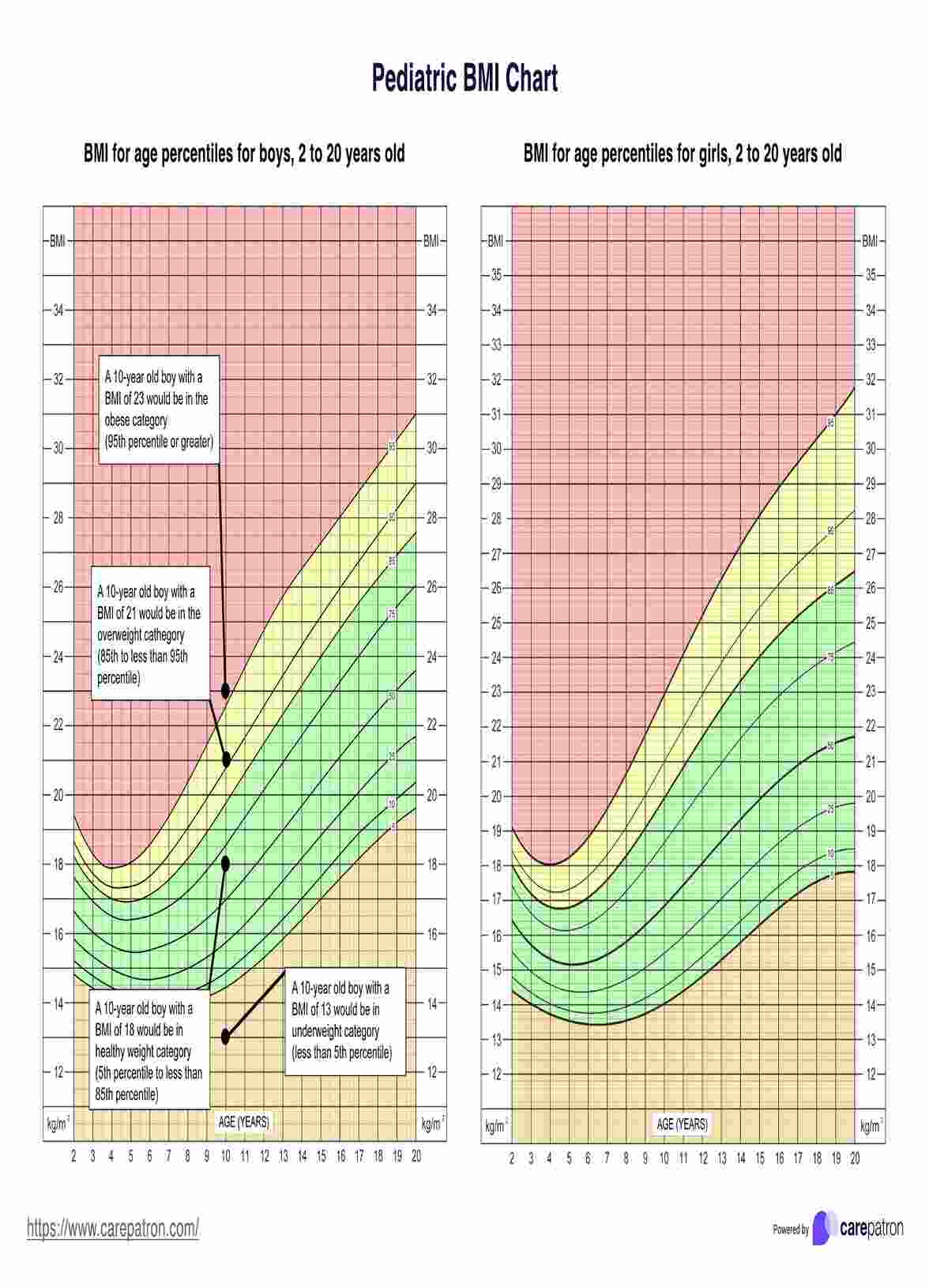
Energy-giving Food Chart
Discover the power of our Energy-giving Food Chart Template, designed for health professionals to guide clients to an energy-boosting diet. Download now!


