Nursing Diagnosis for Pneumonia
Explore our guide on pneumonia, including symptoms, treatments, and how our free template can help form accurate nursing diagnoses.


What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lungs that primarily affects the microscopic air sacs known as alveoli. It occurs when these air sacs fill with fluid or pus due to infection, which bacteria, viruses, or fungi can cause. This inflammation leads to impaired gas exchange and can cause respiratory symptoms.
There are several types of pneumonia:
- Bacterial pneumonia: The most common type and is primarily caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumonia. Subtypes include lobar pneumonia and bronchopneumonia.
- Viral pneumonia: Caused by viruses such as influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and coronaviruses (including SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19).
- Mycoplasma pneumonia: Caused by the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae and is often referred to as "walking pneumonia" due to its milder symptoms.
- Atypical pneumonia: Caused by various atypical pathogens such as Chlamydophila pneumoniae and Legionella pneumophila.
- Fungal pneumonia: Typically occurs in individuals with weakened immune systems, can be caused by fungi such as Pneumocystis jirovecii, which is associated with AIDS, or other fungi like Histoplasma and Coccidioides.
- Aspiration pneumonia: Occurs when food, liquid, or vomit is inhaled into the lungs, leading to infection.
Additional types such as community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) are named after how they spread; CAP spreads outside a healthcare setting, while HAP develops while a person is hospitalized and is often caused by more resistant bacteria.
Pneumonia symptoms
Pneumonia presents a range of symptoms that can differ in severity based on the individual's health and the type of pneumonia. The most typical symptoms include:
- Cough: Often a response to increased production of respiratory secretions such as phlegm or mucus, which may be green, yellow, bloody, or purulent.
- Fever: Accompanied by sweating and shaking chills.
- Respiratory distress: May worsen with activity or as pleural effusion sets in.
- Chest pain: Sharp or stabbing pain that intensifies with coughing and deep breathing, or may be pleuritic chest pain.
- Fatigue: General tiredness and low energy.
- Loss of appetite: Reduced desire to eat.
- Nausea or vomiting: Especially common in children.
- Rapid breathing: Shallow and fast breathing.
- Rapid pulse: Increased heart rate.
- Bluish tint: A bluish color to lips or fingernails, indicating low oxygen levels.
- Confusion: Particularly in older adults, who may experience changes in mental awareness or delirium.
Other symptoms present in older adults, younger children, or those with comorbidities such as chronic lung disease or compromised immune systems:
- Older adults: Confusion or changes in mental awareness, lower-than-normal body temperature, milder presentation of other symptoms
- Infants and young children: Fussiness and restlessness, trouble feeding, noisy breathing or grunting, pale skin or limpness, and decreased urination.
Viral pneumonia symptoms also include muscle pain and weakness alongside other typical pneumonia symptoms.
Causes of pneumonia
Pneumonia can be classified into types based on how the infection was acquired: community-acquired, hospital-acquired, or ventilator-associated pneumonia. Influenza, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and respiratory syncytial virus can all lead to developing pneumonia, especially in vulnerable populations like the young or elderly.
