Thompson Test
Learn about the Thompson Test for diagnosing Achilles ruptures, its procedure, interpretation, and benefits. Download our free Thompson Test template for healthcare professionals.


What is an Achilles rupture?
An Achilles rupture is a serious injury involving a tear in the Achilles tendon, the largest tendon in the body. This tendon connects the calf muscles to the heel bone and plays a crucial role in walking, running, and jumping.
When it ruptures, it can cause significant pain and loss of function in your lower leg. Achilles ruptures often occur suddenly and may feel like being kicked or hit in the back of the ankle.
It can happen to anyone, but it is most common in athletes and middle-aged adults who participate in sports or intensive physical activities.
Symptoms of an Achilles rupture
Recognizing the symptoms of an Achilles rupture is vital for early diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden, sharp pain in the back of your ankle or calf
- A popping or snapping sound at the time of injury
- Swelling and bruising near the heel
- Difficulty walking, particularly pushing off with the affected foot
- A visible gap or indentation above your heel where the tendon has torn
Causes of Achilles ruptures
Several factors can contribute to an Achilles rupture:
- Overuse: Repetitive stress from activities like running or jumping can weaken the tendon over time.
- Sudden increase in activity: Rapidly increasing the intensity or frequency of physical activity can strain the tendon.
- Age: As you age, the Achilles tendon loses flexibility and strength, making it more susceptible to tears.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and some antibiotics, have been linked to an increased risk of tendon rupture.
- Existing conditions: Conditions like tendonitis, which causes tendon inflammation, can predispose you to a rupture.
Potential complications Achilles ruptures may lead to:
An untreated Achilles rupture can lead to various complications, including:
- Chronic pain: Persistent pain in the affected area.
- Limited mobility: Difficulty walking or performing daily activities.
- Re-rupture: The tendon may tear again, especially if not properly rehabilitated.
- Muscle weakness: Reduced strength in the calf muscles.
- Scar tissue: Excessive scarring can lead to stiffness and reduced flexibility.
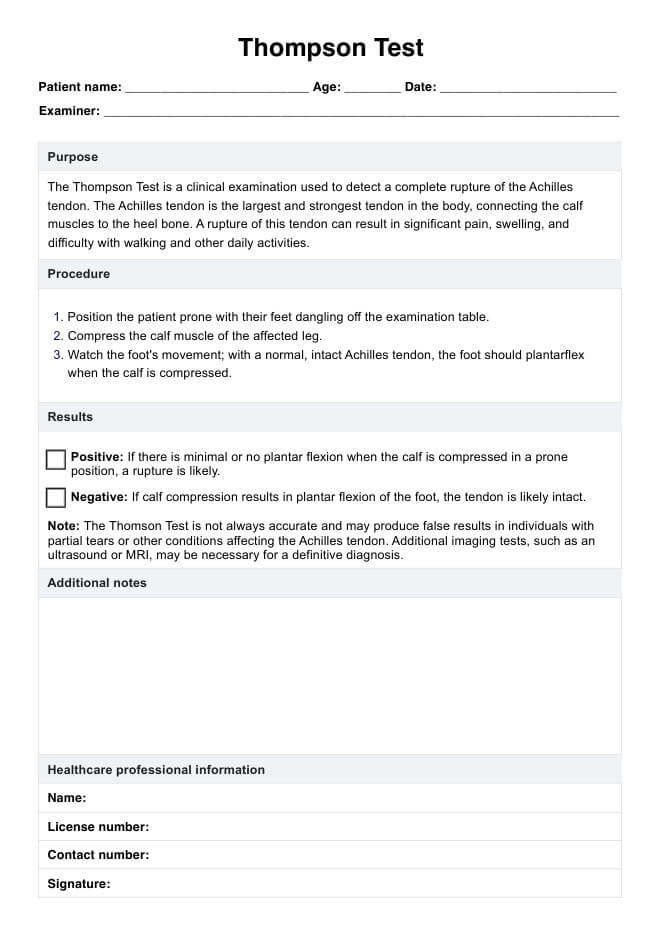
Thompson Test Template
Thompson Test Sample
What is the Thompson Test?
The Thompson Test, or the Squeeze Test, is a clinical diagnostic test used to determine whether a patient has an Achilles tendon rupture. This test is simple yet effective and is often one of the first steps in diagnosing a suspected rupture.
How is this test conducted?
To perform the Thompson Test, the patient lies face down on an examination table with their legs hanging off the edge. The clinician then squeezes the patient's calf muscle, which should cause the foot to flex downward. This movement is known as plantar flexion.
If there is a rupture present, squeezing the calf muscle will not result in any movement of the foot. This lack of movement indicates that there is a tear or complete rupture in the Achilles tendon. In some cases, there may be a partial tear which can also result in limited or no movement of the foot during this test.
A negative Thompson Test, where there is movement in the foot upon squeezing the calf muscle, indicates that there is no rupture present. However, it is important to note that this test should not be used as the sole diagnostic tool for an Achilles tendon injury. Other imaging tests such as an MRI or ultrasound may be required for a complete and accurate diagnosis.
Benefits of using our free Thompson Test template
Our free Thompson Test template offers several benefits:
Fully digital
Our template is fully digital, making it easy to access and use from any device with an internet connection. This eliminates the need for physical copies of the test and allows for easier sharing and collaboration among team members.
Customizable
While our template provides pre-set content and structure, it is also fully customizable. You can tailor the test to fit their specific needs and preferences, making it a versatile tool for various purposes.
Time-saving
With our free Thompson Test template, you can save time by not having to create the test from scratch. The template already includes essential components such as instructions and fields for patient details and results.
Achilles rupture treatments
Treating an Achilles rupture typically involves surgical and nonsurgical treatments such as:
- Rest and immobilization: Wearing a cast or walking boot can help keep the tendon in place and allow it to heal.
- Physical therapy: After surgery, physical therapy is essential to regain strength and mobility in the affected area.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These medications can help reduce pain and swelling during the healing process.
- Percutaneous repair: This minimally invasive surgery involves making small incisions and using special instruments to reattach the ruptured Achilles tendon.
- Open repair: This traditional approach involves making a larger incision along the length of the tendon and directly sewing the torn ends together.
- Tendon transfer: In this procedure, a nearby tendon is used to replace the damaged portion of the Achilles tendon.
Commonly asked questions
The Thompson Test is less effective for diagnosing partial Achilles tendor tear. In cases where a partial tear is suspected, further imaging, such as an MRI or ultrasound, is recommended for a definitive diagnosis.
Yes, the Thompson Test is highly reliable for diagnosing a complete Achilles tendon tear. When the Achilles tendon is completely ruptured, squeezing the calf muscle will not produce any movement of the foot, indicating a positive result for this test. Nevertheless, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention for an acute Achilles tendon rupture to confirm the diagnosis and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
If the patient is accessible, the Thompson Test can be performed immediately after the injury. Early testing helps in quick diagnosis and timely intervention, crucial for optimal recovery outcomes.
The Thompson Test should be performed with caution if there is significant swelling, open wounds, or if the patient is experiencing severe pain that may hinder an accurate assessment. In such cases, imaging studies might be a better initial approach.

.jpg)