Head To Toe Assessments
Learn how healthcare professionals perform a thorough Head to Toe Assessment of patients and use the results to assess a patient's health state.


What is a Head-to-Toe Assessment?
As a healthcare professional, a Head-to-Toe Assessment is vital to a patient's physical examination. This comprehensive evaluation of the body systems, often called a complete health assessment, allows you to assess and monitor your patient's overall health status and all the body systems, detect potential health issues, and create individualized care plans.
A Head-to-Toe Assessment provides healthcare professionals with a comprehensive understanding of their patient's health history and status, which is crucial for developing effective care plans. This initial assessment allows you to identify potential health problems, monitor progress, and intervene early, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
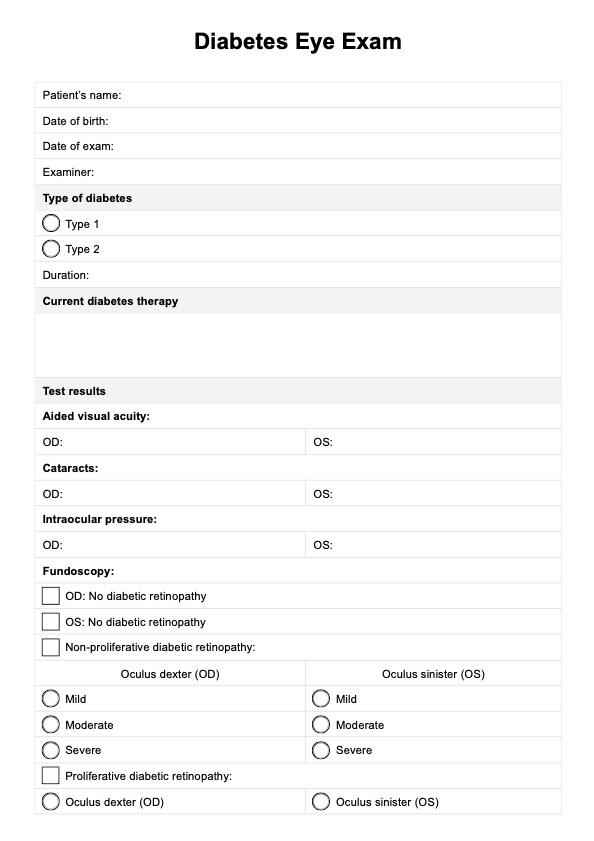
Head To Toe Assessments Template
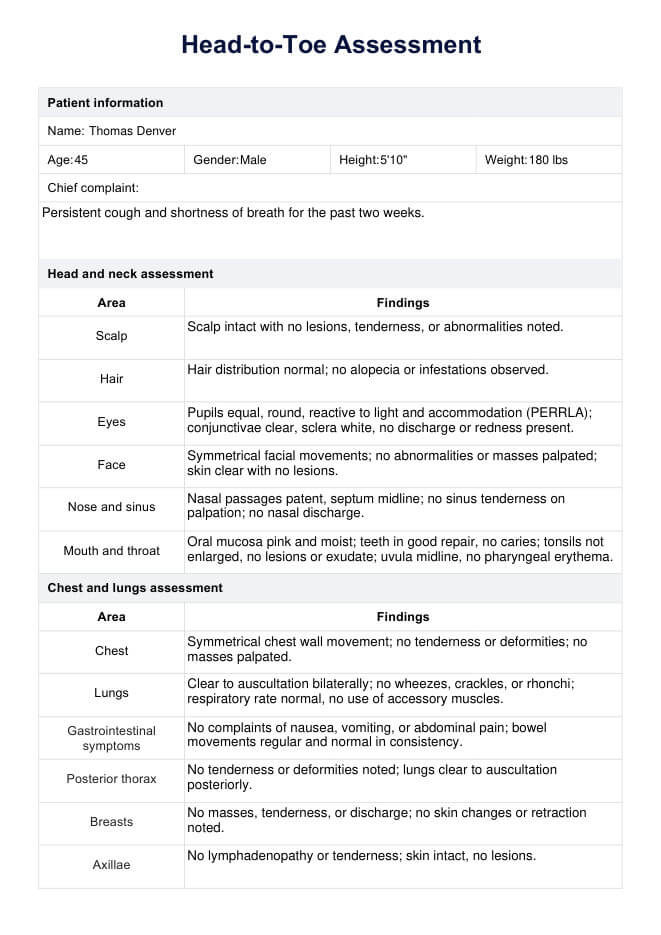
Head To Toe Assessments Example
How to conduct a Head-to-Toe Assessment
Performing a Head-to-Toe Assessment is essential to a healthcare professional's job. Conducting a thorough and accurate physical assessment ensures that the patient receives the appropriate care and treatment.