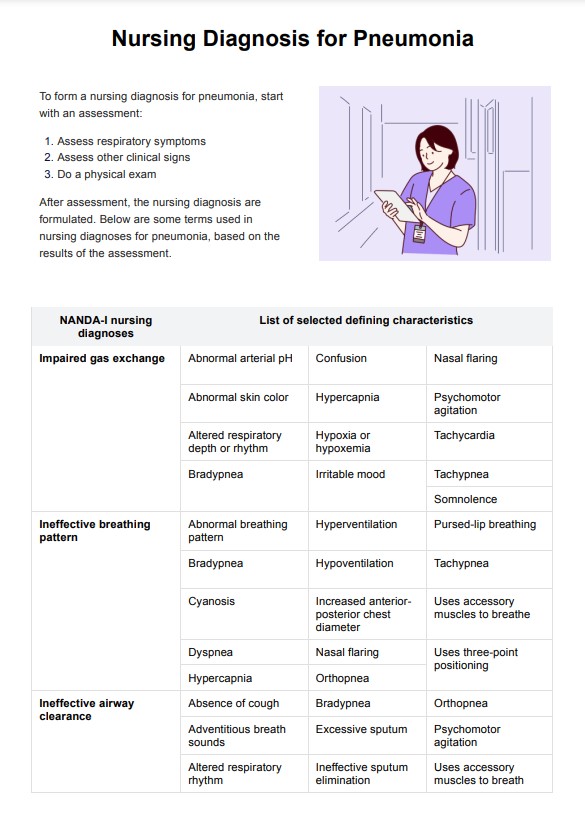
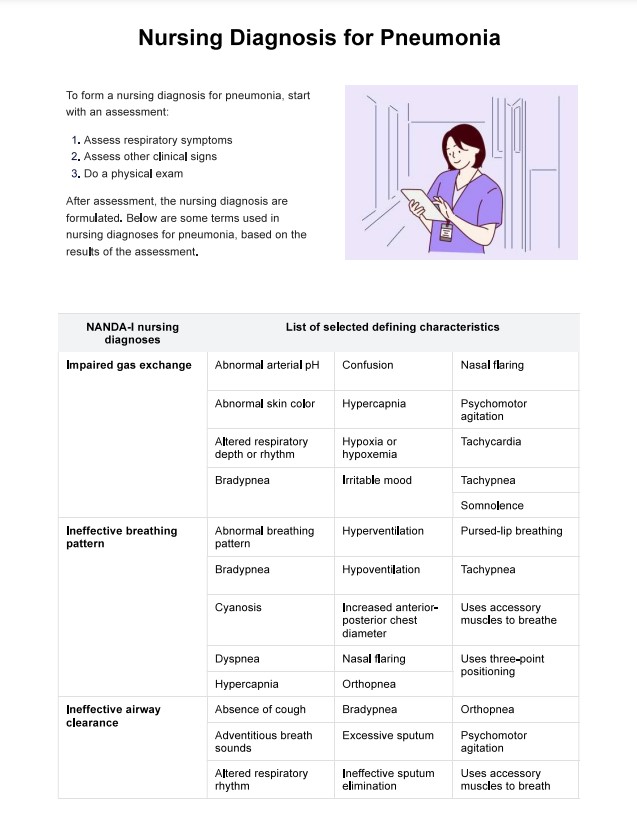
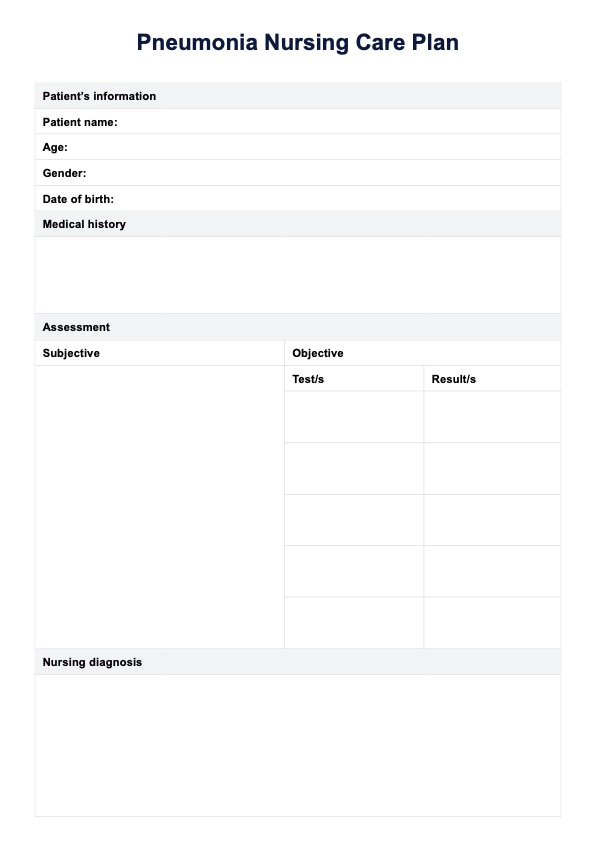
Nursing Diagnosis for Pneumonia Template
Nursing Diagnosis for Pneumonia Example
How to use our Nursing Diagnosis for Pneumonia template
Here's how to use our template:
Step 1: Access the template
Begin by downloading the Nursing Diagnosis for Pneumonia template. You can access it by clicking the "Use template" or "Download" buttons available on this page.
