Obesity Chart
Access a free Obesity Chart PDF template. Use this to streamline your clinical documentation.


What is obesity?
Obesity is a complex, chronic disease characterized by the excessive accumulation of body fat that can impair health (World Health Organization, 2024). It differs from being overweight or simply having excess body weight.
Obesity is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, bone health issues, reproductive complications, and certain cancers. It can also significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, making daily tasks such as moving and sleeping more difficult.
The causes of obesity are complex and multifactorial, often involving a combination of obesogenic environments, genetic factors, and social influences. Contributing factors to an obesogenic environment include the high cost of healthy foods, limited access to physical activity opportunities, and a lack of supportive regulatory policies.
Two primary metrics are commonly used to assess obesity: body mass index (BMI) and body fat percentage.
BMI is a measure of body fat based on a person’s weight and height. It is calculated by dividing weight by the square of height. BMI provides a numerical indicator to categorize an individual’s weight status into one of four groups: underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. The World Health Organization defines the following obesity categories based on BMI, according to age (World Health Organization, 2024):
- Adults: BMI ≥ 30
- Children under 5 years: Weight-for-height greater than three standard deviations above the WHO Child Growth Standards.
- Children aged 5-19 years: BMI more significant than two standard deviations above the WHO Growth Reference median.
Body fat percentage measures the proportion of body weight composed of fat tissue (Rai et al., 2023). While BMI provides a general indication of weight status, body fat percentage offers a more precise assessment of body composition and the distribution of excess fat (Rai et al., 2023). Obesity is defined as a body fat percentage of 42% or higher for both men and women (Potter et al., 2024). When determining obesity, it is essential to consider BMI, body fat percentage, and the effects of gender and age.
Waist circumference is also an important indicator for estimating central obesity. A waist circumference greater than 102 cm in men and greater than 88 cm in women indicates abdominal obesity (Ma et al., 2012).
Obesity Chart Template
Obesity Chart Example
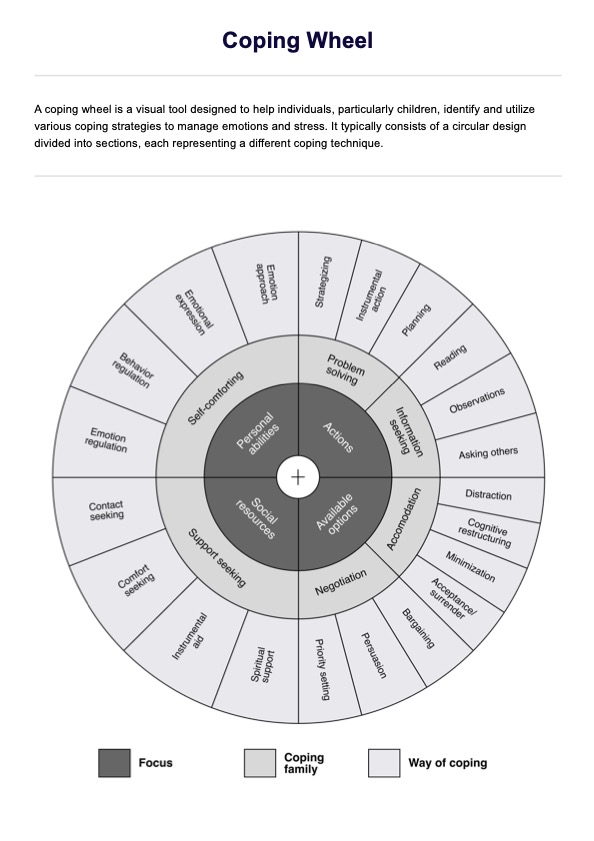
What is an Obesity Chart?
An Obesity Chart is a valuable tool for evaluating and tracking an individual's weight status and overall health. It includes key metrics such as BMI, body fat percentage, and waist circumference. The chart features reference tables for BMI, guidelines for interpreting body fat percentage based on age and gender, and established thresholds for waist circumference. By regularly monitoring these measurements, both individuals and healthcare providers can identify trends, track progress, and make well-informed decisions about effective weight management strategies.
How does our Obesity Chart template work?
