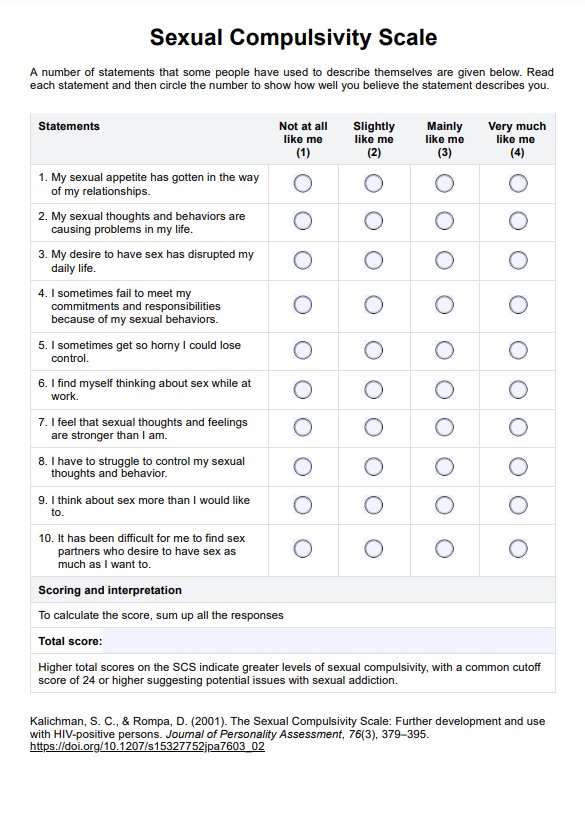
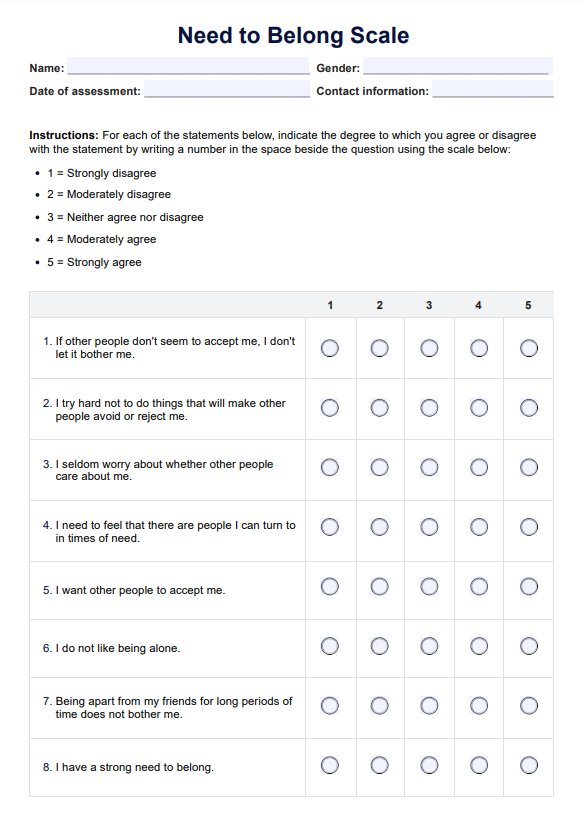
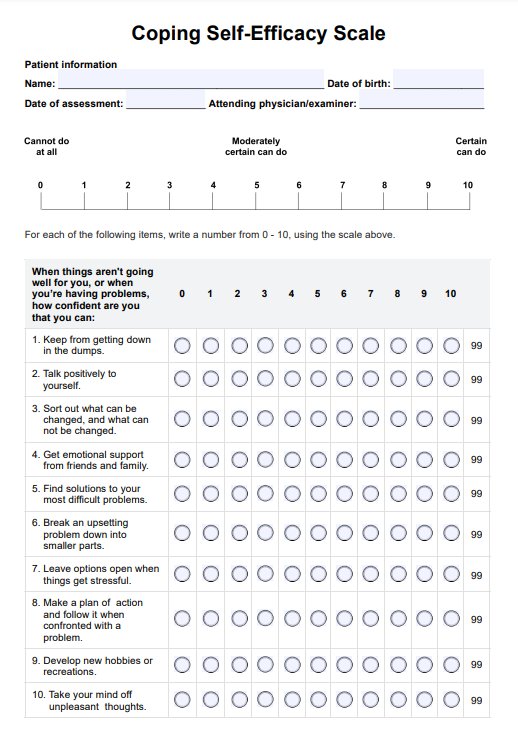
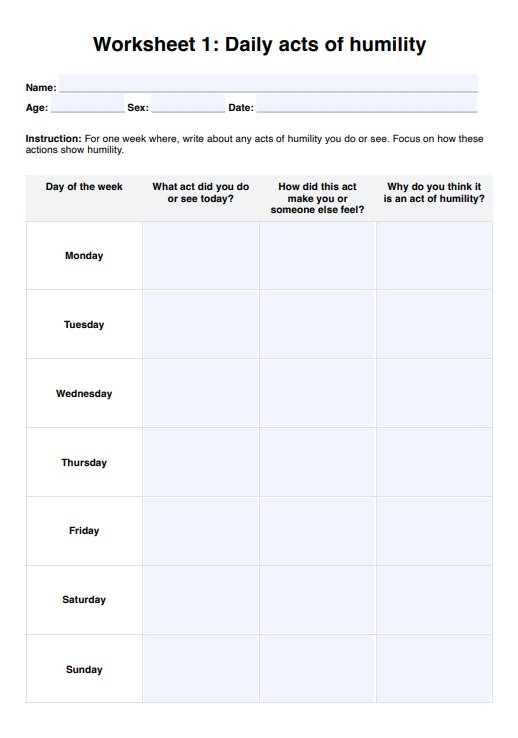
Healthy and Unhealthy Food Worksheet
Get our free Healthy and Unhealthy Food Worksheet to assess your client's diet, identify nutritious choices, and create a balanced meal plan.


What is nutrition education?
As a dietitian or nutritionist, you work with clients to assess and assist them in improving their health and addressing nutrition issues. However, you aren't always there with them when they prepare a grocery list or plan their meals. This is why it is essential to introduce your clients to the concept of nutrition education in your sessions with them.
Nutrition education involves engaging individuals in activities or programs that promote the voluntary adoption of healthy eating and nutrition-related behaviors (Washington State Department of Social and Health Services, n.d.). It is essential to teach nutrition education to help clients consume healthy food groups and learn how to make healthy choices.
Importance of nutrition education
Nutrition education empowers individuals to nourish themselves and their families, make informed food choices, and promote healthy eating. Beyond households, it extends to schools and rural communities.
When people understand what important nutrients are needed, they become more mindful of what they consume. Teaching nutrition at a young age helps children learn the importance of healthy food and develop lifelong habits for overall well-being.
In the U.S., in 2023, 23 states reported that more than one in three adults (35%) have obesity. Before 2013, no state had an obesity rate that high. At least 20% of adults in every U.S. state are living with obesity, showing the increase in obesity rates over the past decade (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024). This significantly increases their vulnerability to a variety of health conditions, such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and cancer.
Main differences between healthy and unhealthy food
The choice of food matters. Being mindful will help people achieve better health. This act is also an application of nutrition education, where individuals make healthy eating choices by knowing the nutritional components of a particular food. Sometimes, what they contain are just empty calories.
The difference between healthy and unhealthy food boils down to its nutritional value. Healthy foods provide one's body with essential nutrients such as vitamins and minerals to maintain optimal function. Fruits, vegetables, proteins, and healthy fats make the healthy list.
Conversely, unhealthy foods are high in calories, contain saturated fats, and have added sugars. Fast foods, junk foods, and highly processed foods are typical examples.
