may worsen with deep breathing or coughing. Adequate pain management is essential to promote comfort and facilitate effective breathing and coughing.
- Fatigue: The increased work of breathing, systemic inflammation, and overall burden of the infection can lead to fatigue in patients with pneumonia. Patients may report feeling tired, weak, or lacking energy, impacting their ability to participate in self-care activities and engage in therapeutic interventions.
- Deficient knowledge: Some patients may have limited knowledge about pneumonia, its management, and prevention strategies. Patient education is crucial to promoting adherence to treatment plans, encouraging lifestyle modifications, and reducing the risk of future pneumonia episodes.
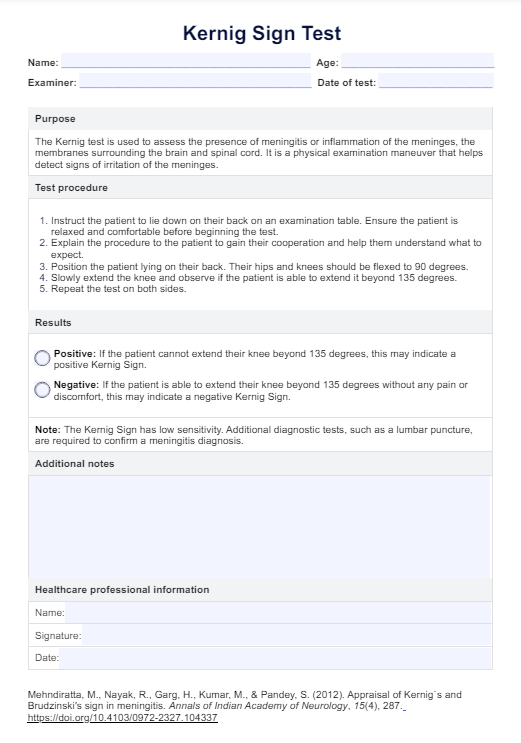
How does it work?
Here is a step-by-step guide for healthcare practitioners on how to use the Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan Template in their practice:
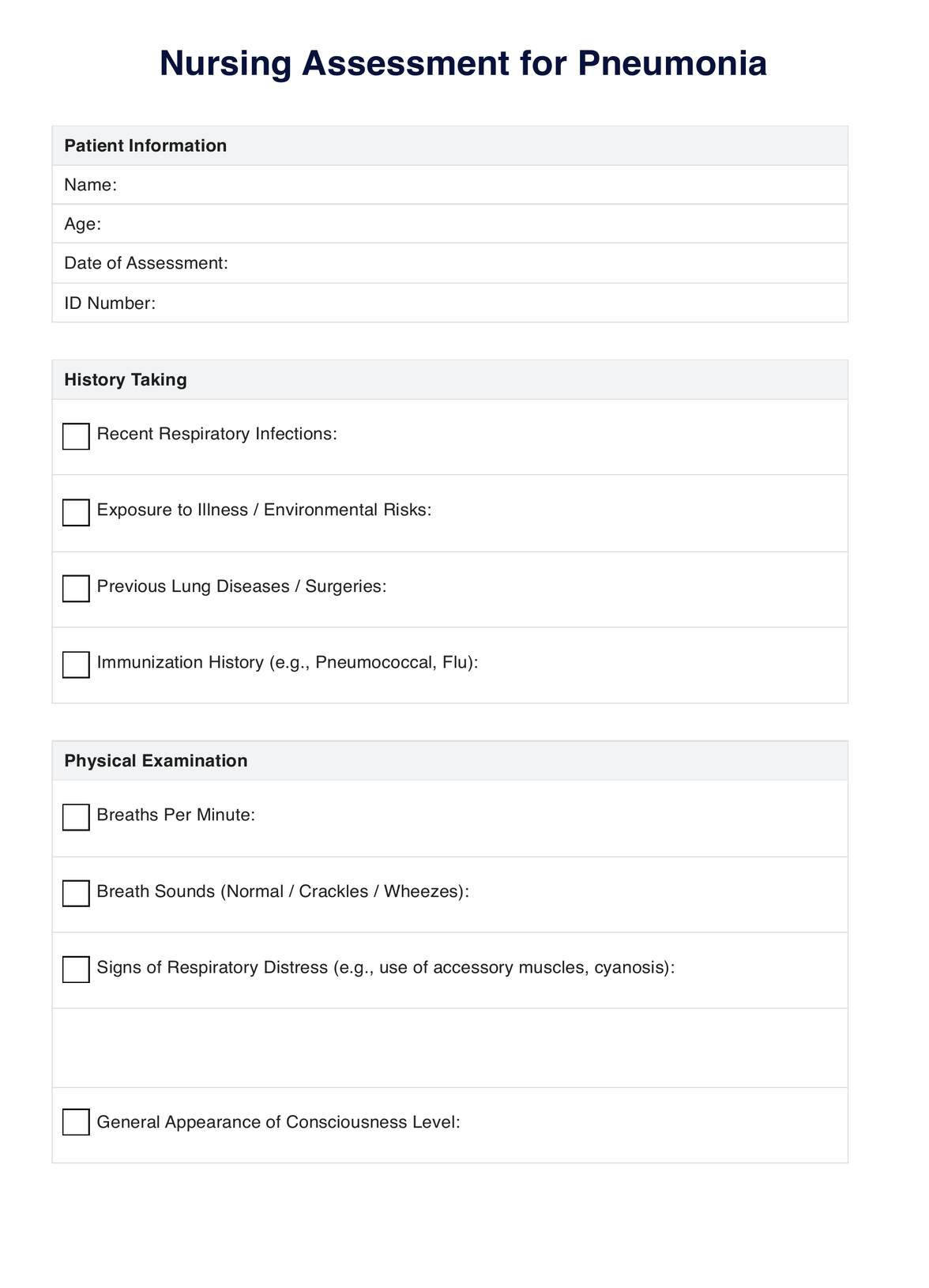
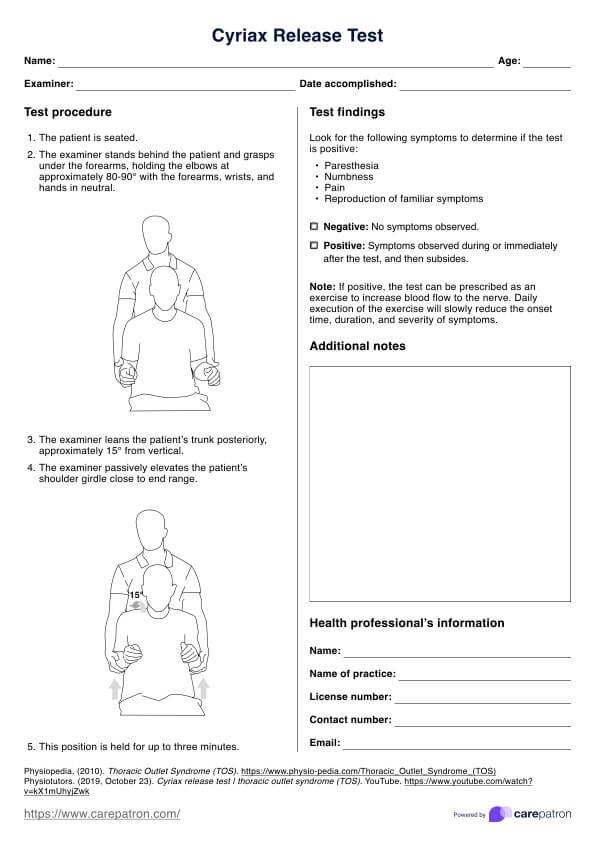
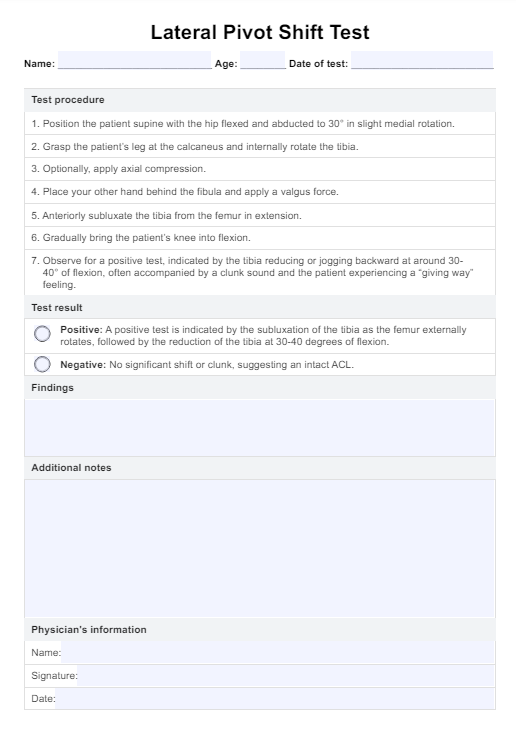
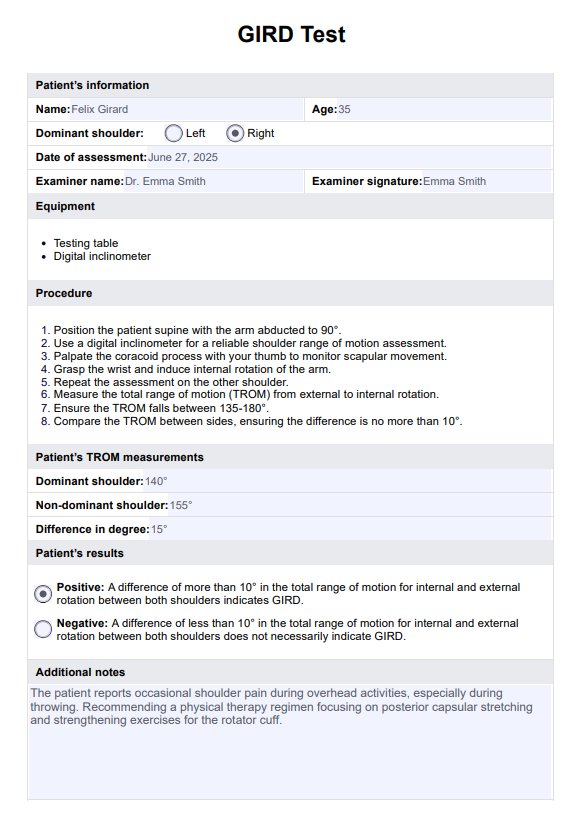
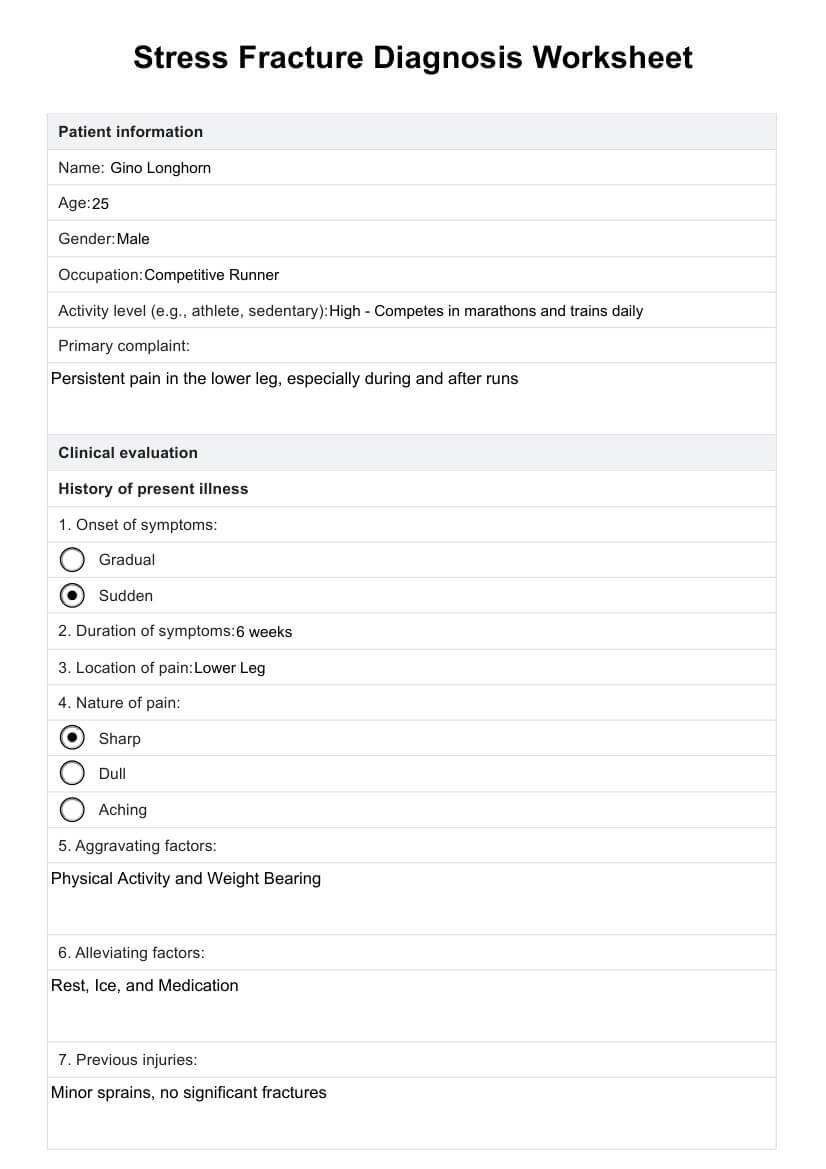
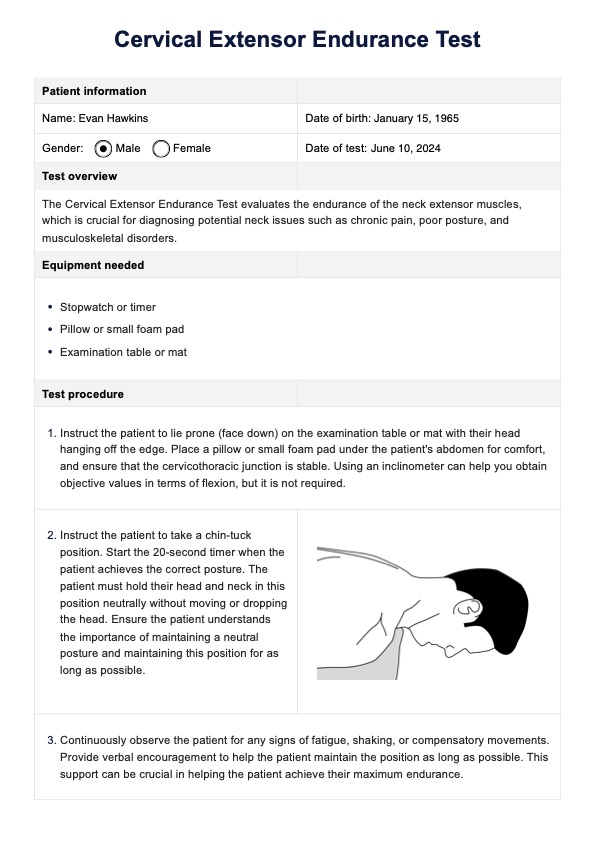
Step 1: Assess the patient's airway clearance and gas exchange
Begin with a physical examination and also explore the patient's medical history. Follow this by thoroughly assessing the patient's respiratory status. Evaluate possible pneumonia symptoms, changes in respiratory rate, rhythm, depth, and the patient's ability to cough effectively. Assess lung sounds, vital signs, mental status, and oxygenation status using pulse oximetry and arterial blood gases (ABGs) to determine the severity of the patient's condition. You can use our Nursing Assessment for Pneumonia template to make this easier.
Step 2: Select interventions
Based on the nursing assessment findings, appropriate interventions to promote airway clearance should be selected. Assist with movement and positioning changes to promote lung expansion for immobile patients. Provide supplemental oxygen as needed to maintain adequate oxygen saturation levels and manage impaired gas exchange.
Step 3: Collaborate and document
Work closely with the physician to ensure a comprehensive patient care approach and treatment regimen. Document the nursing care plan, including the assessment findings, interventions, and the physician's input, to ensure continuity of care and effective communication among the healthcare team.
