Blood Tests for Lupus
Download a free Blood Tests for Lupus template. Learn the various types of tests used to diagnose this disease.


What is lupus?
Lupus is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, causing inflammation, pain, and damage in various parts of the body. It's characterized by its diversity in symptoms, which can range from mild to life-threatening. The exact causes of lupus remain unclear, but it's believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and possibly hormonal factors.
Blood Tests for Lupus Template
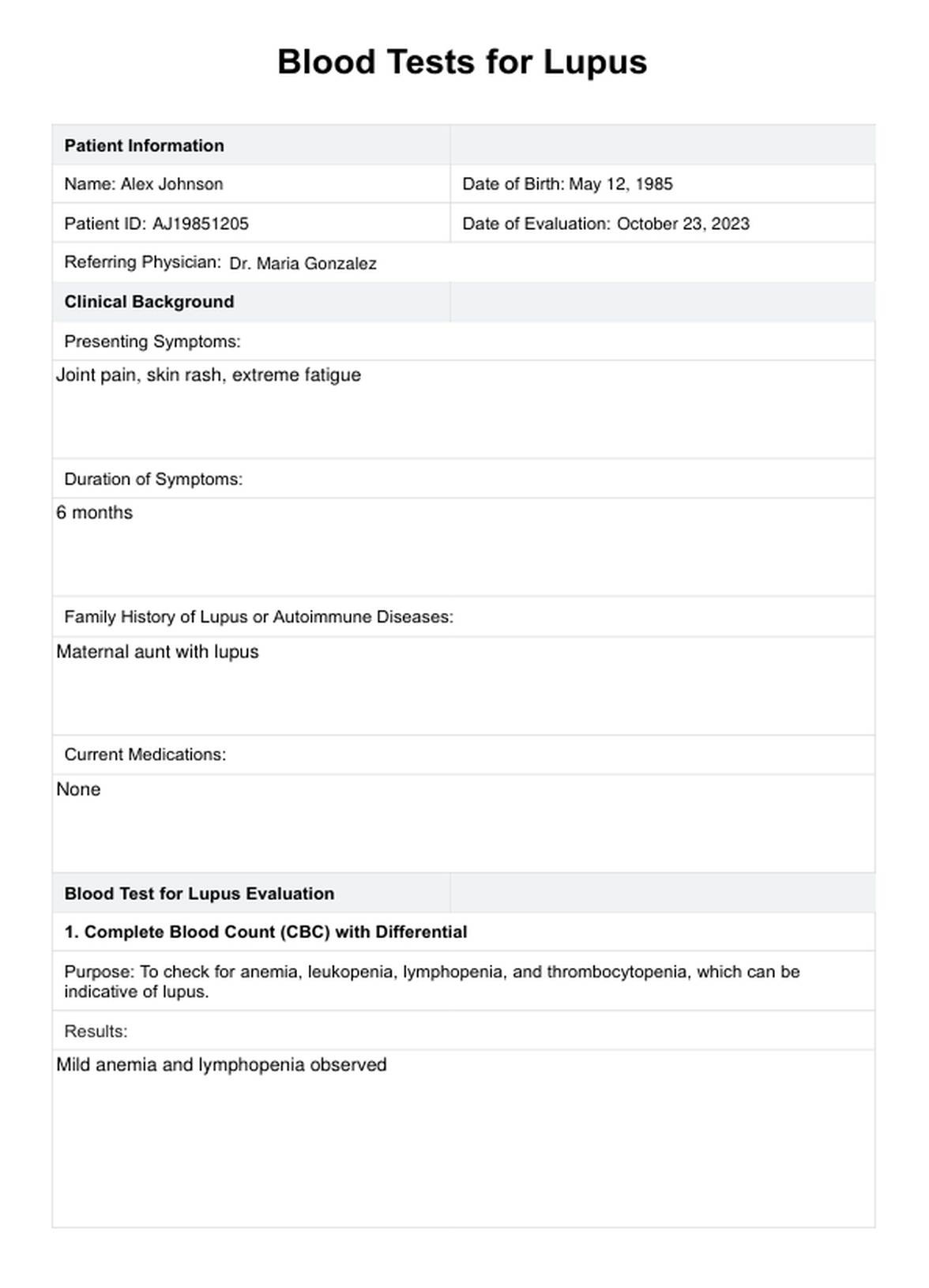
Blood Tests for Lupus Example
What are the characteristics of lupus?
The characteristics of lupus are complex and vary widely among individuals, making it a challenging disease to diagnose and manage. At its core, lupus is marked by periods of illness, known as flares, during which lupus symptoms worsen significantly, interspersed with periods of wellness or remission, when symptoms may improve or disappear entirely. Commonly reported symptoms include joint pain and stiffness, which can be debilitating, and distinctive skin rashes, notably the butterfly rash across the cheeks and nose. Fatigue is another prevalent symptom, often profound and limiting daily activities. Fever, unexplained and recurrent, may also signal the presence of lupus.
Beyond these more visible manifestations, lupus's systemic nature can affect multiple body systems. The skin and joints are frequently involved, but the disease can also impact the kidneys, leading to nephritis, which can be serious and require specific treatment. Neurological complications are possible, including headaches, dizziness, and even seizures or strokes in severe cases. The cardiovascular system can be affected, with an increased risk of heart disease and inflammation of various heart components. The lungs and respiratory system may also experience complications, such as pleuritis, leading to breathing difficulties.
The range and severity of symptoms can vary greatly, not just from person to person but also over time within the same individual. This variability, along with lupus's ability to mimic other conditions, underscores the need for careful and comprehensive evaluation for accurate diagnosis and management. Understanding the full spectrum of lupus characteristics is crucial for healthcare providers to deliver effective, personalized care and for patients to navigate the challenges of living with this chronic autoimmune disease.