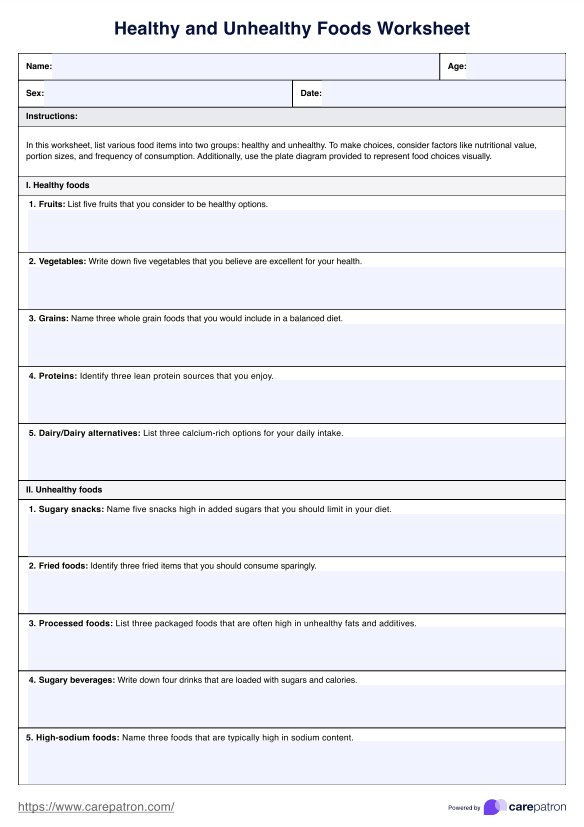
Healthy and Unhealthy Food Worksheet Template
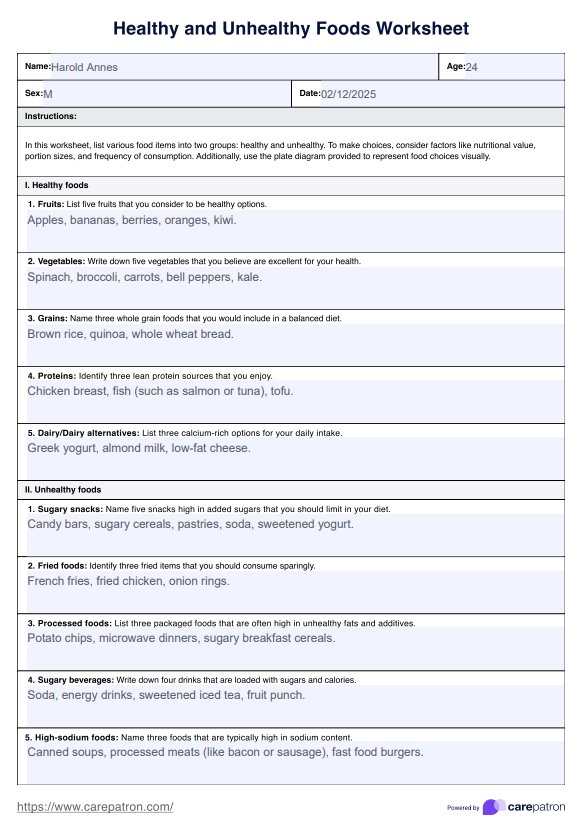
Healthy and Unhealthy Food Worksheet Example
How does our Healthy and Unhealthy Food Worksheet work?
Helping clients get started on healthy eating should not be a problem with our worksheet. We've listed down these easy steps to follow:
Step 1: Access the worksheet
Click "Use template" from this guide to access and edit the template within the Carepatron app before you can print or send it as an online worksheet. You can also click on "Download" for a fillable PDF template.
Step 2: Review the instructions
Distribute the worksheet to the clients and have them read the instructions carefully to understand the purpose. They should familiarize themselves with the categories of healthy and unhealthy foods. Explain the process to your clients to guide them.
