Understanding anatomy is crucial because it helps practitioners accurately locate the nerves and surrounding structures, such as the axillary artery. This minimizes the risk of complications and increases the success rate of the block.
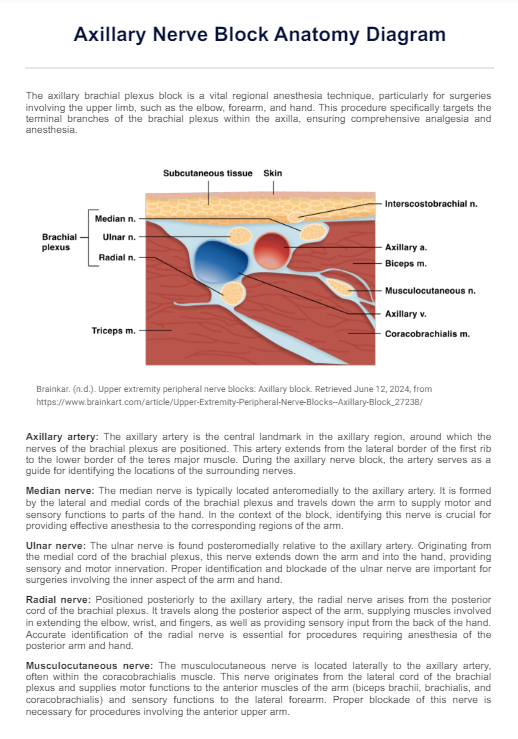
Axillary Nerve Block Anatomy Diagram
Our anatomy diagram enhances your understanding of the axillary nerve block. Download our free PDF template to guide your upper limb procedures.
Use Template
Axillary Nerve Block Anatomy Diagram Template
Commonly asked questions
An Axillary Nerve Block Anatomy Diagram typically includes the axillary artery, median, and ulnar nerves, radial, and musculocutaneous nerve.
The diagram can be used as a visual aid during pre-procedural planning, helping to identify and understand the location of nerves and other critical structures.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











