Patient Positioning in Bed PDF
Be well informed about patient positions in bed, their uses, and their importance. Take advantage of our Patient Positioning in Bed PDF cheat sheet!


The importance of patient positioning
A patient's position is a fundamental and often underestimated component of healthcare, wielding profound implications for patient well-being and the successful execution of medical procedures. Here are the reasons why proper patient positioning is essential:
- Improved patient outcomes: By aligning the patient's body optimally without hyperextension or extreme lateral rotation, unless asked, healthcare professionals facilitate seamless medical procedures. During a patient risk assessment prior to surgery, determining the right positioning helps mitigate the risk of complications and foster an environment conducive to healing.
- Increase patient comfort: Appropriate positioning can minimize pain and discomfort; proper position helps relieve pressure points, especially in the hip and knee joints.
- Easy facilitation of medical procedures: Whether it be a surgical procedure, an imaging study, or a diagnostic test, optimal positioning provides healthcare professionals with enhanced access to the targeted area, streamlining procedures and refining visualization.
- Prevention of complications: Proper patient position also helps preserve a patient's neutral body alignment, thereby averting potential complications arising from immobility and injury.
- Maintains patient dignity and privacy: Minimizing exposure during procedures not only upholds the patient's privacy but also acknowledges the vulnerability often felt by individuals in perioperative contexts.
- Allows maximum visibility and access: Proper positioning optimizes visibility and surgical access, which can help boost surgery success and assist with administering anesthesia effectively during the perioperative phase.
From the familiar supine and prone positions to more nuanced postures like the Sims position and Trendelenburg position, the diversity of options underscores the versatility required in providing patient-centric care.
As healthcare evolves, a steadfast commitment to mastering the nuances of patient positioning remains paramount. This ensures that each patient receives care that is not only clinically adept but also profoundly humane.
Patient Positioning in Bed PDF Template
Patient Positioning in Bed PDF Example
Common patient positions in bed
Here are some of the most common positioning of patients in bed:
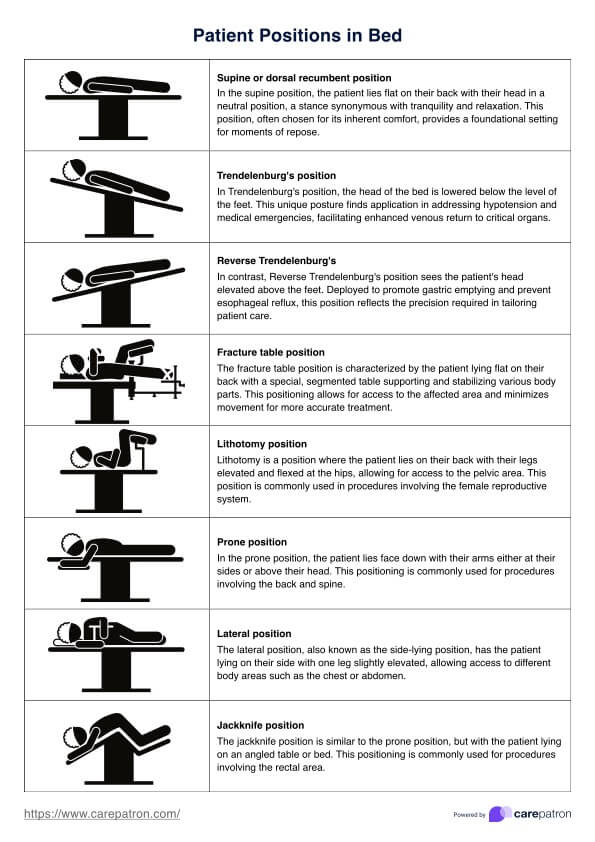
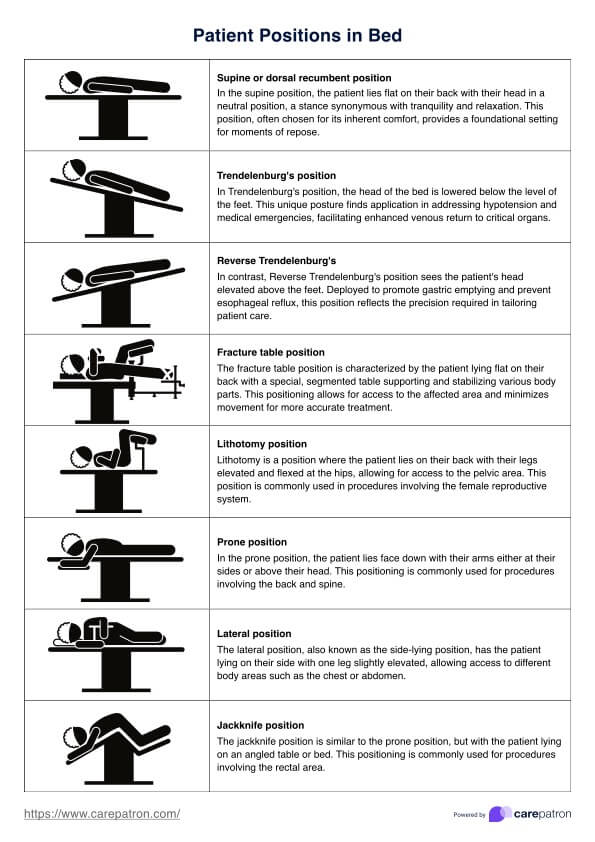
Supine or dorsal recumbent position
In the supine position, the patient lies flat on their back with their head in a neutral position, a stance synonymous with tranquility and relaxation. This position, often chosen for its inherent comfort, provides a foundational setting for moments of repose.
