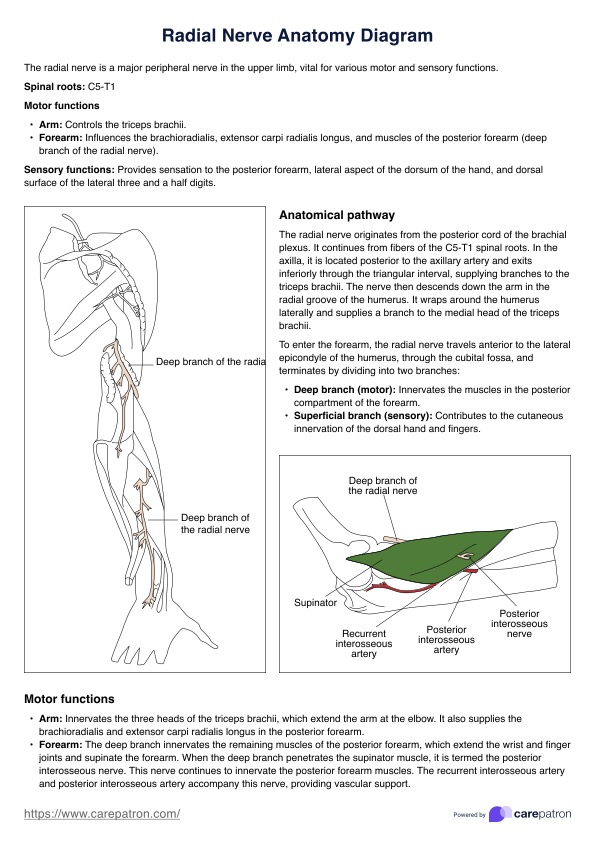
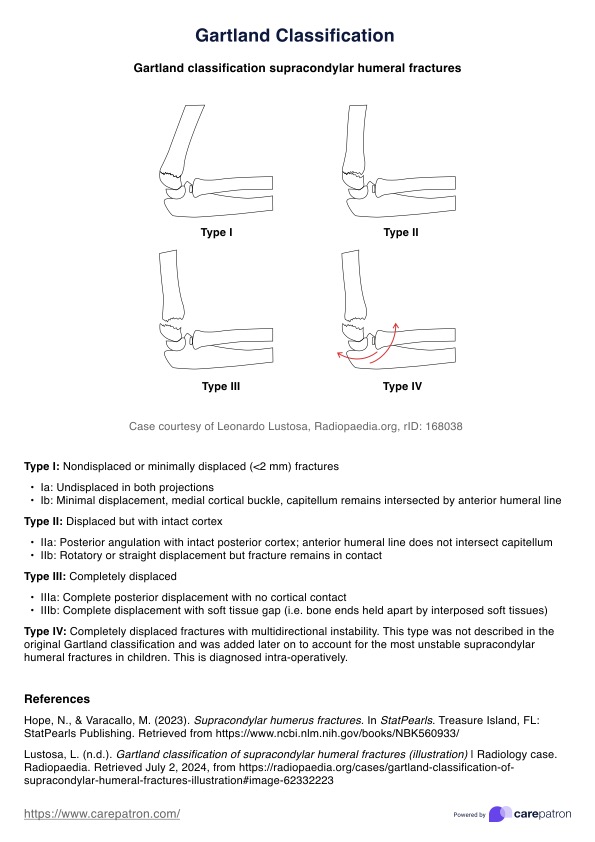
Nursing Vital Signs Chart
Optimize patient care with our Nursing Vital Signs Chart. Track and analyze crucial health indicators for informed healthcare decisions.