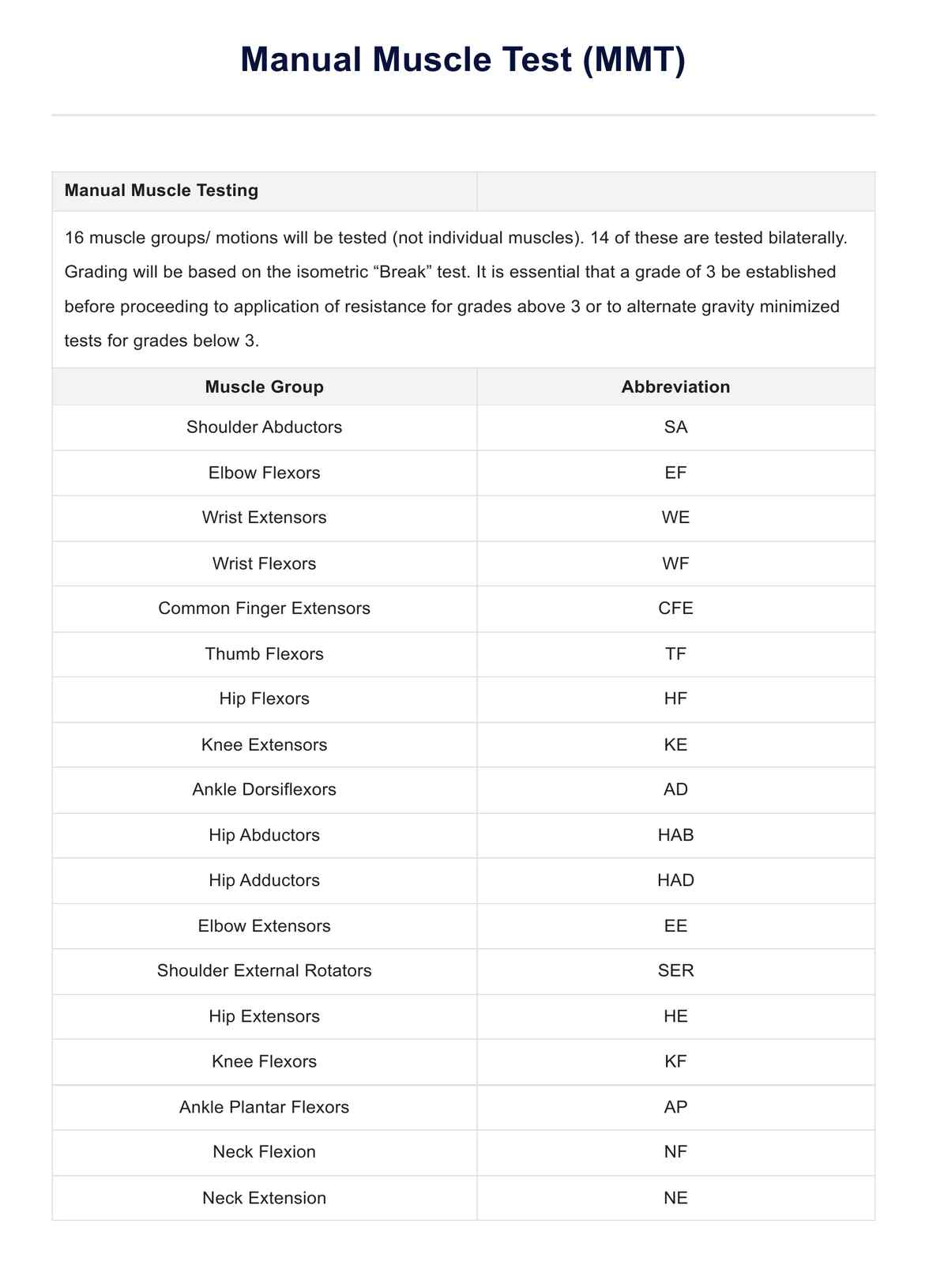
What is an Energy-Giving Food Chart?
