Nutrition Care Plan
Use Carepatron's free Nutrition Care Plan PDF and provide the right nutritional needs of clients in healthcare settings.


What is a Nutrition Care Plan?
A Nutrition Care Plan is a structured guide designed by healthcare professionals, particularly registered dietitians, to manage and optimize a patient’s nutritional status (Biringer, 2023). This plan is an essential component of the broader nutrition care process, which encompasses nursing assessment, diagnosis, nursing interventions, monitoring, and evaluation of a patient's dietary needs.
When crafting a Nutrition Care Plan, it is important to set clear, measurable goals and desired outcomes. These goals are tailored to the patient’s specific nutritional needs, whether weight loss, recovery from nutritional deficiencies, or maintenance of a healthy body weight. Goals are set collaboratively, involving the patient and considering their personal preferences and lifestyle, ensuring they are both achievable and sustainable.
Moreover, Nutrition Care Plans are vital tools in clinical settings such as hospitals, nursing homes, and community health departments. These plans not only guide the dietary management of patients with various health conditions but also serve as educational resources that empower patients to make informed choices and achieve adequate nutrition. By adhering to a well-constructed plan, you can significantly influence the health outcomes of patients and improve their nutritional intake, making it a fundamental aspect of patient care in diverse medical environments.
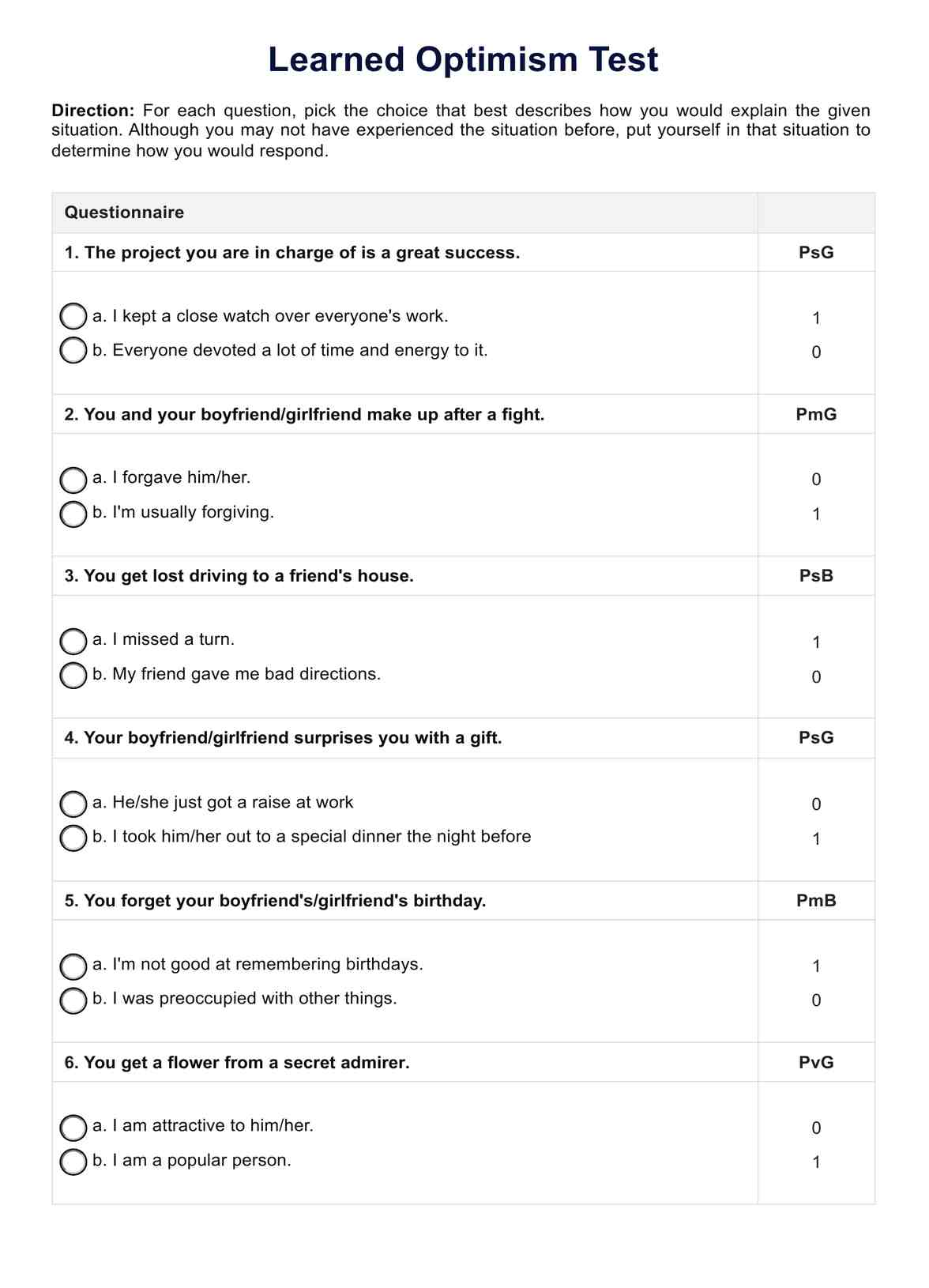
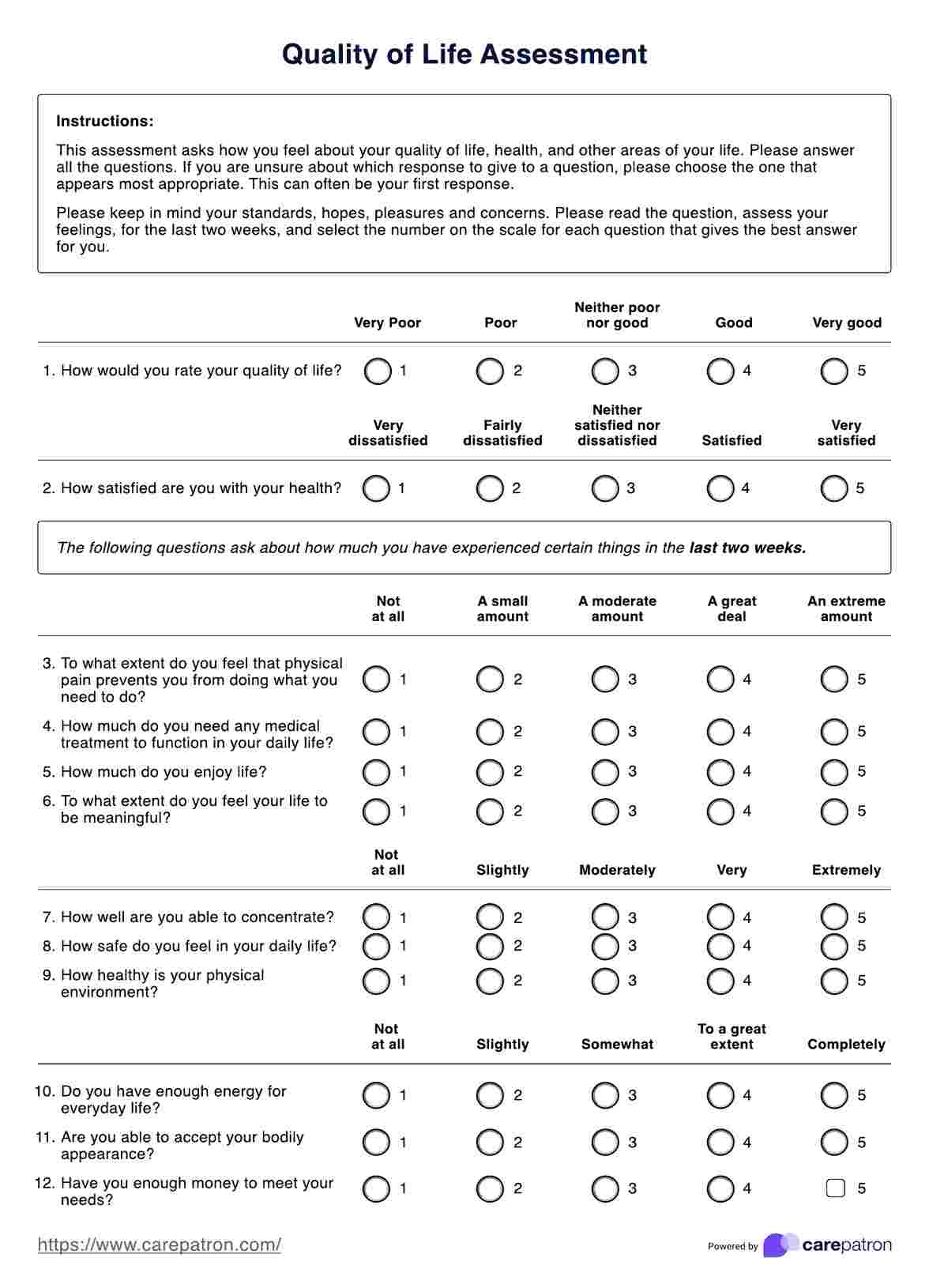
Nutrition Care Plan Template
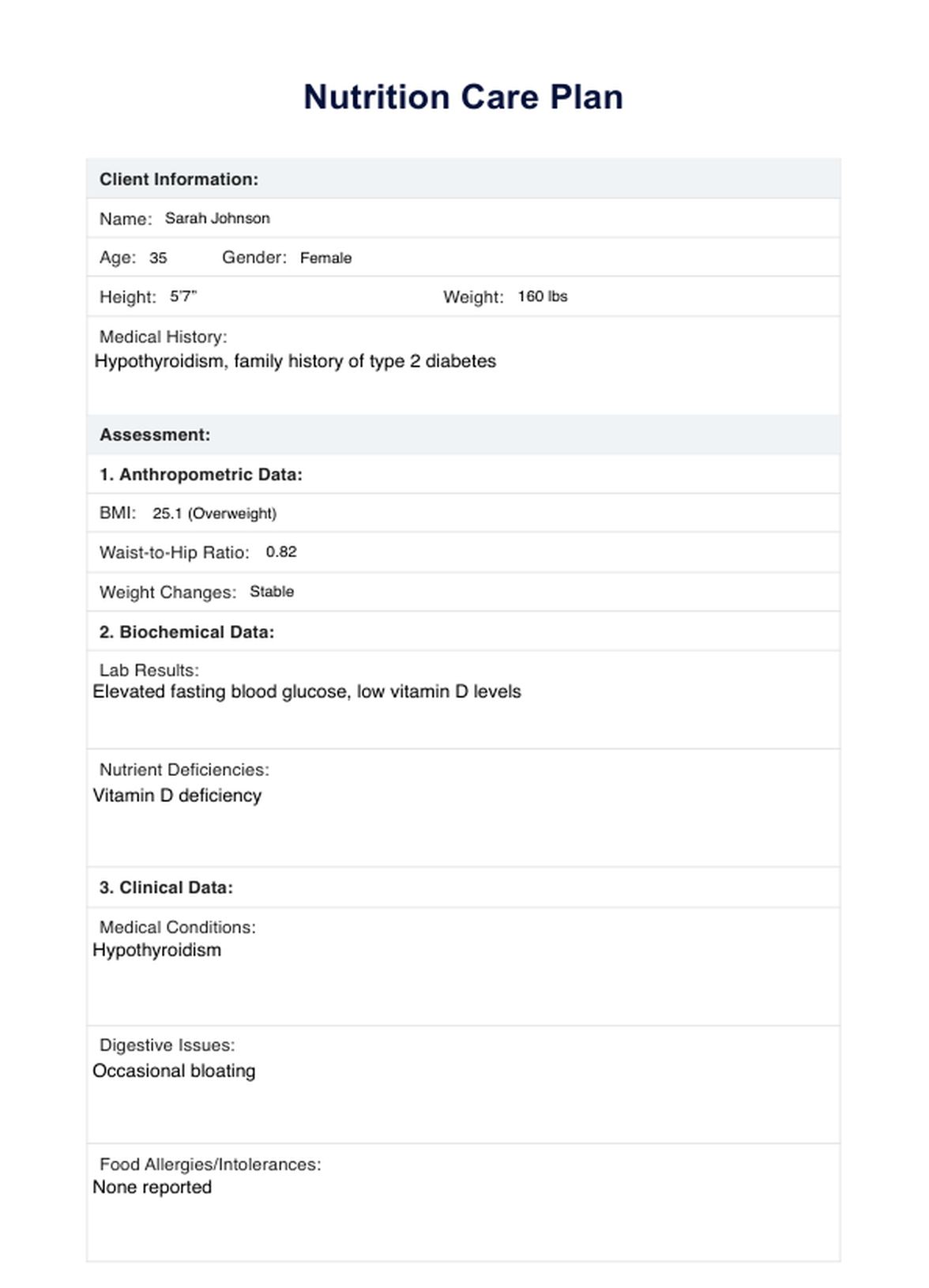
Nutrition Care Plan Example
Nutrition care process
The nutrition care process (NCP) is a standardized, evidence-based approach employed by medical professionals to provide high-quality nutrition care. It is designed to improve patient outcomes through a tailored and systematic method, addressing individual dietary needs and health conditions. This comprehensive process involves several key steps (Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, n.d.).
Nutrition assessment
The first critical step in the NCP is the nutritional assessment. During this phase, registered dietitian nutritionists (RDNs) gather crucial information to form a complete picture of the patient's nutritional status. This includes collecting data on food intake, biochemical data from medical tests, body mass index (BMI), and other anthropometric measurements. RDNs also consider factors like disease prevention needs and cultural influences on dietary habits. This thorough evaluation helps identify any nutritional risks or deficiencies, setting the stage for accurate diagnosis and effective intervention.
