Common examples include medication reconciliation checklists, fall prevention checklists, and infection control checklists. During surgery, implementing protocols such as those outlined in the WHO Surgical Safety Checklist can significantly reduce the incidence of errors in the operating room.
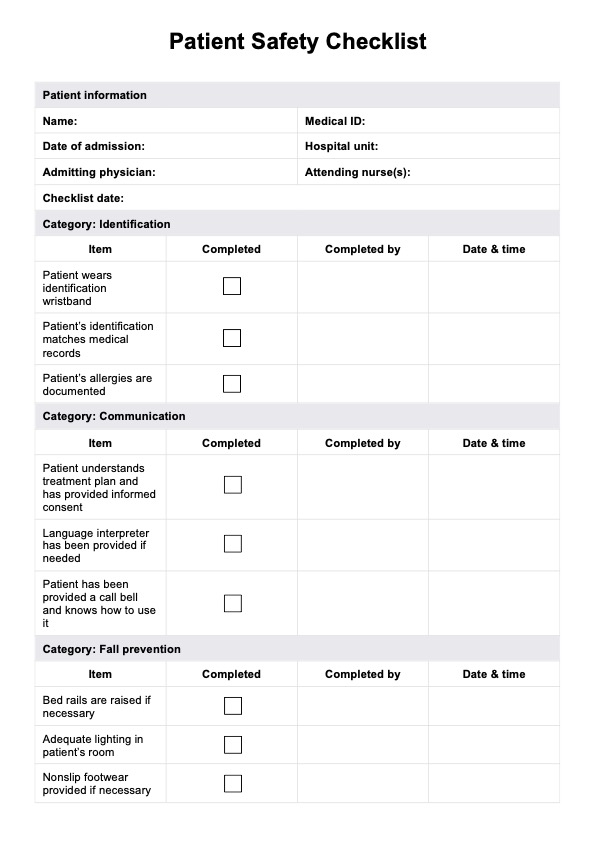
Patient Safety Checklist
Enhance safety in healthcare processes and ensure adherence to essential protocols with the Patient Safety Checklist.
Use Template
Patient Safety Checklist Template
Commonly asked questions
Patient safety checklists promote a safety culture by standardizing procedures, encouraging communication among healthcare teams, and emphasizing the importance of systematic error prevention.
While initially developed for hospital settings, Patient Safety Checklists can be adapted and utilized in various healthcare settings, including clinics, ambulatory care centers, and long-term care facilities, to enhance safety across healthcare environments.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