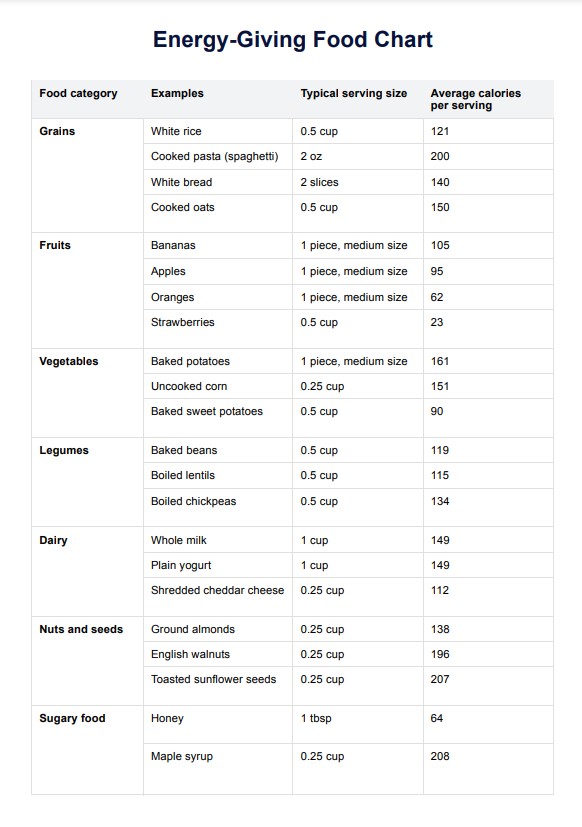
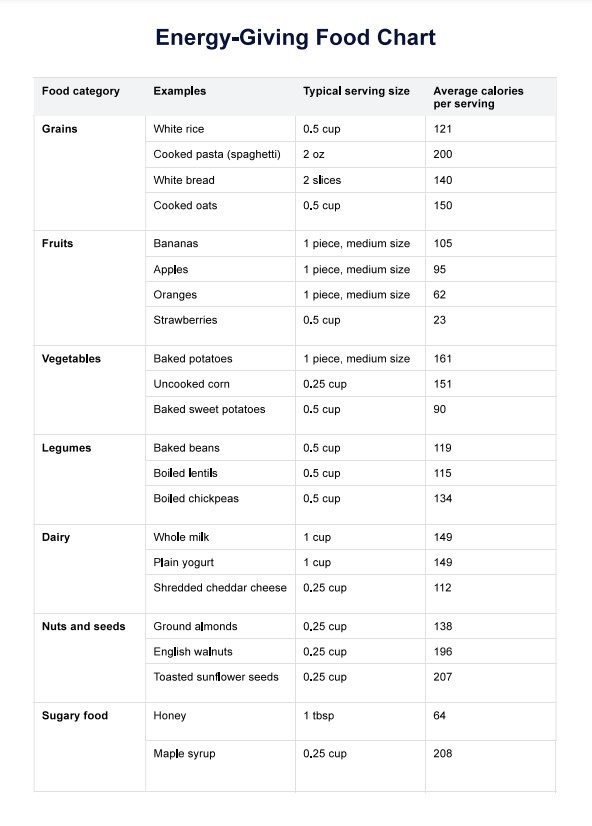
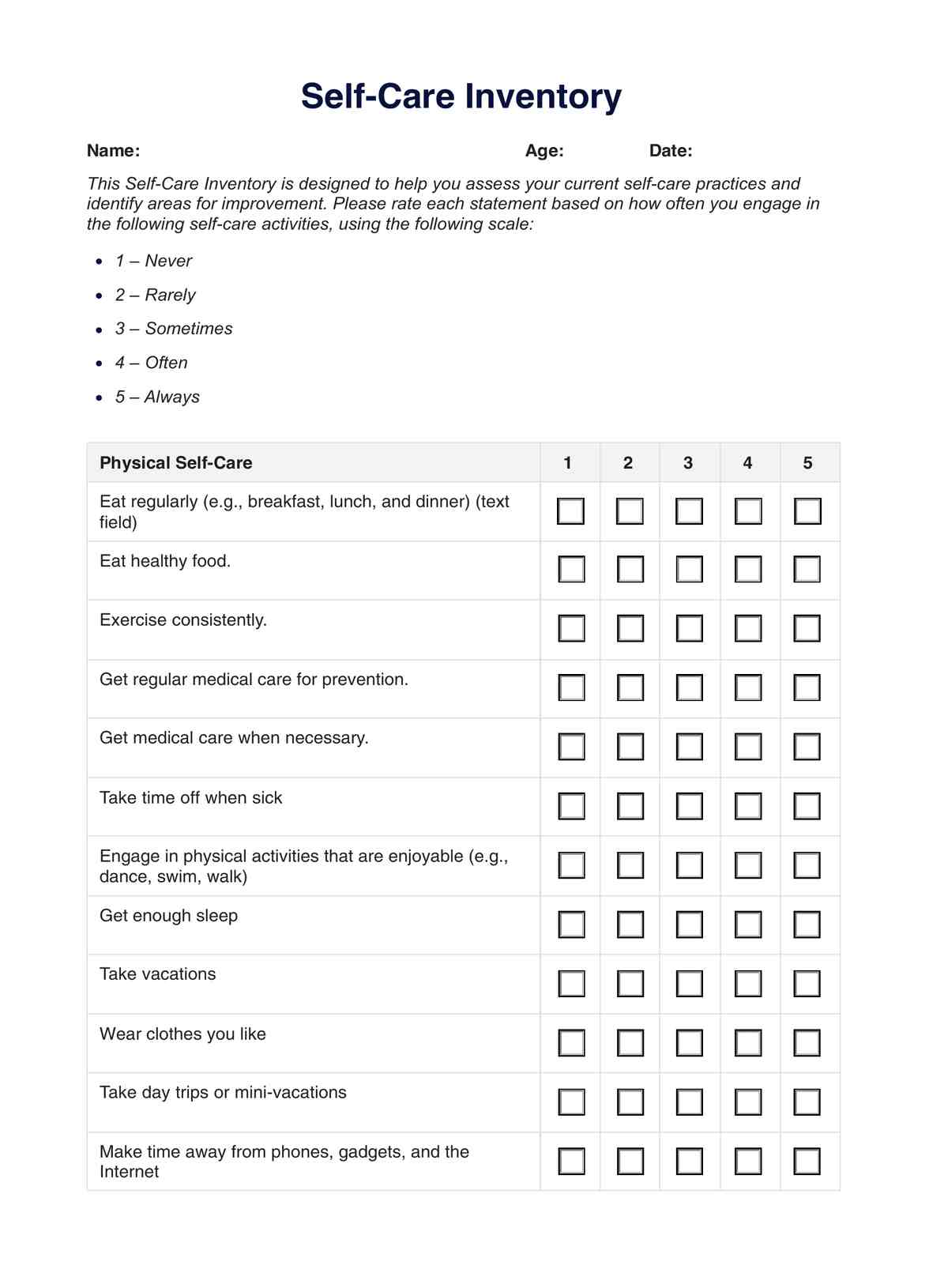
An Energy-Giving Food Chart is a valuable tool designed to help individuals identify and incorporate foods that are rich in energy, providing nutrients into their diet and focusing on the nutritional value of each food. The chart typically categorizes foods based on their nutrient content and energy-yielding potential, making it easier for users to make informed choices about their meals and snacks.
Energy is the fuel that powers the human body and allows people to perform daily activities, from breathing and thinking to exercising and working. It is derived primarily from food, particularly carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, broken down into glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids. These nutrients provide the energy needed for various bodily functions and are stored in the body as glycogen in the liver and muscles, and as fat in adipose tissues.
The glycemic index (GI) is also an important factor in energy management. High GI diets, which include foods that cause a quick spike in blood sugar levels, provide an instant energy boost but often lead to energy crashes. In