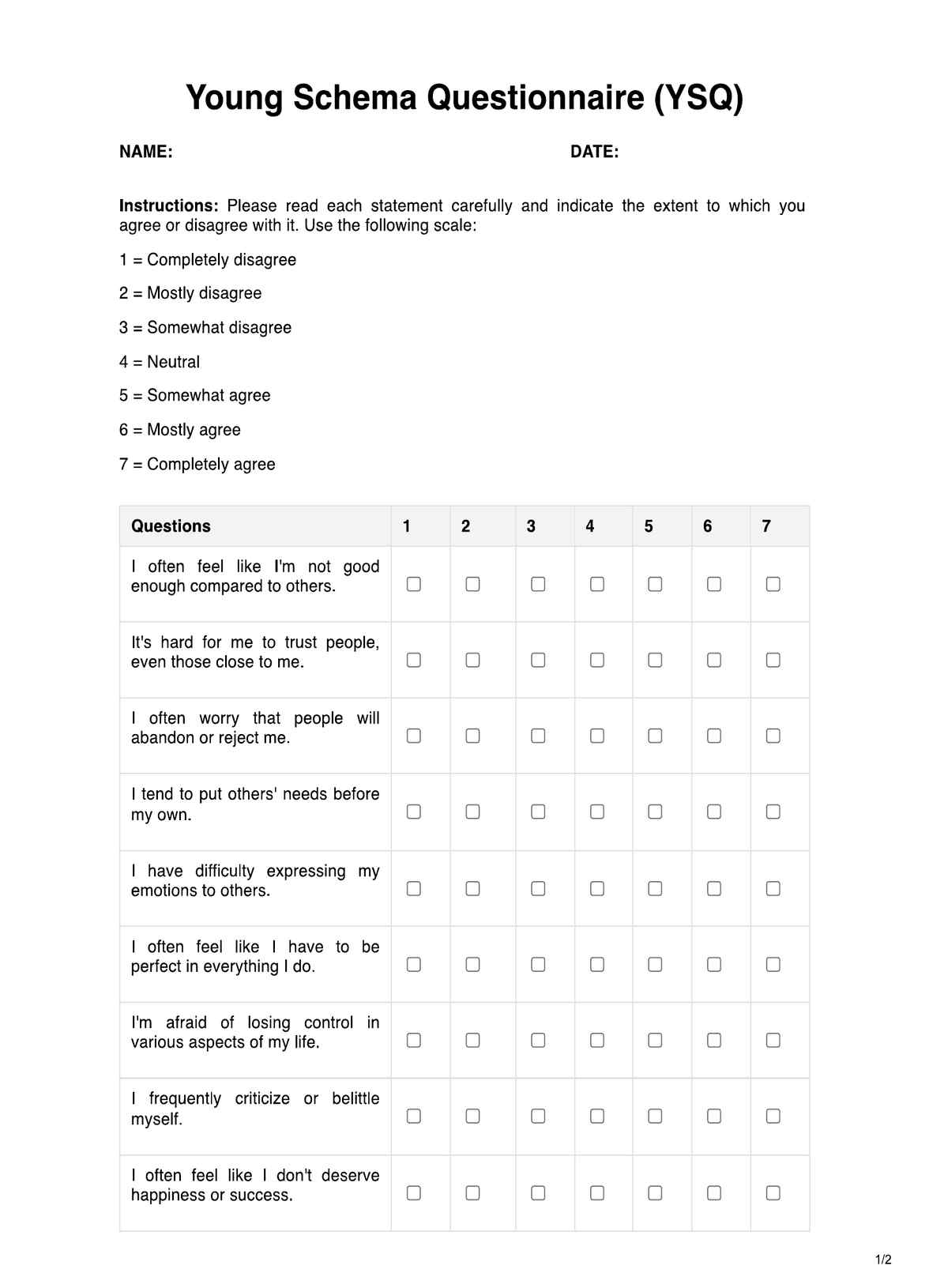
The mJOA score is used to evaluate the severity of spinal cord injuries, particularly in cases of cervical myelopathy, and to assess the functional status of patients with cervical back before and after treatment.

mJOA Score
Learn about the mJOA Score, a crucial tool for assessing spinal cord injuries and planning effective treatments.
Use Template
mJOA Score Template
Commonly asked questions
The mJOA score is calculated by assessing motor function in the upper and lower extremities, sensory function, and bladder control. Each category is assigned a specific point value that reflects the patient's degree of impairment.
A low mJOA score indicates severe impairment and a greater extent of neurological dysfunction, suggesting that the patient may require more intensive treatment and management strategies.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments