Diet Plan for Obesity
Explore effective obesity management with our Diet Plan for Obesity, tailored for health professionals to guide patients toward sustainable weight loss.


What is obesity?
Obesity is a medical condition characterized by excessive body fat that poses a health risk. A person is considered obese when their Body Mass Index (BMI)—a calculation derived from their weight and height—exceeds 30. It's not merely a concern about physical appearance but a significant health issue that increases the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, certain cancers, and more.
It became recognized as a health risk in the 20th century, with the World Health Organization (2024) now classifying it as a global epidemic. This shift reflects a deeper understanding of the health implications of excess weight gain and the complex interplay of factors contributing to obesity.
What causes it?
Obesity's causes are multifaceted, including genetic predispositions, lifestyle choices, environmental factors, and psychological conditions. Modern diet and lifestyle patterns, characterized by high-calorie diets and physical inactivity, significantly contribute to the rising prevalence of obesity. Recognizing obesity as a health condition necessitates a comprehensive approach to management and prevention, focusing on dietary changes, increased physical activity, and sometimes medical interventions.
What are its symptoms?
The main symptom of obesity is having a high amount of body fat, especially around the waist. Some other common symptoms and signs of obesity include:
- Excess body fat, especially around the waist
- Back pain
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Heavy sweating
- Difficulty performing physical tasks
- Snoring and breathing problems
- Joint and back pain
- Low confidence and self-esteem
- Feeling isolated
Obesity can also lead to psychological issues like depression that may affect relationships and quality of life. The excess weight puts additional stress on the body, leading to problems like breathlessness, insomnia, and reduced fertility. That said, weight loss diets are important to combat obesity.
Diet Plan for Obesity Template
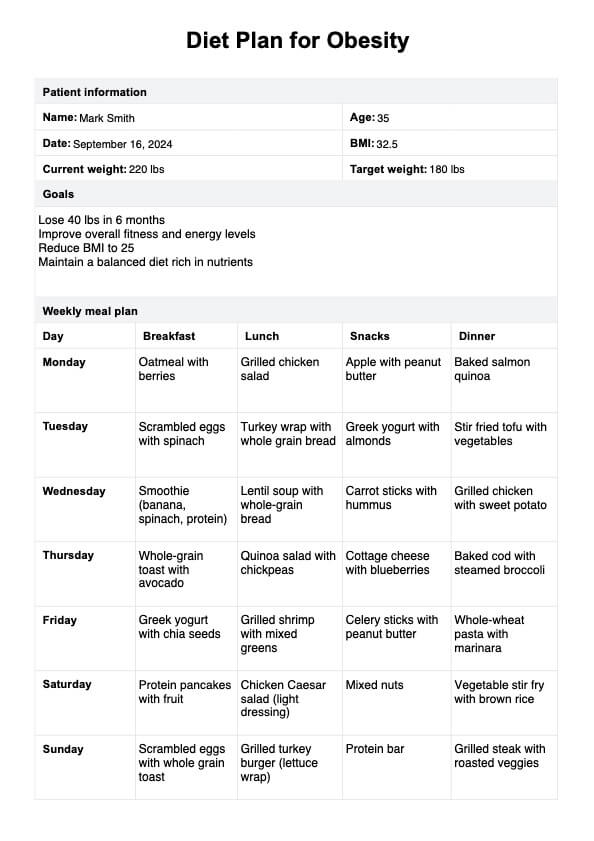
Diet Plan for Obesity Example
What is a diet plan?
A diet plan is a structured approach to eating that aims to meet specific health goals, such as weight loss, weight management, or improving overall nutrition. It involves determining the appropriate types and amounts of healthy foods to consume regularly to provide the body with the necessary nutrients while controlling calorie intake. Some of the most common Diet Plan for Obesity is a Mediterranean diet which includes fewer calories but more healthy fats.
Diet planning is crucial for resolving and preventing several medical conditions, including obesity, diabetes, osteoporosis, and hypertension. Weight management together with a healthy meal plan reduces the metabolic risk factors, leading to a sustainable weight loss program that can go in the long run.
A well-designed diet plan should be balanced, providing adequate amounts of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and dietary fat) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) to support optimal health. The acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR) recommends that daily caloric intake should consist of 45-65% carbohydrates, 20-35% lipids, and 10-35% proteins (Lee et al., 2015). Additionally, according to the Institute of Medicine (US) Subcommittee on Interpretation and Uses of Dietary Reference Intakes (2012), the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) provide guidelines for nutrient intake based on age, gender, and life stage to ensure adequate nutrition.
How to use this Diet Plan for Obesity
This plan is designed to aid health professionals in guiding their patients toward sustainable weight loss and improved health through nutritional adjustments. Here's how to effectively utilize the diet plan:
Step 1: Download the template
Click "Use Template" to utilize the Diet Plan for Obesity template via the Carepatron app. You can also get a PDF version by selecting the "Download" button.