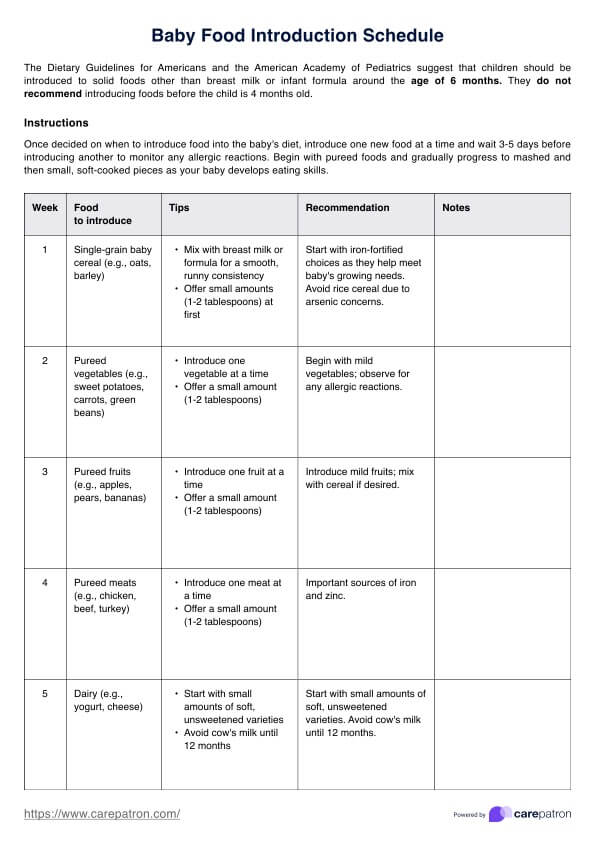
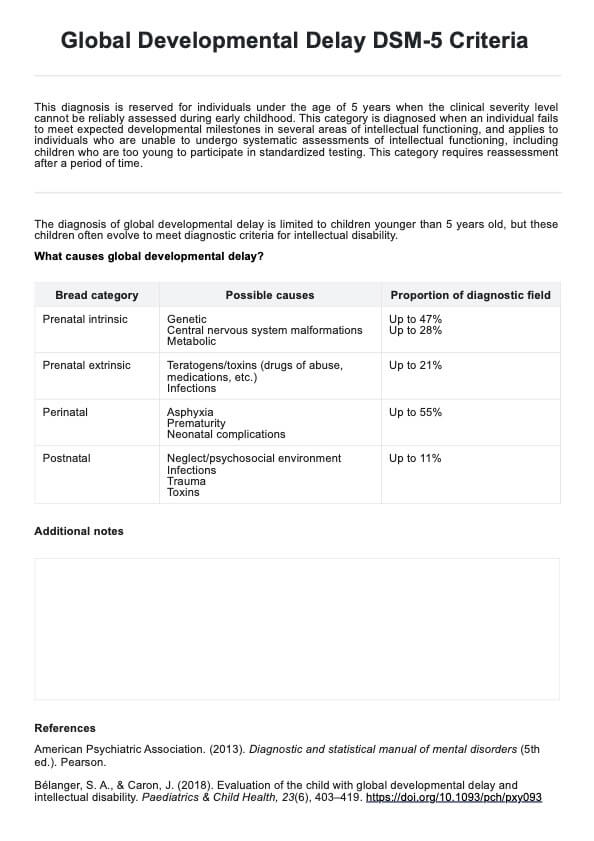
What is a Nursing Vital Signs Chart?
Vital signs are the body's way of sending us important messages about its health. Heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, oxygen saturation, and breathing rate are all key signs that tell us a lot about a patient's health as it reflects the essential body functions.
A Nursing Vital Signs Chart is a simple tool that helps nurses keep track of these numbers over time. By regularly writing down these vital signs, nurses can spot changes that might signal something's off, like an infection or a blood pressure issue. It's also a great way for the whole healthcare team to stay on the same page about how the patient is doing. It's all about staying proactive and catching problems early to avoid complications like high blood pressure. Our chart includes the reference ranges for normal blood pressure, body temperature, respiratory rate, heart rate, and oxygen saturation to make it more convenient for you.