Step 2: Do an assessment
Conduct a thorough assessment of the patient. This includes doing a respiratory assessment to find symptoms such as cough, dyspnea, and sputum production, as well as other clinical signs like blood pressure, fever, and chest pain. Perform a physical exam to identify adventitious breath sounds, changes in skin color, or the use of accessory muscles for breathing.
Step 3: Form a diagnosis and a care plan
Based on the assessment, form a nursing diagnosis using the terms provided in the template, such as "Impaired gas exchange" or "Ineffective airway clearance." Develop a care plan tailored to the patient's needs, which may include interventions such as administering oxygen, encouraging effective coughing, or monitoring vital signs.
Step 4: Implement nursing interventions
Put the care plan into action by implementing the identified nursing interventions. This could involve administering prescribed medications, providing respiratory support, educating the patient on deep breathing exercises, and ensuring proper hydration. Track the patient’s progress and update the care plan as needed.
Step 5: Monitor and review
Continuously monitor the patient's response to the interventions. Assess for improvements in symptoms, changes in respiratory function, and overall patient condition. Document any changes in the "Additional notes" section of the template. Regularly review and adjust the care plan based on the patient's progress to ensure optimal outcomes.
Benefits of using this template
Utilizing our free Nursing Diagnosis for Pneumonia offers multiple benefits that enhance patient care:
Standardized assessment
The template provides a structured format that standardizes the assessment process across healthcare providers. This ensures that all relevant clinical information, such as symptoms, onset, and pneumonia severity, is consistently documented.
Improved diagnostic accuracy
The template helps nurses make more accurate diagnoses by guiding them through a detailed checklist of symptoms, risk factors, and physical examination findings. This ensures that no critical information is missed.
Enhanced communication
The standardized format facilitates clearer and more efficient communication among the healthcare team. This is particularly beneficial in multidisciplinary teams where nurses, doctors, and specialists must share information quickly and clearly.
Prompt and appropriate interventions
With a comprehensive understanding of the patient's condition, healthcare providers can implement appropriate interventions more swiftly. This might include initiating antibiotic therapy, respiratory support, or other necessary treatments without undue delay.
Improved patient outcomes
The template improves patient outcomes by enabling early and accurate diagnosis and timely treatment. It helps reduce the complication rates associated with pneumonia, such as respiratory failure and sepsis, potentially shortening hospital stays and improving recovery times.
Documentation efficiency
The template streamlines the documentation process, saving time and reducing the likelihood of errors. This efficiency is crucial in busy clinical settings, allowing nurses to spend more time on direct patient care rather than paperwork.
The pneumonia nursing diagnosis template is a valuable tool that supports healthcare providers in delivering high-quality care and enhances patient safety and treatment effectiveness.
Commonly asked questions
A NANDA nursing diagnosis for respiratory patients is a standardized statement that identifies specific health issues related to respiratory function. Examples include "Impaired gas exchange related to alveolar-capillary membrane changes" and "Ineffective airway clearance related to increased sputum production."
Nurses assess respiratory status, administer medications, provide supplemental oxygen or do oxygen therapy, and educate patients on breathing exercises and infection prevention. They also monitor vital signs, ensure adequate hydration, and support patients in managing symptoms like cough and fever.
The primary goals of care for pneumonia are to clear the infection, improve gas exchange, manage symptoms, prevent complications, and promote recovery. This involves reducing inflammation, maintaining oxygenation, and ensuring patient comfort.

.jpg)