Fowler's position or sitting position
Fowler's position involves elevating the head of the patient's bed between 45 and 60 degrees. This position is widely employed to enhance patient comfort and care and benefits individuals with cardiac or respiratory conditions. Its versatility makes it a staple in the healthcare professional's toolkit.
Prone position
In the prone position, the patient lies on their stomach with the head turned to the side. This unconventional posture finds utility in specific medical procedures, demonstrating the adaptability of patient positioning in varied healthcare contexts.
Lateral position
Designed to relieve pressure on the coccyx, the lateral position involves the patient lying on the side of the body with the top leg positioned over the bottom leg. This simple yet effective positioning enhances comfort and prevents pressure-related complications.
Lithotomy position
Reserved for gynecological, urological, and rectal examinations and surgeries, the lithotomy position involves raising the patient's legs and positioning them in stirrups. Precision and access are paramount in this specialized stance.
Trendelenburg's position
In Trendelenburg's position, the head of the bed is lowered below the level of the feet. This unique posture finds application in addressing hypotension and medical emergencies, facilitating enhanced venous return to critical organs.
Reverse Trendelenburg's position
In contrast, Reverse Trendelenburg's position sees the patient's head elevated above the feet. Deployed to promote gastric emptying and prevent esophageal reflux, this position reflects the precision required in tailoring patient care.
Knee-chest position
Reserved for rectal and vaginal examinations, the knee-chest position involves the patient being on their knees with the chest resting on the bed. This specialized posture underscores the specificity of patient positioning in facilitating thorough examinations.
Kidney position
The kidney position in bed refers to a specialized surgical posture wherein the patient is positioned in a modified lateral stance, with the side undergoing surgery facing upward. This precise arrangement is strategically chosen to optimize access and visibility during kidney-related surgical procedures.
Other positions that may be used are Sims position, High Fowler's position, and Kidney position. To learn more about patient positions, download our template by clicking "Use Template" for an in-app version and "Download" for a PDF version.
Materials required to ensure proper patient positioning
Here are the best materials to have when ensuring proper patient positioning:
- Bed boards made of sturdy plywood to ensure body alignment maintenance and back support for the patient.
- Robust plastic foot boots for keeping feet flexed at precise angles to help maintain a neutral body alignment.
- Hand rolls maintain optimal hand positioning, keep fingers flexed, and ensure thumbs are adducted in alignment with other fingers.
- Supportive items like pillows, rolls, wedges, and blankets cushion pressure points and provide lumbar support, elevation adjustment, and comfort.
When should you use this PDF?
A patient positioning in-bed template, often colloquially called a "cheat sheet" or guide, is a valuable resource for healthcare professionals, specifically nurses and caregivers. Utilizing such a template is integral in various scenarios, each contributing to optimal patient care and adherence to established guidelines.
Training and education
One primary instance where a patient positioning bed template finds its utility is in training and education. It is a comprehensive tool for instructing new healthcare staff and students on the diverse patient positions and their respective purposes. This ensures a standardized approach and fosters a foundational understanding of the nuances involved in patient positioning.
Reference
As a quick reference guide, the template becomes an indispensable aid for healthcare professionals. Whether seasoned practitioners or those seeking a momentary reminder, having a visual guide at their disposal ensures that correct positioning techniques are consistently applied. This not only upholds the quality of patient care but also bolsters caregivers' confidence in their decision-making.
Patient care
The bed template is a practical tool during patient care to ensure that the correct position is employed based on the individual patient's condition and specific treatment needs. Adherence to prescribed positions contributes to enhanced patient comfort, prevention of complications, and overall efficacy of the care provided.
Documentation
The bed template proves invaluable in the meticulous realm of healthcare documentation. It facilitates accurate and consistent recording of patient positioning in medical records, ensuring that a comprehensive and standardized account of patient care is maintained. This, in turn, contributes to the continuity of care and facilitates communication among healthcare professionals.
Prevention of complications
An overarching role of the bed template is to prevent complications associated with incorrect patient positioning. Providing a visual guide to proper techniques becomes an ally in averting potential issues such as pressure ulcers and contractures. In this context, the template is a proactive measure to ensure patient safety and well-being.
Commonly asked questions
That will depend on the patient's procedure, test, or treatment plan, as each position is designed for specific purposes.
Though there are multiple, Fowler's position is the most common, significantly when reducing lower back pain and administering medication.
You can reposition a patient by rolling them towards a side and then back to you. Until you've repositioned them, your patient will be in a specific position based on their capabilities. If this process is challenging, it's best to ask for a helping hand.