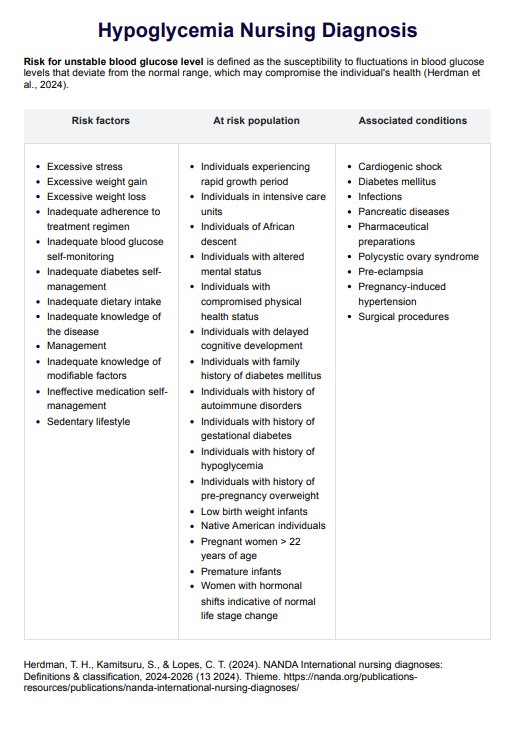
A nursing diagnosis of hypoglycemia involves identifying the patient's risk for unstable blood glucose levels and implementing interventions to prevent and manage low blood sugar.
Hypoglycemia Nursing Diagnosis
Learn about hypoglycemia nursing diagnosis and get Carepatron's free PDF download with examples to help you better understand and manage this condition.
Hypoglycemia Nursing Diagnosis Template
Commonly asked questions
Nurses manage hypoglycemia by conducting frequent blood glucose monitoring, administering fast-acting carbohydrates like glucose tablets, and adjusting insulin administration when necessary. Monitoring vital signs and ensuring medication adherence also help maintain glucose levels within the safe range.
Interventions for hypoglycemia include administering oral glucose or intravenous dextrose, monitoring blood glucose levels, providing carbohydrate-containing snacks or meals, and educating the patient on hypoglycemia prevention and management strategies.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