Here, we'll go through the physical examination process and provide a step-by-step approach to performing a physical examination or Head-to-toe Assessment.
Step 1: Gather patient information and vital signs
Begin by gathering patient information, such as the patient's name, age, gender, height, weight, occupation, and the patient's chief complaint on the template. Record this information in the “patient information” section of the form. Additionally, include the patient's medical history to ensure a comprehensive understanding of their conditions, medications, allergies, and recent tests.
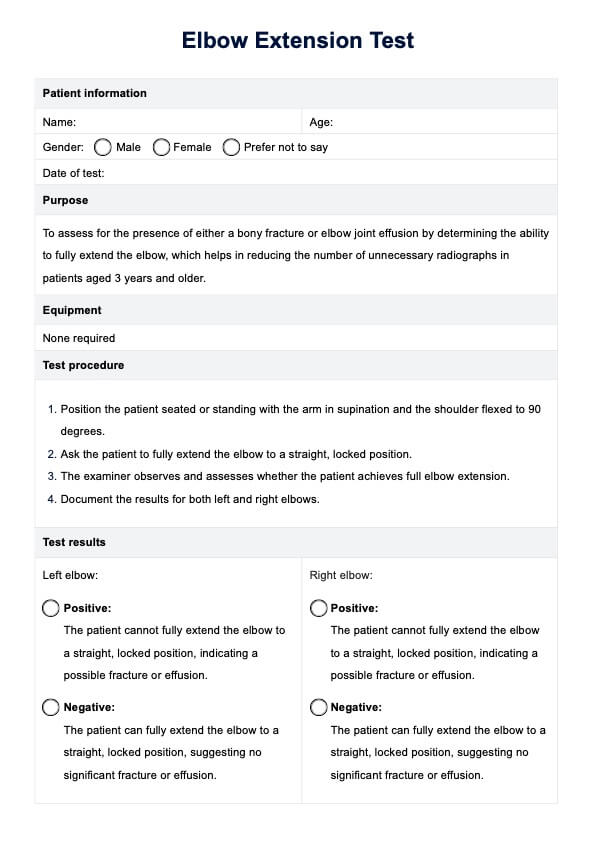
Step 2: Head and neck assessment
Start the assessment with the head and neck. Inspect the scalp for any signs of injury or abnormalities. Check the hair for cleanliness and grooming. Inspect the face for symmetry and signs of lesions or asymmetry. Check the eyes for clarity and reaction to light. Examine the ears for any signs of abnormalities. Palpate the lymph nodes in the head and neck for any swelling or tenderness caused by an enlarged thyroid gland. Inspect the nose for signs of congestion. Check the mouth and throat for any signs of infection. Document findings in the corresponding section.
Step 3: Chest and lungs assessment
Proceed with the chest and lungs assessment. Inspect the chest for standard shape and symmetry. Listen to the lungs using a stethoscope for any random or unusual sounds, such as wheezes or crackles. Take note of observations in the "chest and lungs assessment" section.
Step 4: Cardiovascular system assessment
Evaluate the cardiovascular system for any possible arterial or venous disease. Listen to the heart for murmurs or gallops. Check the peripheral pulses for strength and equality bilaterally. Examine the lower extremities for any signs of edema. Record your findings in the "cardiovascular system assessment" section of the form.
Step 5: Peripheral vascular system assessment
Gather information regarding the client's lifestyle and health factors that could potentially impact peripheral vascular health. Check for skin texture or coloration of the hands and arms. Observe the size and venous pattern of the arm. Inspect the distribution of hair in the leg area.