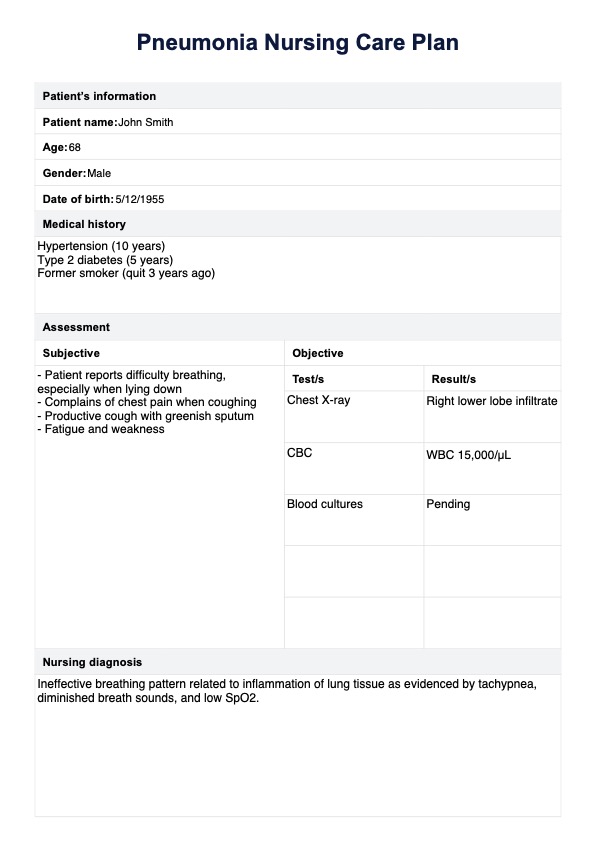
Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan Template example (sample)
Access a free, downloadable, and printable Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan Template PDF filled out with fictional data to guide you in using this tool to track your patient's needs.
This sample template is designed to assist you in efficiently utilizing the chart and evaluating the goals of care for patients diagnosed with pneumonia. It includes dedicated sections for evaluation, interventions, and symptom tracking. Secure your copy by either previewing the sample below or clicking the "Download Example PDF" button.
Download this Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan Template example (sample):
.png)
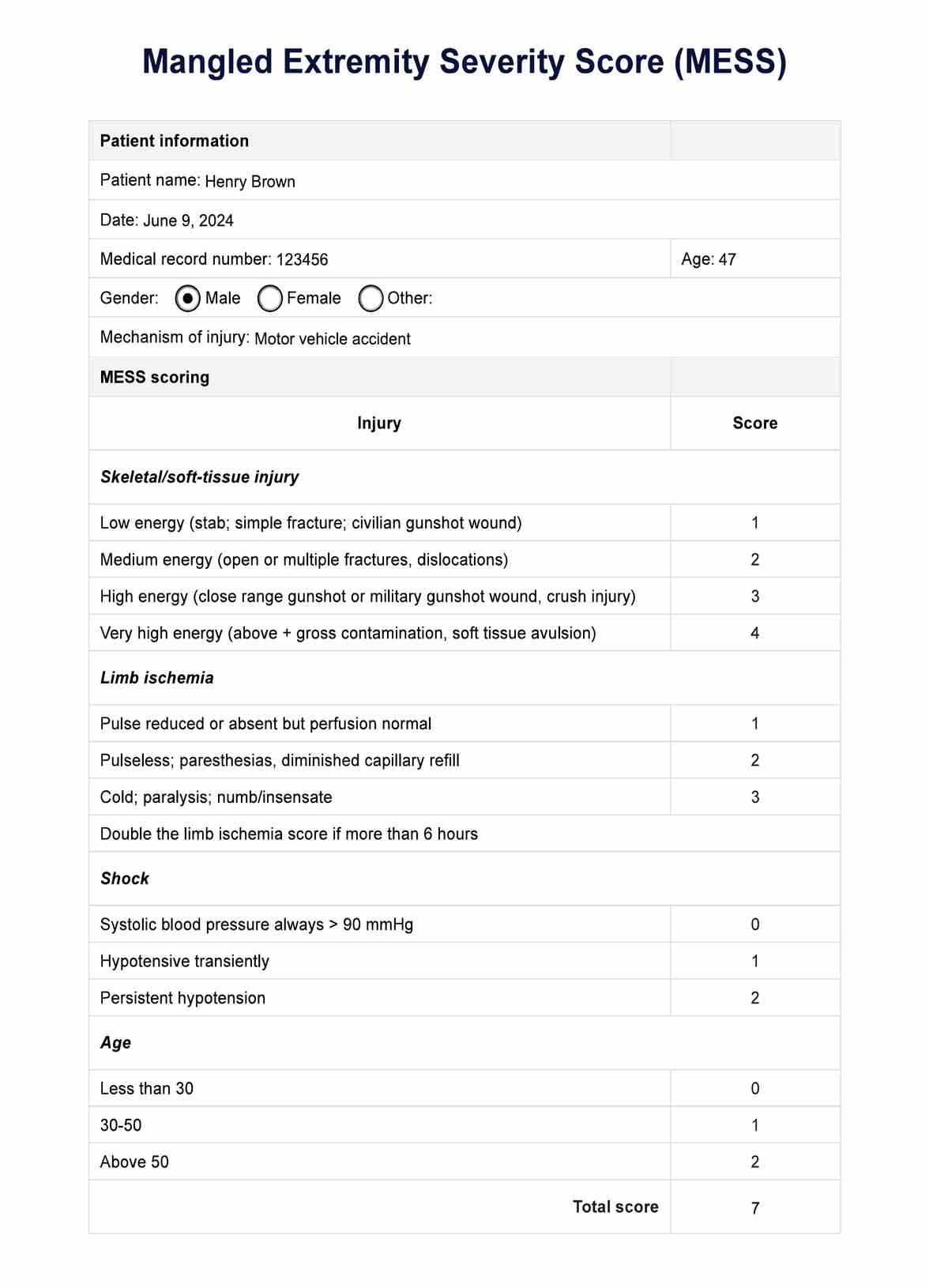
Nursing interventions
When designing a nursing care plan for pneumonia patients, it is essential to consider a range of interventions that address various aspects of the patient's health and well-being.
