Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status (PEDS)
Discover the Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status (PEDS), a tool for identifying children's developmental issues.


What is the Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status (PEDS)?
The Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status (PEDS) is a standardized behavioral screening tool designed to capture parental concern about children's development, behavior, and mental health. It aims to identify young children at risk for social-emotional and developmental-behavioral problems. PEDS is widely used in various healthcare settings to facilitate early detection. It also facilitates quality improvement initiatives and interventions for these young children.
How is PEDS structured, and how is it answered?
PEDS is a brief questionnaire comprising 10 open-ended questions about parents' concerns about their child's learning, development, and behavior. Parents are asked to fill out the questionnaire, usually in a healthcare setting, before a well-child visit. The questions are designed to be straightforward and non-leading, encouraging parents to provide concerns about their child or young children's development alone.
How is the assessment scored and how are the results interpreted?
Scoring the PEDS involves categorizing parental concerns into different developmental pathways: predictive, non-predictive, and those requiring further observation. A specific scoring form is used to determine the level of risk based on the type of community child health and the number of concerns cited. High-risk responses suggest significant developmental issues, moderate-risk responses indicate a need for further surveillance, and low-risk responses typically lead to routine developmental monitoring.
Next steps after using the PEDS
Based on the results from the PEDS screening, several next steps may be recommended:
- No concerns or low-risk concerns: Continue routine developmental surveillance and provide parental guidance.
- Moderate risk concerns: Conduct further developmental and behavioral assessments or refer to early intervention services.
- High-risk concerns: Refer immediately for more comprehensive developmental evaluations and consider referrals to specialists such as pediatric neurologists, developmental-behavioral pediatricians, or child psychologists.
These steps ensure that each child receives the appropriate level of care and intervention based on the specific needs identified through the PEDS and screening tests.
Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status (PEDS) Template
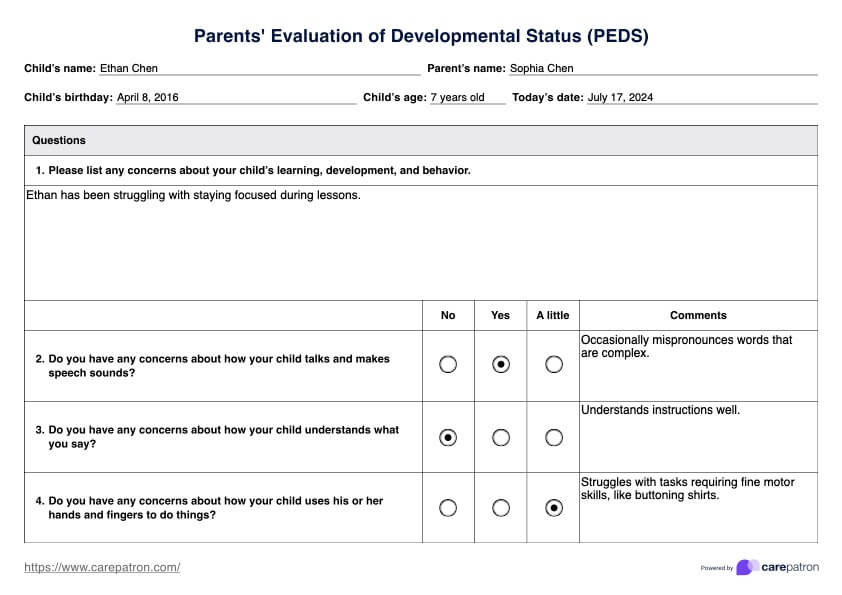
Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status (PEDS) Example
How to use our Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status (PEDS) template
PEDS is a valuable tool for identifying and addressing developmental delays and behavioral concerns in children. In this case, our template is based on the Centre for Community Child Health's (2006) adaptation of the PEDS originally developed by Glascoe (1998). This adapted template includes only the PEDS Response, Scoring, and Interpretation forms. Follow these steps to utilize our PEDS template effectively.
Step 1: Gather background information
Begin by collecting comprehensive background information about the child. This includes medical history, family history, and any previous evaluations or interventions. This step ensures you completely understand the child's context and potential factors affecting their development.
Step 2: Administer the response form
Provide the PEDS Response Form to the child's parents or primary caregivers. Encourage them to answer each question thoughtfully and honestly. The response form consists of 10 questions designed to identify parental concerns about the child’s development and behavior.
Step 3: Score the response form
After the parents complete the response form, score their responses according to the guidelines provided in the template. Each answer is assigned a score that indicates the parent's education level of concern. Pay special attention to high-scoring items, which may signal significant developmental issues.
Step 4: Interpret the results
Analyze the scores to determine the child's developmental status. Use the interpretation guide included in the PEDS template to categorize the results into areas such as no concern, needs monitoring, or requires further evaluation. This step helps prioritize the next actions based on the severity of the developmental concerns above.
Step 5: Develop an action plan
Based on interpreting the results, create a tailored action plan that addresses parents' concerns. This may include monitoring the child's development over time, referring the child to specialists for further evaluation, or implementing specific interventions. Ensure the action plan is comprehensive and addresses all identified concerns.
Step 6: Communicate with parents
Discuss the results and the action plan with the parents. Provide clear explanations of your findings and the recommended next steps. Address any questions or concerns they may have. Effective communication is crucial to ensure parents understand the process and are engaged in their child's developmental journey.
Step 7: Follow-up and reassessment
Schedule follow-up appointments to monitor the child's progress and reassess their development as needed. Continuously update the child development action plan based on new findings and ensure effective interventions. Regular follow-ups help maintain a proactive approach to the child's developmental health.
How this assessment benefits pediatricians
The PEDS is a valuable tool for pediatricians, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of developmental screenings in young children. Pediatricians gain insights into a child's developmental milestones and potential delays without lengthy testing using a simple questionnaire that parents fill out. This approach streamlines visits and utilizes parental observations, identifying behaviors and developmental problems that might not be evident during a clinical exam.
PEDS enables early detection of developmental issues, allowing for timely intervention. Early identification leads to better management strategies during critical developmental periods. Pediatricians can direct resources, refer to specialists, and advise on early intervention programs, optimizing outcomes. Additionally, PEDS helps pediatricians meet care guidelines for developmental developmental and behavioral screening only, ensuring compliance with healthcare policies and reducing oversight risks.
References
Centre for Community Child Health. (2006). PEDS Response Form - Authorised Australian Version. Bear Creek Pediatric Clinic. https://shobhanakamdarmd.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/peds.pdf
Glascoe, F. P. (1998). The value of 'parents' evaluations of developmental status’ in detecting and addressing children’s developmental and behavioral problems. Diagnostique, 23(4), 185-203. https://doi.org/10.1177/073724779802300401
Commonly asked questions
The Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status (PEDS) is a screening tool used by healthcare professionals to identify developmental and behavioral problems in children from birth to 8 years of age. It involves a series of questions answered by parents to have health professionals assess their child's development.
Early developmental screening helps identify children who may have developmental delays or disabilities. Early detection of developmental disabilities allows for timely intervention, significantly improving outcomes for the child's growth, learning, and overall well-being.
The Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status (PEDS) questionnaire is designed for parents or primary caregivers who are most familiar with the child's behaviors and developmental milestones to complete.