Nutrition diagnosis
After the assessment, the RDN synthesizes the collected information to formulate a nutritional diagnosis. This diagnosis pinpoints the specific nutritional issues affecting the patient, such as serum protein decreases or other abnormalities identified during the assessment. It clearly names the problem, allowing for targeted and effective interventions that address the root causes of the nutritional issues.
Nutrition interventions
With a clear diagnosis and set goals, the RDN develops a nutrition intervention plan. This plan may include dietary modifications, nutritional support, and nutrition education tailored to the patient's specific needs and diagnosis. Interventions are designed to directly address the etiology of the diagnosed nutrition problem, using evidence-based strategies that can include meal planning, supplementation, or therapeutic diets.
Nutrition monitoring and evaluation
The final step in the NCP is ongoing monitoring and evaluation. This continuous process allows the RDN to outline steps for tracking the patient’s progress toward achieving their nutritional goals. Regular reassessments are conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the intervention, with adjustments made as necessary. This step ensures that the nutrition care provided remains relevant and effective, adapting to changes in the patient's condition or response to the intervention.
How does it work?
Using the Nutrition Care Plan from Carepatron is straightforward and efficient, and it is designed to enhance patient care by medical professionals. Here’s a simple breakdown of the steps involved in implementing this tool in medical practice:
Step 1: Access and use the template
Click "Use template" to instantly access and personalize the Nutrition Care Plan within the Carepatron app. This ready-to-use template includes editable fields and practical examples to streamline the documentation process. If you want a ready-to-print PDF copy, click "Download."
Step 2: Fill out the care plan and explain it to the patient
Fill out the template and introduce the Nutrition Care Plan to the patient. Explain its purpose and how it forms part of their overall health strategy. Discuss the specifics of the Nutrition Care Plan with the patient, detailing how each part of the plan is designed to address their unique dietary and health needs. It would be much better if they are with their family members or caregivers, too, so they could be involved in the process.
Step 3: Provide further patient education and next steps
Finish the consultation by providing the patient with educational resources and clear instructions on the next steps. This ensures they feel supported and informed throughout their treatment journey.
Benefits of using this care plan
The Nutrition Care Plan is an invaluable tool for medical professionals, enhancing the effectiveness of nutritional management across various patient scenarios. This plan not only deepens your client's nutrition knowledge but also streamlines the nutrition care process step by step. By using this plan, you can systematically identify and address nutrient deficiencies and imbalances through detailed nutrition screening and assessment techniques.
For patients with specific needs, such as those managing heart disease, eating disorders, or requiring weight gain, the care plan helps you tailor interventions based on thorough client history and laboratory tests. This ensures that all aspects of a patient's nutrition are considered, from macro- and micronutrient intake to overall eating patterns. Furthermore, the plan facilitates better coordination within the interdisciplinary team, enabling dietitians, doctors, and other healthcare team members to work together more effectively.
Ultimately, this structured approach to nutritional care helps prevent and manage health conditions more efficiently, ensuring patients receive the most appropriate nutrition interventions based on their individual health status and dietary needs.
References
Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. (n.d.). The nutrition care process (NCP). Electronic Nutrition Care Process Terminology (eNCPT). https://www.ncpro.org/nutrition-care-process
Biringer, K. (2023). Nutritional care planning: A comprehensive approach to health and wellness. Clinical Nutrition and Hospital Dietetics, 43(4), 1–2. https://doi.org/10.12873/0211-6057.43.04.212
Commonly asked questions
An effective Nutrition Care Plan is precisely tailored to the individual's specific health needs and dietary requirements, ensuring comprehensive coverage of all nutritional aspects. It relies on accurate and thorough assessments, including client history, laboratory tests, and a detailed examination of dietary habits. Consider checking out Nutrition Care Plan examples to get an idea of how they're crafted.
The Nutrition Care Plan process involves a systematic approach that includes assessing the patient's nutritional status, diagnosing nutrition-related health issues, planning and implementing interventions, and monitoring and evaluating progress over time. When planning one, consider also diet restrictions and patient allergies. This ensures that all aspects of patient care are addressed, leading to more effective management of dietary needs.
Implementations of an NCP typically involve creating a detailed action plan that includes dietary adjustments, education, and support systems tailored to the patient's conditions, such as managing diabetes or heart disease. It also requires ongoing collaboration with the interdisciplinary healthcare team to ensure that interventions are appropriate and effective in achieving desired health outcomes and providing optimal care.













-template.jpg)