Respiratory support and airway management
Administer oxygen therapy as prescribed to maintain adequate oxygenation. Encouraging coughing and deep breathing exercises further helps promote lung expansion and secretion clearance. Chest physiotherapy techniques, such as percussion and vibration, can also mobilize secretions.
Medication administration and management
Administering antibiotic treatment as the physician prescribes is essential to treat the underlying bacterial infection, such as bacterial pneumonia. Providing analgesics and antipyretics helps manage pain and fever, but close monitoring for potential side effects is necessary. Administering bronchodilators and mucolytics as ordered can also further improve airway patency and facilitate secretion clearance.
Patient education and health promotion
It is essential to educate hospitalized patients and caregivers about pneumonia, its causes, risk factors in developing pneumonia, and prevention strategies. Proper hand hygiene techniques and emphasizing their importance help reduce the spread of infection. Promoting smoking cessation and providing resources and support can also help patients quit. Furthermore, practitioners can encourage frequent rest periods, a balanced diet, adequate hydration, and regular physical activity to support overall health and recovery.
Monitoring and assessment
It is also important to regularly assess and monitor vital signs, including respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, blood pressure, and temperature. Monitoring sputum characteristics, such as color, consistency, and volume, helps assess the effectiveness of interventions and identify potential complications. Evaluating the patient's response to treatments and adjusting the care plan accordingly is also crucial in the treatment process.
Why use Carepatron as your Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan app?
Using Carepatron as your Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan app can benefit healthcare professionals, especially nurses managing patients with pneumonia. Carepatron provides a centralized workspace, allowing you to manage clinical documents and electronic patient records, set patient appointment reminders, and handle medical billing seamlessly and efficiently within a single platform.
Carepatron is also dedicated to offering a highly efficient and productive platform for thousands of healthcare professionals. We enable customizing tools like this Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan Template within our clinical documentation software so we can meet your unique needs.
Our portable medical dictation software simplifies clinical note-making and updates, ensuring an effortless process. With great accessibility comes great responsibility, and we prioritize the security of all notes, clinical records, results, and practitioner data by complying with global security requirements, including HIPAA, GDPR, and HITRUST.
Ready to experience this transformation in how you provide care? Choose Carepatron.
Sign up for a free trial!