Step 2: Complete the fields
Fill in the required fields including patient information, current weight, and health goals. This will help tailor the diet plan to meet the specific needs of each individual.
Step 3: Create a weekly meal plan
Use the template to tailor a weekly meal plan based on the patient's needs. Make sure to include a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to ensure a balanced diet. Encourage patients to track their meals and adhere to the plan for best results.
Step 4: Write notes as needed
Use the "Additional notes" section to add any extra information or advice for the patient. This can include tips for managing cravings, incorporating exercise, or addressing any food allergies or sensitivities.
Step 5: Review and revise as needed
Regularly review the diet plan with the patient and make necessary revisions based on their progress and feedback. Encourage open communication between you and your patient to ensure that the plan is effective and sustainable.
Other considerations
When embarking on a Diet Plan for Obesity , it's crucial to take a holistic approach beyond simple dietary changes. Here are some key considerations to ensure the plan is comprehensive, sustainable, and tailored to individual needs:
Address underlying health conditions
Many individuals with obesity also have coexisting health conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, or heart disease. It's essential to manage these conditions alongside weight loss efforts. Ignoring underlying health issues can hinder weight loss progress and exacerbate health risks.
Consider psychological factors
Obesity and eating habits are often closely linked with psychological factors, including stress, anxiety, and emotional eating. Without addressing the psychological drivers of eating behavior, individuals may find it challenging to maintain dietary changes in the long term.
Nutritional adequacy
Ensuring the diet plan provides all essential nutrients is critical for overall health and well-being. A diet lacking specific vitamins, minerals, or other nutrients can lead to deficiencies and health problems. Each meal and snack should be balanced to include a variety of nutrients necessary for good health.
Personal preferences and lifestyle
Diet plans should be adaptable to fit personal preferences and lifestyles. This includes considering food preferences, cooking skills, budget, and time constraints. A plan that doesn't consider these factors will unlikely be followed for long. Customizing the diet plan ensures it is enjoyable and fits seamlessly into daily life.
Weight loss during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Special considerations should be taken for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding. Weight loss efforts during these times should be approached with caution and under medical supervision to ensure the mother's and child's health and well-being. The focus should be on maintaining a balanced, nutrient-rich diet rather than on calorie restriction or weight loss.
Medications
Some medications can affect weight or interact with diet changes. Discuss any medications you take with a healthcare provider to understand their impact on weight and dietary considerations. Adjustments to medications may be necessary as part of the diet plan.
Foods to include in an obesity diet plan
When creating an obesity diet plan, healthy eating is important. It's essential to include nutrient-dense foods that support healthy weight management. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, helping to reduce calorie intake without compromising on nutrition. Incorporating fruit juices in moderation, especially those low in added sugars, can offer additional vitamins while still aligning with a balanced dietary intake.
Opt for whole grains like brown rice over refined grains to improve digestion and provide longer-lasting energy. Healthy fats, such as those from olive oil, are beneficial in moderation, and lean protein sources like chicken breast are excellent options for a low carbohydrate diet. Effective meal planning and limiting processed food intake are crucial to creating healthy meals that sustain your weight loss program.
Foods to avoid in the obesity diet plan
In an obesity diet plan, it's important to avoid foods that contribute to excessive weight gain and poor health. Limiting processed foods unhealthy fats is crucial, as these can lead to increased fat accumulation and elevated cholesterol levels. Avoiding processed meats and minimizing the consumption of red and processed meats is highly recommended, as they are often high in saturated fat, which negatively impacts heart health and increases overall fat intake.
Additionally, foods rich in saturated fat—such as fried items, full-fat dairy products, and certain baked goods—should be reduced or eliminated to support a healthier diet. These foods contribute to excess calorie intake and hinder weight loss efforts, making it harder to achieve your goals in a balanced obesity diet plan.
References
Institute of Medicine (US) Subcommittee on Interpretation and Uses of Dietary Reference Intakes, & Institute of Medicine (US) Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes. (2024). Introduction to dietary planning. National Institutes of Health; National Academies Press (US). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK221366
Lee, E., Choi, J., Ahn, A., Oh, E., Kweon, H., & Cho, D. (2015). Acceptable macronutrient distribution ranges and hypertension. Clinical and Experimental Hypertension, 37(6), 463–467. https://doi.org/10.3109/10641963.2015.1013116
World Health Organization. (2024). Obesity. https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity#tab=tab_1
Commonly asked questions
Adopt a healthy diet rich in whole foods, increase physical activity, and ensure adequate hydration. Consistency and a focus on lifestyle changes are essential to maintain a healthy weight.
The best low-fat diet plan is personalized, focusing on reducing calorie intake through balanced portions of whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats while incorporating regular physical activity.
Diet is crucial because it determines your calorie intake. Eating nutrient-dense, lower-calorie foods helps create a calorie deficit, essential for weight loss.
Yes, meal planning helps control calorie intake, ensure nutritional balance, and reduce the temptation to choose unhealthy food.