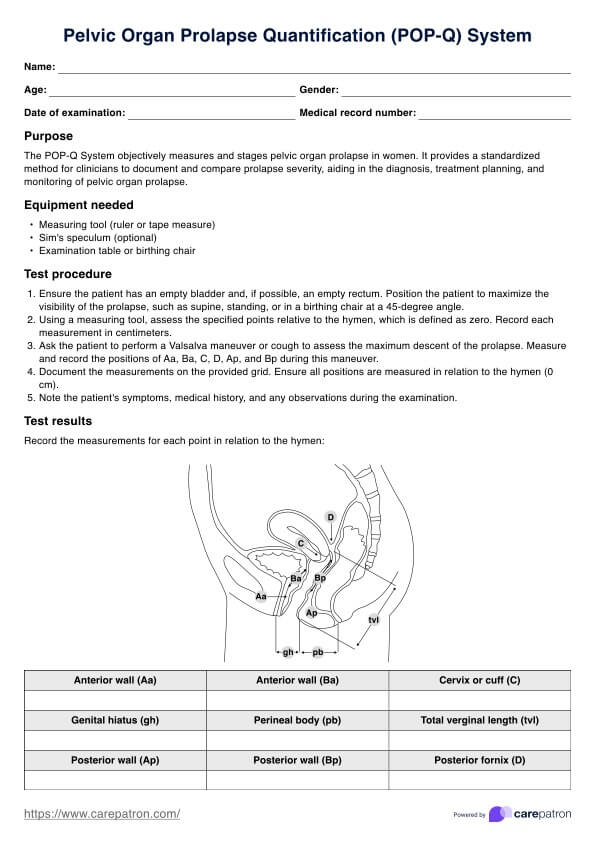
Step 6: Abdominal assessment
Continue with the abdominal assessment. Palpate the abdomen for any tenderness or distension. Listen to the bowel sounds for normalcy. Write down your findings in the "abdominal assessment" section of the form.
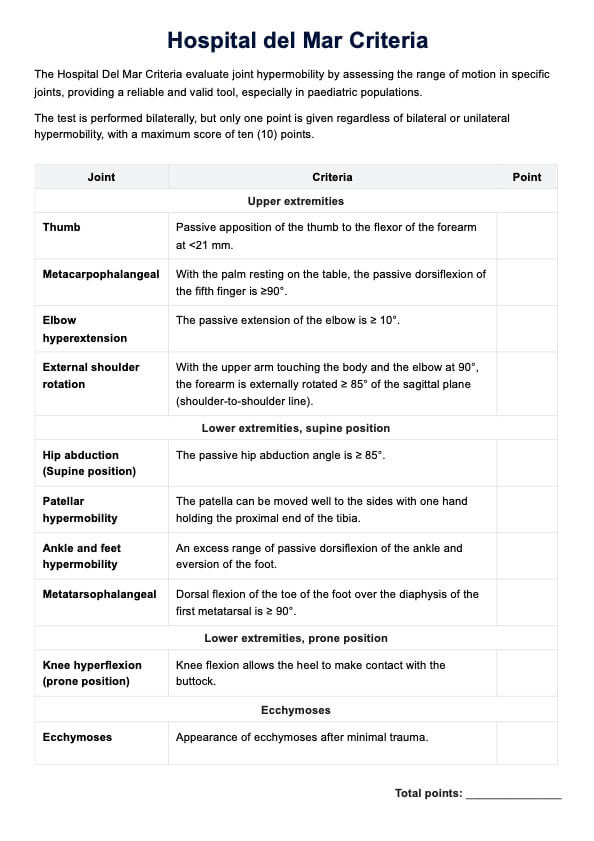
Step 7: Musculoskeletal system assessment
Evaluate the musculoskeletal system. Observe the gait and check for any signs of limping or difficulty walking. Check the range of motion in all joints and observe for any tenderness or deformities. Record your findings in the "Musculoskeletal system" section of the form.