contrast, low GI diets, consisting of foods that release glucose slowly, offer sustained energy production over a longer period. By choosing foods with natural sugars, lean protein, and healthy fats, individuals can maintain steady energy levels and improve overall health.
By using an Energy-Giving Food Chart, individuals can create balanced meals that provide sustained energy throughout the day, support physical activity, and maintain overall health. It is particularly useful for athletes, busy professionals, and anyone looking to optimize their energy levels and nutritional intake.
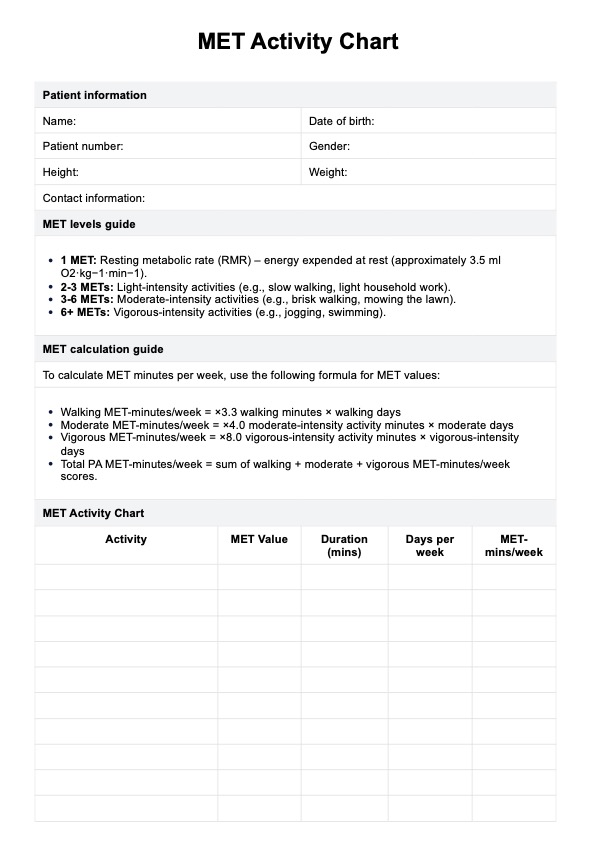
Energy-giving Food Chart Template
Energy-giving Food Chart Example
How to use our Energy-Giving Food Chart template
Our template contains a list of energy-rich foods, complete with serving sizes and average calories, along with sections for healthcare professionals to add notes and reminders for their patients. Follow these steps to effectively use the chart:
Step 1: Access the template
First, click the "Use template" button to open the chart in the Carepatron app, where you can customize it for your patient’s needs. Alternatively, you can download the template as a non-customizable PDF by clicking the "Download" button.
