Muscle Test
Discover everything you need to know about muscle testing, examples, and Carepatron's free PDF download to help you better understand this technique.


What is a Muscle Test?
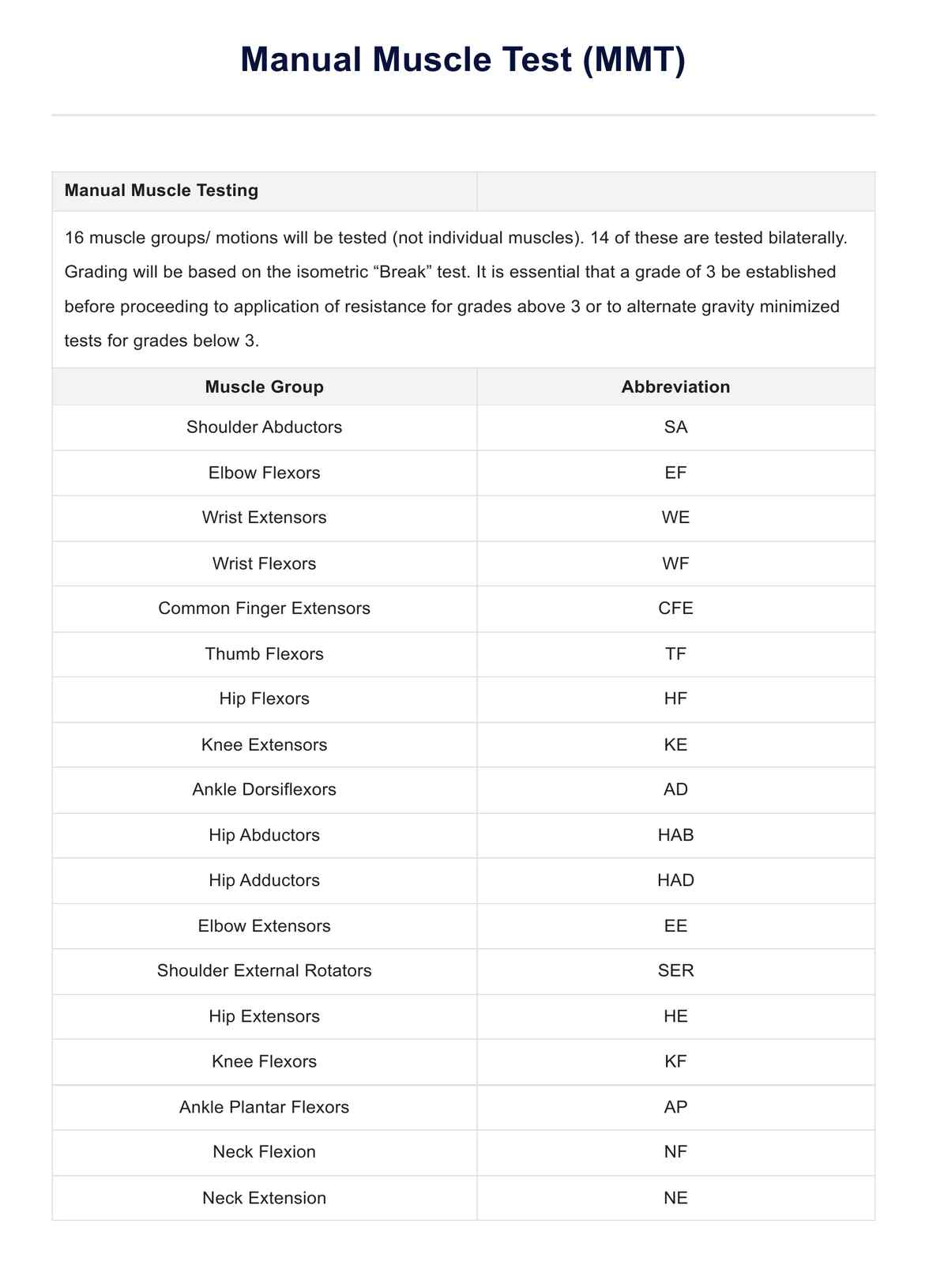
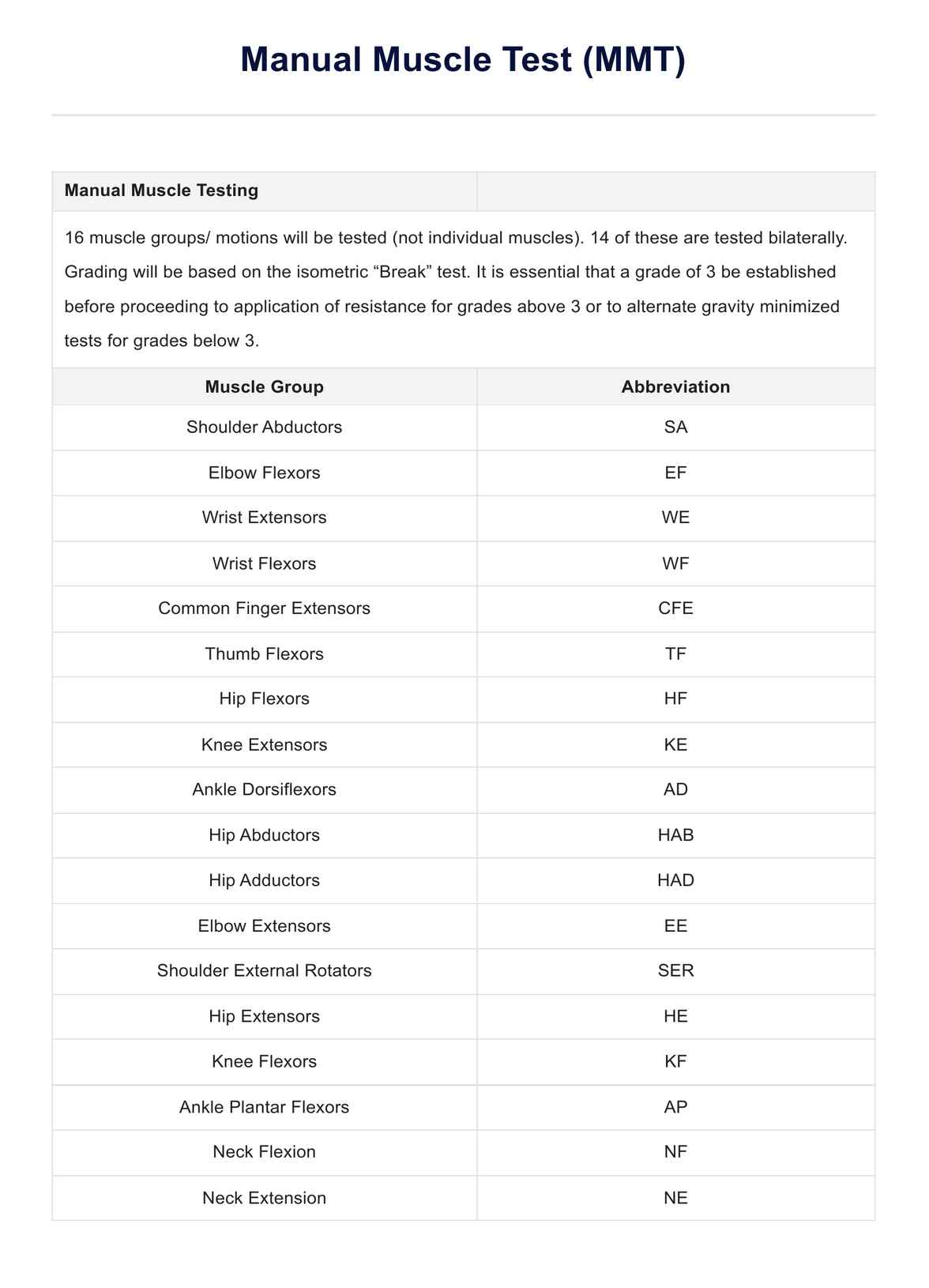
Muscle testing, also known as manual muscle testing (MMT) or applied kinesiology, is a diagnostic technique used to assess the strength and function of muscles in the body. It involves applying gentle pressure to specific muscles while the tested individual resists that pressure. The response of the muscle provides valuable information about its strength, integrity, and potential weaknesses.
This method is rooted in the understanding that muscles respond to neurological signals from the nervous system. When a muscle is functioning optimally, it should be able to resist pressure applied to it. However, if there is weakness or imbalance within the muscle or its associated neurological pathways, it may not be able to withstand the pressure, resulting in a "weak" response during testing.
Muscle testing is utilized in various fields, including physical therapy, chiropractic care, sports medicine, and holistic health practices. Its versatility lies in its ability to provide insights into musculoskeletal issues and potential imbalances within the nervous system and overall body function.
The significance of muscle testing extends beyond mere assessment; it serves as a tool for identifying underlying causes of dysfunction and guiding appropriate treatment strategies. By pinpointing areas of muscle weakness or imbalance, practitioners can tailor interventions to address specific needs through targeted exercises, manual therapies, or lifestyle modifications.