Causes of lupus
The causes of lupus are not fully understood but involve a complex interplay of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers such as sunlight, infections, and possibly certain medications or hormones. These factors can initiate or exacerbate the autoimmune response in susceptible individuals.
How does a professional conduct a lupus diagnosis?
A lupus diagnosis is challenging due to the variety of its symptoms, which can mimic other diseases. Professionals rely on medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests, including blood and urine tests, to diagnose lupus. A positive ANA (antinuclear antibody) test is common in people with lupus but must be considered alongside other diagnostic criteria due to its presence in other autoimmune diseases.
Examples of Blood Tests for Lupus
Here are some tests used for lupus:
Complete blood count (CBC)
The CBC is a fundamental blood test that evaluates the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. In lupus, it may reveal anemia (low red blood cell count), leukopenia (low white blood cell count), or thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), indicating the disease's impact on the blood.
Antinuclear antibody (ANA) test
This test detects antibodies that target the nucleus of the cells, common in autoimmune diseases. A positive ANA test is often the first indicator of lupus, although not exclusive to it.
Anti-double stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) test
Specific to lupus, a positive anti-dsDNA test indicates a high likelihood of the disease. This test is often used to confirm a diagnosis of lupus when other signs and symptoms are present.
Anti-smith (Anti-Sm) antibody test
The Anti-Sm test is highly specific for lupus and helps confirm the diagnosis, especially in a positive ANA test.
What are the benefits of taking this test?
The benefits of undergoing blood tests for lupus are multifaceted, significantly impacting both the clinical approach to managing lupus and the quality of life for those diagnosed with the condition. Here’s an expanded look at these advantages:
Early detection and diagnosis
Blood tests play a crucial role in identifying lupus at an early stage. Since lupus can mimic other conditions and its symptoms vary widely, these tests are instrumental in guiding healthcare professionals toward a correct diagnosis. Early detection enables the initiation of treatment strategies that can significantly mitigate the disease's progression, reducing the risk of severe organ damage.
Monitoring disease activity
Lupus is known for its unpredictable flares, where symptoms worsen before returning to a state of remission. Regular blood testing helps track the disease's activity over time, providing essential information about how active the lupus is and whether it's responding to current treatment regimens. This continuous monitoring is crucial for adjusting medications and interventions to manage the condition better.
Evaluating treatment effectiveness
Treatment for lupus often involves a combination of medications tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and disease severity. Blood tests can reveal how well these treatments are working by showing changes in antibody levels, inflammation markers, and organ function. This information is vital for healthcare providers to determine if a treatment plan should be continued, adjusted, or changed.
Preventing complications
By closely monitoring lupus through blood tests, healthcare professionals can anticipate and prevent potential complications. For example, tests that show worsening kidney function can prompt immediate interventions to prevent irreversible kidney disease or damage. Similarly, adjustments in treatment based on blood test results can prevent complications such as cardiovascular disease, one of the leading causes of death in lupus patients.
Guiding medication adjustments
The results of lupus blood tests can lead to adjustments in medications to minimize side effects while maximizing benefits. For instance, if blood tests indicate a high risk of blood clots, healthcare providers may prescribe blood thinners alongside standard lupus treatments.
Personalized treatment plans
Ultimately, the information gleaned from these tests enables the creation of personalized treatment plans. Understanding how lupus uniquely affects an individual allows healthcare providers to tailor treatments to the patient's specific needs, improving outcomes and enhancing the quality of life.
Blood Tests for Lupus are not only foundational in diagnosing and understanding the disease but also in creating a dynamic, responsive approach to treatment. They offer a window into the patient's health status, guiding decisions that lead to more effective management of lupus, reducing the burden of the disease, and empowering patients and their families.
How does our template work?
Our free Blood Test for Lupus template aids doctors in creating personalized treatment plans. Here's a streamlined process:
Step 1: Download our lupus treatment template
Start by downloading our comprehensive template designed for healthcare professionals. This resource aids in organizing patient information, treatment plans, and monitoring progress.
Step 2: Conduct a detailed patient consultation
Use the template during patient consultations to gather essential information on symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle. This step is crucial for tailoring the treatment plan to the individual's needs.
Step 3: Order and review blood tests
Based on the initial consultation, the necessary blood tests are ordered to confirm the diagnosis of lupus and assess disease activity. Our template includes a section for recording and interpreting these results.
Step 4: Develop a personalized treatment plan
Utilizing the template, outline a treatment strategy that addresses the patient's specific symptoms and disease severity. This may include NSAIDs, antimalarial drugs, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants.
Step 5: Schedule regular follow-up appointments
Plan for regular follow-ups to monitor the patient's response to treatment, adjusting the plan as necessary. The template facilitates tracking progress and making timely adjustments.
Step 6: Provide holistic care recommendations
Beyond medication, lifestyle changes and supportive therapies can be recommended to improve the patient's quality of life. Document these recommendations in the template for a holistic treatment approach.
Step 7: Use the template for ongoing disease management
The template is designed for long-term use, assisting in managing lupus over time. It helps document flare-ups, treatment adjustments, and overall progress.
By following these steps and utilizing our comprehensive lupus treatment template, doctors can enhance the care provided to lupus patients, ensuring a personalized and effective treatment strategy.
Commonly asked questions
No single test can diagnose lupus. A combination of blood tests, clinical examination, and patient history is necessary for a diagnosis.
When you test positive on an ANA test, it suggests an autoimmune process. It is common in lupus but can occur in other autoimmune diseases and some healthy individuals.
Certain tests, like complement levels and anti-dsDNA, may help predict flares by indicating increased disease activity.

.jpg)