Step 3: List healthy and unhealthy foods
Tell them to list their preferred healthy foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Then, identify unhealthy options, such as sugary snacks, fried foods, and processed items. Remind them to consider portion sizes and frequency of consumption.
Step 4: Create a plate
Prompt them to use the provided plate diagram to represent food choices visually. Encourage them to aim for a balanced plate that follows the right proportions, with more healthy options than unhealthy ones.
Step 5: Reflect and adjust
Set a time to reflect on food choices and the balance of their plate. Consider how to incorporate more healthy foods into the diet while reducing the intake of unhealthy options. Use this reflection as a guide for making sustainable changes to eating habits.
Examples of healthy and unhealthy food
To help your clients avoid the pitfalls of unhealthy eating and stay on track with a healthy diet, here are some examples of healthy and unhealthy foods:
Healthy foods items
Here are examples of food that nourish and fortify the body with every bite. Your client's diet should include some of these:
- Fruits: Fruits are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. They promote overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Examples include apples, which are rich in antioxidants, and berries, known for their high vitamin C content.
- Vegetables: Vegetables, especially leafy greens, are low in calories but high in nutrients. They help improve digestion and reduce inflammation. Examples include spinach, a great source of iron and folate, and broccoli, which is rich in vitamin K and fiber.
- Grains: Whole grains provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals essential for heart health and digestion. Examples include brown rice, which offers sustained energy and B vitamins, and quinoa, a complete protein source rich in magnesium and fiber.
- Proteins: Lean protein sources support muscle growth and repair, aid in weight management, and contribute to overall satiety. Examples include chicken breast, which provides high-quality protein with low saturated fat, and fish like salmon, which is rich in omega-3 fatty acids for heart health.
Non healthy foods
These types of food may taste good, but they're not the best for the body. Here are the foods to minimize to maintain your client's health and wellness:
- Sugary snacks: These treats pack a lot of sugar. Too much sugar can leave an individual feeling sluggish and contribute to weight gain. Think candy bars, pastries, and sweetened cereals.
- Fried foods: Fried goodies are loaded with unhealthy fats and calories, making them a double whammy for health. Examples are French fries, fried chicken, and onion rings.
- Sugary beverages: Sipping on these sugary drinks can pile on the pounds and lead to a higher risk of diseases like diabetes. While soda, energy drinks, and sweetened iced tea can refresh a person, especially on hot days, it is best to limit them.
- High-sodium foods: Foods high in sodium can raise blood pressure and increase the risk of heart problems. Canned soups, processed meats like bacon, and fast-food burgers are some examples.
When to use the worksheet
This worksheet can help gain insights into one's dietary habits. Here are four instances when it can be helpful:
- Self-assessment: The worksheet can be used to evaluate current eating habits and help individuals reflect on which areas of their diet need improvement.
- Meal planning: Because the worksheet helps identify healthy and unhealthy foods, clients can adjust their meal planning by incorporating the essential foods into their plates.
- Health challenges: During health challenges or wellness programs, clients can utilize the worksheet to track their progress and stay on track with their goals.
- Nutrition education: Teachers and educators can utilize the worksheet in nutrition education programs to teach students about healthy eating habits.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024, September 12). New CDC data show adult obesity prevalence remains high. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2024/p0912-adult-obesity.html
Washington State Department of Social and Health Services. (n.d.). Nutrition education. https://www.dshs.wa.gov/altsa/program-services/nutrition-education
Commonly asked questions
Completing the worksheet takes about 15 to 30 minutes on average. The time may vary depending on the depth of reflection and discussion involved.
The worksheet is ideal for individuals looking to improve their dietary habits, dietitians and nutritionists working with clients, educators teaching nutrition, and those participating in wellness programs.
The worksheet helps individuals assess their eating habits, make informed food choices, and create a balanced plate. It also supports nutrition education, meal planning, and goal-setting for a healthier lifestyle.

















-template.jpg)