What is the core belief that informs muscle testing?
Muscle testing operates on the principle that muscles respond to neurological signals from the nervous system, reflecting the body's overall health and function. This technique, commonly known as manual muscle testing, is rooted in specific core beliefs that inform its practice and application. Below are some of the fundamental principles guiding muscle testing:
- It operates on the principle that muscles respond to neurological signals from the nervous system, reflecting the body's overall health and function.
- The technique is based on the understanding that manual muscle tests can reveal weaknesses or imbalances within specific muscles, indicating areas of dysfunction or stress.
- Practitioners believe muscle strength testing can provide valuable insights into underlying issues affecting physical well-being beyond what may be apparent through standard clinical assessments.
- Muscle testing is vital in clinical practice for uncovering subtle imbalances and dysfunctions that may contribute to pain, discomfort, or reduced performance.
- The core belief underlying muscle testing is that it works as a reliable diagnostic tool, offering a non-invasive and holistic approach to assessing the body's structural integrity and functional capacity.
Why would a person need to undergo a Muscle Test?
Muscle testing serves various purposes and can benefit individuals in different situations. Below are some common reasons why a person may need to undergo a muscle test:
- To assess muscle strength and function.
- To identify underlying health issues.
- To guide treatment planning.
- To monitor proper treatment and progress.
- To optimize athletic performance.
- To promote overall wellness.
Muscle Test Template
Muscle Test Example
How do professionals conduct muscle testing?
Professionals conduct muscle testing, also known as manual muscle testing (MMT), with a systematic approach to assess muscle strength and function accurately. Here are the steps typically involved in conducting muscle testing:
1. Preparation
Before beginning the muscle testing procedure, the professional explains the process to the individual and ensures they understand what to expect. This step helps establish rapport and ensures the individual feels comfortable and informed throughout the assessment.
2. Positioning
Depending on the assessed muscle groups, the individual undergoing muscle testing is positioned comfortably, sitting or lying down. Proper positioning ensures optimal access to the muscles being tested and allows for accurate evaluation of strength and function.
3. Muscle selection
The professional selects specific muscles or muscle groups to test based on the individual's symptoms, goals, and the areas of concern. Muscle testing can be targeted to assess muscles relevant to a particular activity, injury, or functional limitation.
4. Application of pressure
Using appropriate techniques, the professional applies gentle pressure to the selected muscle or muscle group while instructing the individual to resist the pressure applied. The pressure is gradually increased to assess the muscle's ability to maintain resistance and withstand force.
5. Observation and assessment
During muscle testing, the professional observes the individual's response to the applied pressure, noting any signs of weakness, fatigue, or compensation patterns. Observations may include changes in muscle tone, trembling, or inability to maintain resistance.
6. Interpretation of results
Based on the individual's responses and observations made during muscle testing, the professional interprets the results to identify any areas of muscle weakness, imbalance, or dysfunction. This step involves analyzing the information gathered to understand the underlying factors contributing to the individual's symptoms or limitations.
7. Documentation and communication
After completing the muscle testing procedure, the professional documents the findings, including the muscles tested, observed responses, and any relevant notes or observations. Clear documentation ensures accurate progress tracking and facilitates communication with other healthcare providers or team members involved in the individual's care.
What are the next steps after gathering results?
After gathering the results of a muscle test, several crucial steps follow to ensure that the information obtained is effectively utilized and incorporated into the individual's care plan. Here are the next steps:
1. Analysis and interpretation
The first step after gathering results is to analyze and interpret the findings accurately. This involves reviewing the observed responses during muscle testing and considering the context of the individual's symptoms, goals, and overall health status. Professionals may also compare the results to baseline measurements or normative data to comprehensively understand the individual's muscle function.
2. Identification of imbalances or dysfunctions
Based on the analysis of the results, professionals identify any imbalances, weaknesses, or dysfunctions detected during muscle testing. This step involves pinpointing specific muscles or muscle groups contributing to the individual's symptoms or limitations and assessing how these issues may impact overall movement patterns and functional abilities.
3. Formulation of treatment plan
Once imbalances or dysfunctions are identified, professionals develop a tailored treatment plan to address the underlying issues revealed through muscle testing. This may involve a combination of therapeutic interventions, such as targeted exercises, manual therapies, neuromuscular re-education techniques, or lifestyle modifications designed to restore optimal muscle function and promote overall well-being.