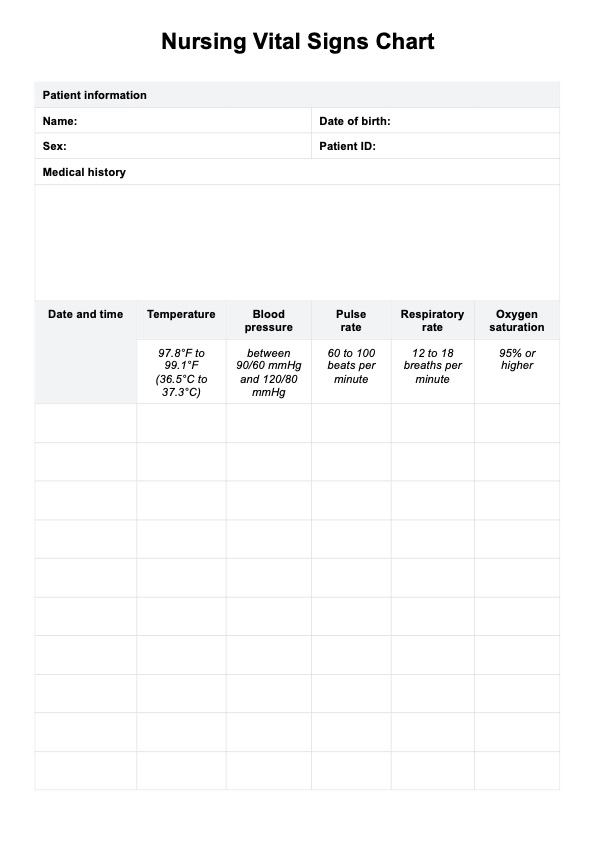
Nursing Vital Signs Chart Template
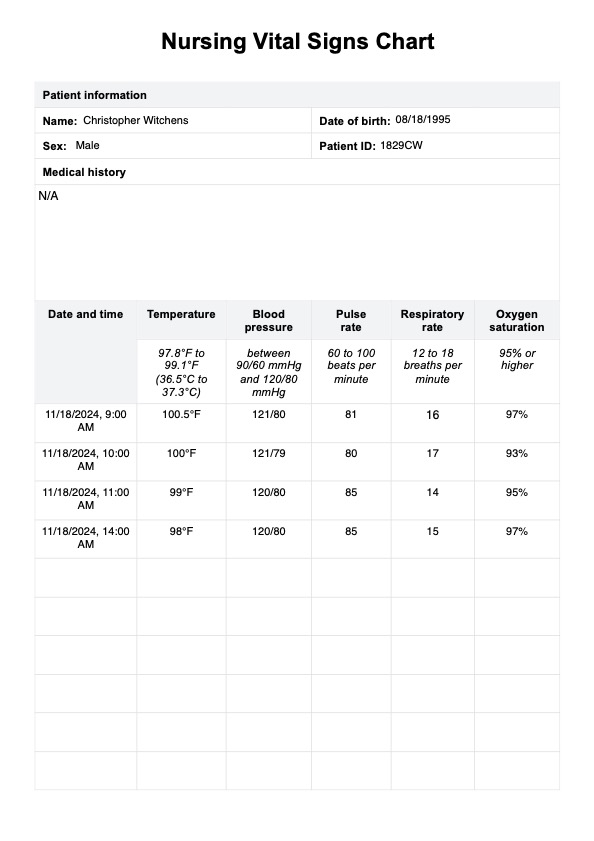
Nursing Vital Signs Chart Example
How does this nursing normal vital signs chart work?
Using the chart helps you monitor vital signs, essential for ensuring patients get the care they need before things get worse. Here's how to use it:
Step 1: Download the template
The template is included in this guide. Click "Use template" to open it on the Carepatron platform, where you can customize it to suit your needs. Alternatively, click "Download" to get a free fillable PDF version of the form.
Step 2: Measure and record the vital signs
Measure blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, oxygen saturation, and respiratory rate. Record each of these values in the corresponding sections on the chart.