Using the Obesity Chart template is a simple and straightforward. Follow these steps to get started:
Step 1: Download the template
Access the Obesity Chart template by clicking "Use a template," allowing you to edit the resource via the Carepatron app. For a PDF copy, choose "Download."
Step 2: Introduction to the template
Familiarize the patient with the obesity chart template, highlighting its purpose as a tool for tracking key metrics related to weight management and health. Emphasize its role in visualizing trends and assessing progress over time.
Step 3: Initial assessment and data entry
If available, conduct an initial assessment to ascertain the patient's current weight status, including BMI and body fat percentage. Accurately record the baseline measurements into the Obesity Chart template, ensuring consistency and precision in data entry.
Step 4: Setting realistic goals
Collaborate with the patient to establish achievable weight management and health improvement goals. Discuss target BMI ranges, desired body fat percentage, and other pertinent benchmarks based on the patient's unique circumstances and aspirations.
Step 5: Regular monitoring and updates
Encourage the patient to regularly monitor weight-related metrics using the Obesity Chart template at designated intervals, such as weekly or monthly check-ins. Review the Obesity Chart with the patient during follow-up appointments to analyze trends and address any setbacks encountered along the way to attaining a healthy weight range.
Benefits of using this Obesity Chart
Utilizing an Obesity Chart offers numerous advantages in managing weight and promoting overall health:
- Facilitates goal setting and monitoring progress: The Obesity Chart serves as a roadmap for setting realistic goals related to weight management. Individuals can establish achievable targets and monitor their progress over time by tracking metrics such as BMI and body fat percentage.
- Raises awareness about obesity-related health risks: The visual representation provided by the Obesity Chart helps individuals comprehend the implications of excess weight on their health. By highlighting obesity-related health risks such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and diabetes.
- Encourages proactive lifestyle changes: The Obesity Chart acts as a catalyst for initiating and sustaining lifestyle modifications. By visually depicting the impact of dietary habits, physical activity levels, and other lifestyle factors on weight management, the chart motivates individuals to adopt healthier behaviors and make informed choices.
References
Ma, W.-Y. ., Yang, C.-Y. ., Shih, S.-R. ., Hsieh, H.-J. ., Hung, C. S., Chiu, F.-C. ., Lin, M.-S. ., Liu, P.-H. ., Hua, C.-H. ., Hsein, Y.-C. ., Chuang, L.-M. ., Lin, J.-W. ., Wei, J.-N. ., & Li, H.-Y. . (2012). Measurement of waist circumference: Midabdominal or iliac crest? Diabetes Care, 36(6), 1660–1666. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc12-1452
Rai, R., Ghosh, T., Jangra, S., Sharma, S., Panda, S., & Kochhar, K. P. (2023). Relationship between body mass index and body fat percentage in a group of Indian participants: A cross-sectional study from a tertiary care hospital. Cureus, 15(10), e47817. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.47817
Potter, A. W., Chin, G. C., Looney, D. P., & Friedl, K. E. (2024). Defining overweight and obesity by percent body fat instead of body mass index. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, dgae341. Advanced online publication. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgae341
World Health Organization. (2024). Obesity and overweight. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
Commonly asked questions
Body mass index (BMI) and body fat percentage should ideally be measured regularly, especially for individuals at higher risk of obesity-related health issues. The frequency may vary based on age, health status, and weight management goals.
Effective weight management strategies include adopting a balanced and healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, monitoring portion sizes, staying hydrated, getting adequate sleep, managing stress levels, and seeking support from healthcare professionals or nutritionists.
While a body mass index (BMI) calculator is a commonly used tool for assessing weight status and identifying excess body fat, it has limitations. BMI does not distinguish between muscle mass and fat mass, so individuals with high muscle mass may have a high BMI despite having little fat and being in good health. Additionally, BMI does not account for variations in body composition, which means it may underestimate the level of obesity in some individuals, particularly those with severe obesity, or overestimate it in others. Therefore, while BMI is valid for a general assessment, it should be considered alongside other measures to calculate BMI more accurately for weight management purposes.



















-template.jpg)