Diaphragmatic breathing works by engaging the diaphragm to expand the lungs more effectively. This allows for a more relaxed, slow, and deep breathing pattern that enhances oxygen intake and promotes relaxation.
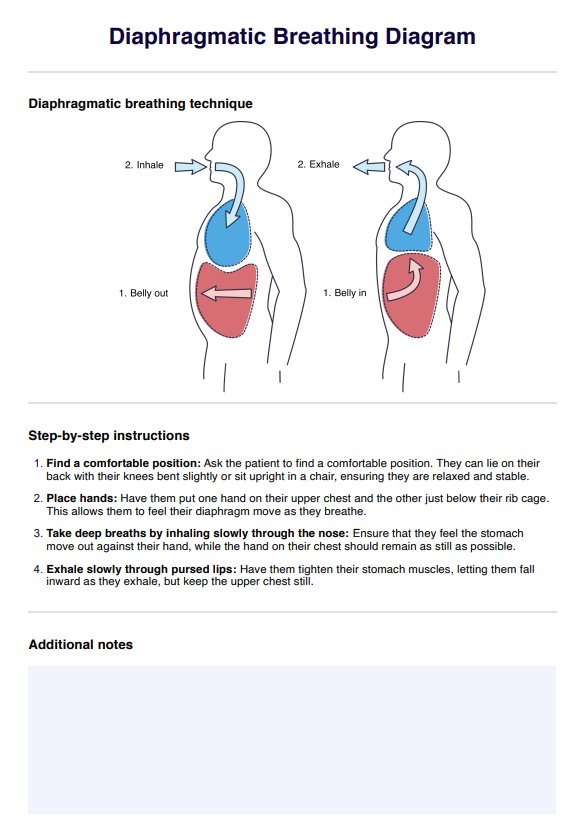
Diaphragmatic Breathing Diagram
Learn diaphragmatic breathing with our free diagram. Understand its benefits, how it works, and how to practice it for better health.
Use Template
Diaphragmatic Breathing Diagram Template
Commonly asked questions
For optimal benefits, practice diaphragmatic breathing for 10 to 20 minutes daily, ideally in a quiet, calm, and comfortable setting.
Yes, diaphragmatic breathing can significantly reduce symptoms of anxiety by activating the body's natural relaxation response and lowering the body and stress levels.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