4. Implementation of interventions
After formulating the treatment plan, professionals implement the recommended interventions in collaboration with the individual. This may include hands-on therapy sessions, guided exercise programs, nutritional counseling, stress management techniques, or other modalities aimed at addressing the root causes of muscle imbalances and promoting optimal function of the musculoskeletal system.
5. Monitoring and adjustment
Professionals closely monitor the individual's progress throughout treatment, periodically reassessing muscle function and adjusting the treatment plan as needed. This ongoing monitoring allows for modifications based on changes in the individual's symptoms, goals, or response to interventions, ensuring that the treatment remains effective and aligned with their evolving needs.
You can also strengthen your practice by utilizing the Care Plan Template alongside the Manual Muscle Testing Template. Combining these resources allows you to create comprehensive, personalized care plans while effectively assessing and monitoring muscle strength, ensuring well-rounded support for your clients.
Benefits of muscle tests
Muscle testing offers several benefits, making it a valuable tool for assessing musculoskeletal health and overall well-being. Here are some of the key advantages:
Comprehensive assessment of muscle function
Muscle tests provide a comprehensive evaluation of muscle strength, integrity, and function, allowing practitioners to identify areas of weakness or imbalance within the musculoskeletal system.
Non-invasive diagnostic tool
Muscle testing is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that does not require complex equipment or invasive procedures. It offers a gentle and safe way to assess muscle function, making it suitable for individuals of all ages and health conditions.
Holistic approach to health assessment
Muscle testing takes into account the interconnectedness of the body's systems, including the nervous system, musculoskeletal system, and energy pathways.
Early detection of dysfunction
Muscle testing can detect subtle signs of dysfunction or imbalance before they manifest as overt symptoms or injuries. Early detection allows for proactive intervention and preventive measures to address potential issues and optimize musculoskeletal health.
Personalized treatment planning
Based on the results of muscle testing, practitioners can develop personalized treatment plans tailored to address the individual's specific needs and goals. Treatment strategies may include targeted exercises, manual therapies, nutritional interventions, and lifestyle modifications.
Monitoring progress and recovery
Muscle testing enables practitioners to monitor progress and track changes in muscle function over time. It provides objective feedback on interventions' effectiveness and helps adjust treatment plans as needed.
Why is muscle testing controversial?
Despite its widespread use in various healthcare settings, muscle testing remains controversial among professionals and researchers. One of the primary reasons for this controversy is the lack of robust scientific evidence supporting its efficacy as a diagnostic tool. Schmitt and Cuthbert (2008) argue that muscle testing lacks consistency and reliability, with some studies highlighting inconsistencies in results and questioning its accuracy.
Another point of contention is the subjectivity inherent in muscle testing. Since the technique heavily relies on the practitioner's interpretation, there's potential for bias to influence the results. Critics suggest that the practitioner's expectations, beliefs, and subtle cues from the tested individual may impact the outcomes.
Additionally, Jensen (2012) points out the possibility of the placebo effect playing a role in the perceived benefits of muscle testing. Research has shown that individuals' beliefs and expectations can influence their responses, leading to false positives or exaggerated results.
Moreover, the lack of standardized protocols adds to the controversy surrounding muscle testing. With no universally accepted guidelines for conducting tests, methodologies vary widely among practitioners, making it difficult to compare results across studies. This inconsistency in methodology hinders the ability to draw definitive conclusions about the efficacy of muscle testing.
While some research supports its use in specific contexts, further investigation and standardization of protocols are needed to address concerns and clarify its role in clinical practice.
References
Schmitt, W. H., & Cuthbert, S. C. (2008). Common errors and clinical guidelines for manual muscle testing: “the arm test” and other inaccurate procedures. Chiropractic & Osteopathy, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-1340-16-16
Jensen, A. M. (2012). Muscle testing (kinesiology): panacea or placebo? The Conversation. https://theconversation.com/muscle-testing-kinesiology-panacea-or-placebo-11075
Commonly asked questions
The legitimacy of muscle testing remains a subject of debate in the scientific community, with some studies suggesting potential limitations in its reliability and validity. While some practitioners find value in its use as a diagnostic tool, others question its effectiveness due to inconsistencies and subjective interpretation.
Muscle testing is typically performed by applying gentle pressure to specific muscles while the tested individual resists that pressure. The response of the muscle provides information about its strength, function, and potential weaknesses.
To test yourself for muscle strength and function, select a specific muscle or muscle group and apply gentle pressure while resisting the force with your own strength. Pay attention to any weaknesses or imbalances in the muscle's response, which may indicate areas for further evaluation or intervention.





















-template.jpg)