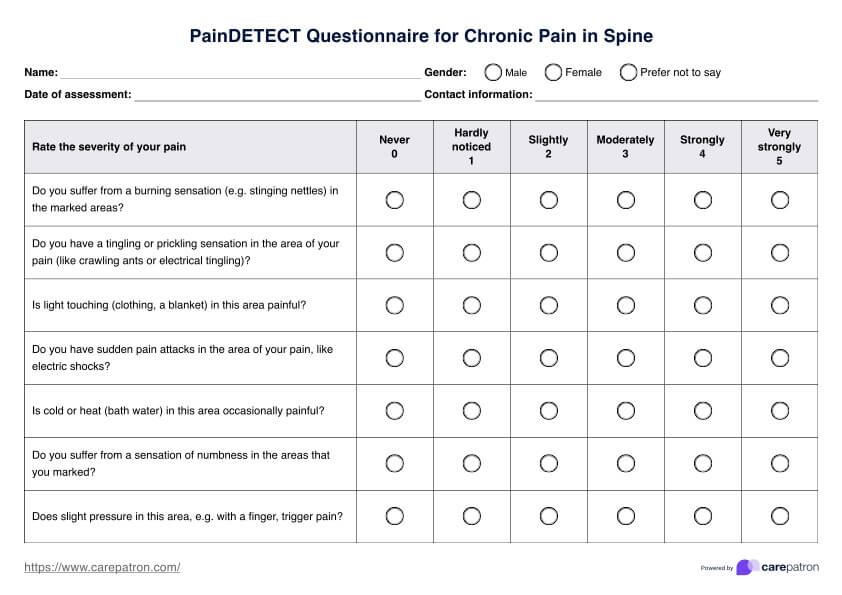
Step 8: Neurological system assessment
Proceed with the neurological assessment. Evaluate the patient's mental status and alertness. Check the cranial nerves and reflexes. Document your findings in the “neurological system” section of the form.
Step 9: Genitourinary system assessment
Finally, evaluate the genitourinary system. Inspect the genital area for any signs of infection or abnormalities. Check the urine test for normalcy. Record your findings in the "Genitourinary System" section of the form.
Step 10: Document assessment findings
Review the assessment notes, discuss any abnormal findings or concerns with the patient, and develop a care plan as necessary. You can also refer to the Care Plan Template to outline specific interventions or identify a focused assessment, set goals, and track progress toward improving the patient's health and well-being. This structured approach ensures comprehensive and personalized care management for better health outcomes.
Using a Head-to-Toe Assessment Checklist
As you conduct the Head-to-Toe Assessment, you may want to use a Head-to-Toe Assessment Checklist. These checklists serve two purposes: they are a refresher for healthcare professionals and ensure all crucial steps are taken to assess the patient's health status by allowing them to document their progress.
Using the checklist is straightforward. Nurses and physicians with this resource simply need to check off or click on the corresponding checkboxes for each examination, indicating completion of the body system assessment.
When should you use this Head-to-Toe Assessment template?
Healthcare professionals typically use this Head-to-toe Assessment during the initial evaluation of a patient. Here are three situations where it may be necessary to use this assessment:
- In emergency situations: When a patient is brought to the emergency department, a Head-to-Toe Assessment can help identify any life-threatening conditions that require immediate intervention.
- Before a medical procedure: Before any medical procedure, healthcare professionals must thoroughly assess the patient to identify any potential risks or complications that may arise during the operation.
- Regular check-ups: Regular check-ups are an essential part of preventative healthcare. A Head-to-Toe Assessment can help you identify any changes in the patient's health that may require further attention or treatment.
Who can use these printable Head-to-Toe Assessments?
Various healthcare professionals use Head-to-Toe Assessment to evaluate a patient's overall health, whether in a hospital, clinic, or other healthcare settings. Here's a list of specific healthcare professionals who may benefit from having a copy of the assessments:
- Nurses: Nurses are often responsible for conducting initial assessments of patients, and a Head-to-Toe Assessment is a crucial part of this process.
- Physician assistants: Physician assistants often work alongside doctors and can perform many of the same duties, including conducting patient assessments.
- Physical therapists: Physical therapists work with patients to help them improve their mobility and reduce pain.
- Occupational therapists: Occupational therapists work with patients to help them perform daily tasks and improve their quality of life.
- Emergency medical technicians (EMTs): EMTs are often the first healthcare professionals to assess a patient in an emergency situation.
Commonly asked questions
To conduct a Head-to-Toe Assessment, gather patient information, then work through a standardized physical examination from head to toe to assess the patient's overall health and identify any potential issues.
The Head-to-Toe Assessment measures a patient's overall physical health and identifies potential issues requiring further examination or treatment.
To document a Head-to-Toe Assessment, healthcare professionals should record their findings clearly, concisely, and organizedly, typically using a standardized checklist or form. As you conduct the assessment, systematically document observations for each body system, including any abnormalities or concerns, while maintaining objectivity and avoiding personal opinions. Ensure that your notes are comprehensive enough to facilitate effective communication among the healthcare team and adhere to agency policies for documentation.