Step 2: Educate the patient about the contents
Go over the chart with the patient, explaining the various food categories and how they contribute to energy production. Highlight the serving sizes and calorie content to help them understand portion control and energy balance.
Step 3: Plan meals together
Help the patient plan their meals based on the chart by selecting a mix of energy-giving foods that suit their dietary preferences and energy needs. You may want to focus on creating a balanced diet that includes carbohydrates, healthy fats, and lean protein for sustained energy throughout the day.
Step 4: Encourage self-monitoring
Teach the patient how to use the chart to track their energy intake. They can record their meals and refer to the chart to ensure they are making energy-boosting food choices consistently.
Step 5: Adjust based on feedback
After the patient has used the chart for a period, schedule a follow-up session to discuss any changes in their energy levels or dietary habits. Use their feedback to make adjustments to the meal plan, if necessary.
Why is having enough energy important?
Maintaining adequate energy levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. It ensures that the human body can absorb protective foods and carry out essential processes like cell repair, immune function, and digestion. Sustained energy throughout the day is necessary for mental clarity, physical stamina, and emotional stability. Consuming a balanced diet with healthy nutrients, including complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help maintain stable energy levels and prevent energy crashes.
Insufficient energy levels can significantly impact an individual's health and daily functioning. When the body lacks the energy it needs, several consequences can arise:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Impaired cognitive function
- Mood disturbances
- Weakened immune system
- Poor physical performance
When to use the Energy-Giving Food Chart
The Energy-Giving Food Chart is a versatile tool that can be utilized in various scenarios to support a patient's nutritional needs and energy levels. Here are some appropriate times to use this chart:
- Diet planning: Utilize the chart when creating a balanced meal plan for patients, ensuring they incorporate a variety of energy-giving foods into their diet.
- Weight management: For patients aiming to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight, the chart can help them choose foods that provide energy without excessive calories.
- Sports nutrition: Athletes or physically active individuals can use the chart to select foods that fuel their workouts and aid in recovery.
- Managing fatigue: Patients experiencing fatigue or low energy levels can benefit from the chart by incorporating more energy-boosting foods into their diet.
- Health conditions: For individuals with specific health conditions like diabetes or heart disease, the chart can guide them in choosing foods that support their energy needs while managing their condition.
By using the Energy-Giving Food Chart at these times, patients can make informed decisions about their food choices, leading to improved energy levels and overall well-being.
What are the benefits of energy-boosting foods?
Incorporating energy-boosting foods into your diet, such as body-building foods, can have several health benefits. Here are some key advantages:
- Boost energy levels: Naturally, energy-boosting foods fuel bodily needs for daily activities, helping a person feel more alert and energized throughout the day.
- Improve blood flow: Some energy-boosting foods, like those rich in antioxidants and healthy fats, can improve blood flow and circulation, contributing to better heart health and overall vitality.
- Enhance brain function: Foods that provide sustained energy, such as whole grains and healthy fats, can also support brain function, improving focus, memory, and cognitive performance.
- Manage weight better: Choosing energy-boosting foods that are nutrient-dense and low in empty calories can aid in weight management by providing satiety without excess calories.
- Strengthen the immune system: Many energy-boosting foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which can help strengthen the immune system and protect against illness.
- Improve physical performance: Energy-boosting foods can enhance endurance, strength, and recovery in athletes and physically active individuals, leading to better performance in sports and workouts.
By incorporating energy-boosting foods into your diet, you can enjoy these health benefits, leading to a more active, balanced, and healthy lifestyle.
Commonly asked questions
To boost energy when feeling tired, consume foods that offer sustained energy like whole grains, fruits, nuts, and lean proteins. Staying hydrated and taking short breaks can also help.
Foods high in refined sugar and simple carbohydrates can lead to energy crashes. Processed foods and heavy, fatty meals can also make you feel sluggish.
Foods rich in fiber, healthy fats, and protein, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, fish, and nuts, can provide sustained energy for elderly individuals. Staying hydrated is also essential for maintaining energy levels.