.png)
References
Herdman, H. T., & Kamitsuru, S. (2017). NANDA international nursing diagnoses. Thieme. https://books.google.com.ph/books?id=sJ0uDwAAQBAJ&pg=PT11&source=gbs_selected_pages&cad=1#v=onepage&q&f=false
Kalil, A. C., Metersky, M. L., Klompas, M., Muscedere, J., Sweeney, D. A., Palmer, L. B., Napolitano, L. M., O'Grady, N. P., Bartlett, J. G., Carratalà, J., El Solh, A. A., Ewig, S., Fey, P. D., File, T. M., Jr, Restrepo, M. I., Roberts, J. A., Waterer, G. W., Cruse, P., Knight, S. L., & Brozek, J. L. (2016). Management of adults with hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia: 2016 clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 63(5), e61–e111. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciw353
Klompas, M., Branson, R., Eichenwald, E. C., Greene, L. R., Howell, M. D., Lee, G., Magill, S. S., Maragakis, L. L., Priebe, G. P., Speck, K., Yokoe, D. S., & Berenholtz, S. M. (2014). Strategies to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia in acute care hospitals: 2014 update. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, 35 Suppl 2, S133–S154. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0899823x00193894
Mandell, L. A., & Niederman, M. S. (2019). Aspiration Pneumonia. The New England Journal of Medicine, 380(7), 651–663. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1714562
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2022, March 24). Pneumonia. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/pneumonia
Commonly asked questions
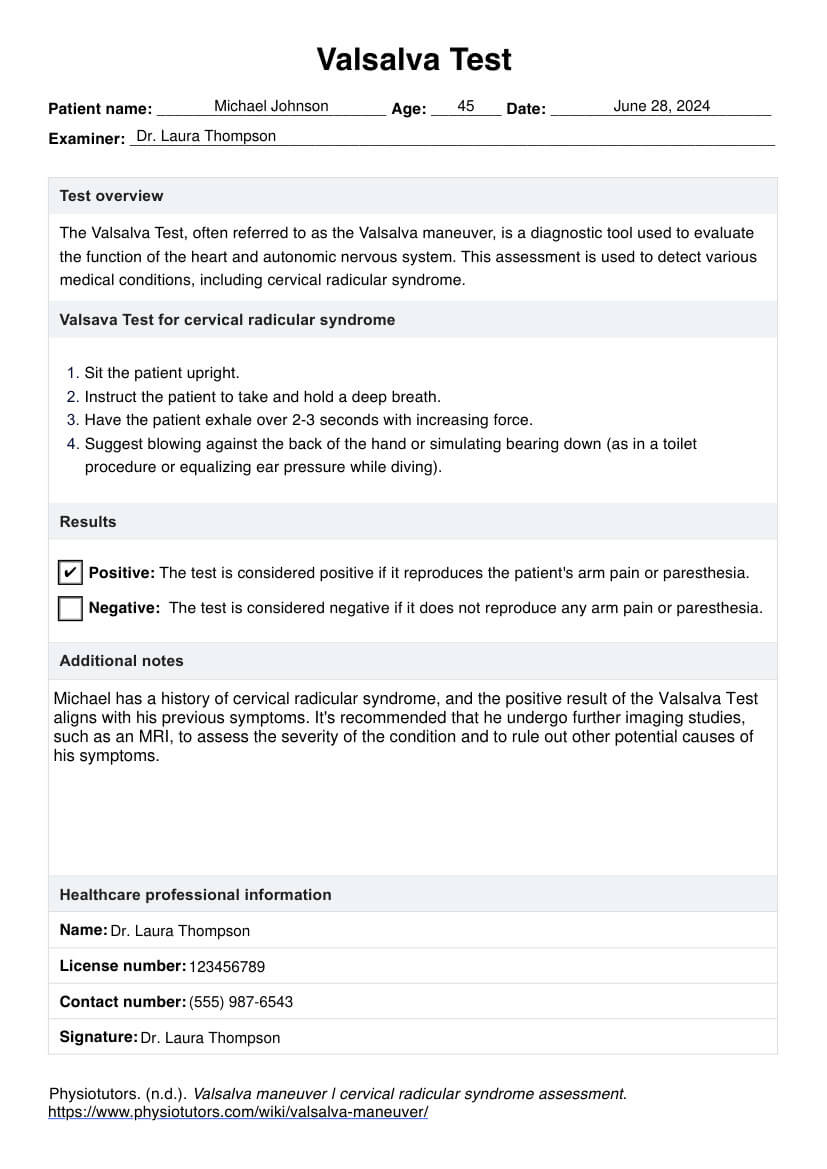
When assessing a patient with pneumonia, the nurse should focus on evaluating respiratory status, including vital signs (temperature, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation), breath sounds, and work of breathing. The nurse should also assess for signs of infection, such as fever and chills, and monitor for complications like pleural effusion or respiratory failure. Additionally, the nurse should assess the patient's overall condition, including level of consciousness, hydration status, and ability to cough and clear secretions.
The goal of pneumonia care is to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and promote recovery. This includes providing oxygen therapy, antibiotics if necessary, and supportive care such as hydration and pain management.
Someone with pneumonia typically needs supportive care, including oxygen therapy, antibiotics if necessary, and hydration. They may also require pain management and respiratory support, such as a humidifier or nebulizer. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide close monitoring and treatment.