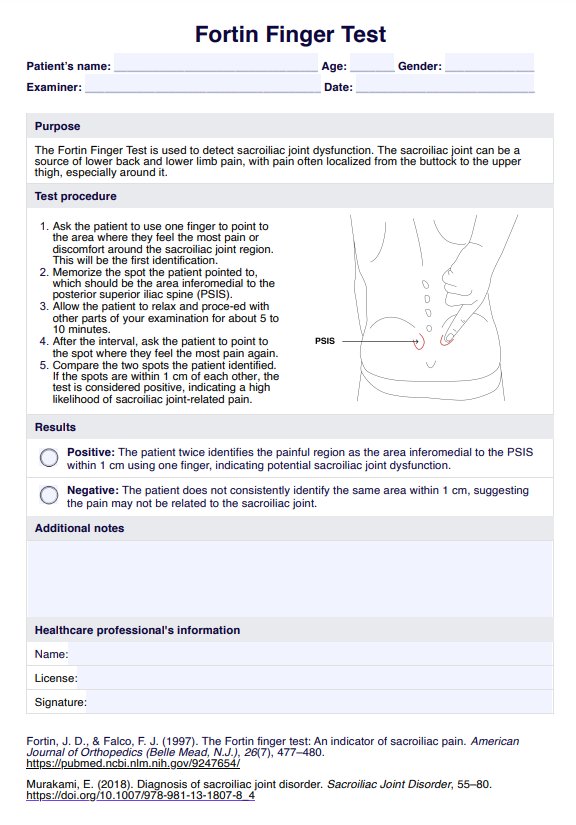
The Fortin Finger Test detects sacroiliac joint pain and dysfunction by having the patient indicate the sacroiliac joint pain and area using one finger.
Fortin Finger Test
Use the simple and easy Fortin Finger Test to screen back pain issues and as the first step to diagnosing sacroiliac joint dysfunction. Learn more about it here.
Use Template
Fortin Finger Test Template
Commonly asked questions
The patient points one finger to the pain area twice, and if the pain is localized within 1 cm of the same spot above the sacroiliac joints each time, the test is considered positive.
Common symptoms include chronic pain in the lower back, pain in the buttocks, and discomfort and pressure that radiates down the legs.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











