Valgus instability is primarily caused by repetitive stress and overuse, leading to damage or laxity in the UCL. It is commonly seen in athletes involved in sports requiring frequent throwing motions.
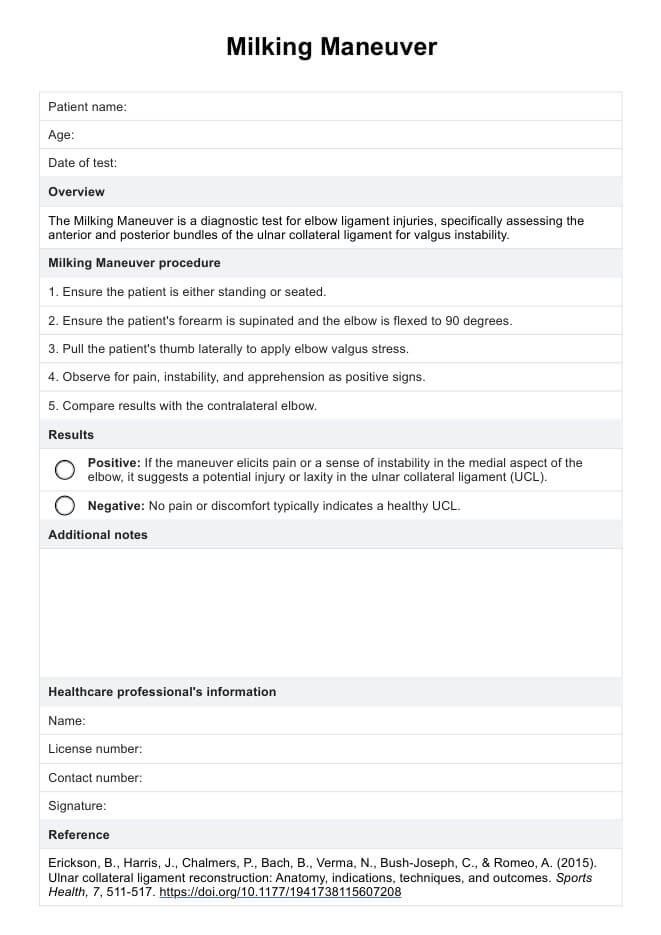
Milking Maneuver
Explore the Milking Maneuver to diagnose valgus instability. Learn how it's conducted, its benefits, and treatment options for better elbow health.
Use Template
Milking Maneuver Template
Commonly asked questions
Symptoms of valgus instability include medial elbow pain, a sensation of instability or "giving way" during arm use, and decreased performance in activities that involve throwing or lifting.
The Milking Maneuver assesses the integrity of the UCL in the elbow, helping to diagnose issues like valgus instability by mimicking the stress placed on the joint capsule and the ligament during throwing motions.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