Step 3: Compare with normal vital sign ranges
After entering the values, compare them to the normal ranges for vital signs. This helps identify any abnormal readings that might require further attention or action. Here are the values for each vital sign (Minnesota Department of Health, 2022; Mount Sinai Health System, 2023):
- Normal body temperature: 97.8°F to 99.1°F (36.5°C to 37.3°C)
- Blood pressure: Between 90/60 mmHg and 120/80 mmHg
- Pulse rate: 60 to 100 beats per minute
- Normal respiratory rate: 12 to 18 breaths per minute
- Oxygen saturation: 95% or higher
It is worth noting that normal vital signs change depending on factors like age, sex, weight, fitness level, and general health. When it comes to pediatric vital signs, they vary from those of adults, so it's essential to follow age-specific guidelines to assess their health properly.
Step 4: Update regularly and track trends
Continue recording the patient's vital signs at regular intervals, updating the chart each time. Our chart has a date and time stamp column, which will help you track trends over time and quickly notice any changes in the patient's condition.
Step 5: Share and communicate with the healthcare team
Ensure you share the updated vital signs chart with the healthcare team to provide a clear patient status overview. Effective communication will help them make informed decisions about their care.
When would you use this chart?
The Nursing Vital Signs Chart proves invaluable across various healthcare scenarios. It is tailored to the dynamic needs of practitioners seeking comprehensive patient assessments.
Routine patient check-ups
Employ the chart during routine check-ups to establish baseline vital sign measurements. This offers a holistic view of a patient's overall health. Regular use ensures practitioners can detect subtle changes over time, prompting timely interventions.
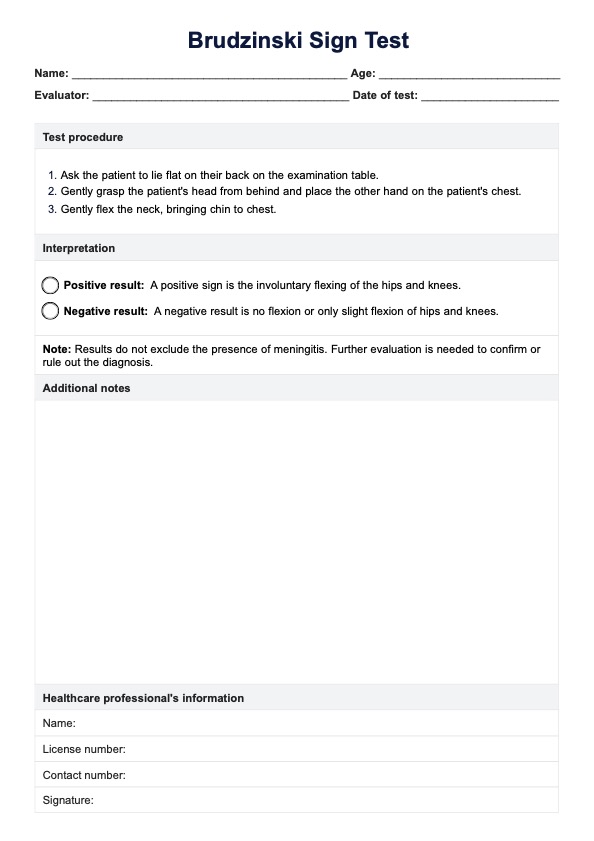
Emergencies
In emergency settings, the chart becomes a rapid reference tool, allowing healthcare providers to swiftly capture and analyze vital signs. This is crucial for making urgent decisions and initiating immediate interventions.
Pre and postoperative monitoring
Before surgery, use the chart to track vital signs and establish a baseline, which helps identify any pre-existing health issues. After surgery, continue using the chart to monitor patients during recovery. Tracking vital signs postoperatively allows you to assess the effectiveness of interventions, spot any potential complications early, and ensure a smooth transition from surgery to recovery.
Home health visits
The chart becomes a portable tool for healthcare providers during home health visits. It ensures accurate documentation of vital signs in diverse environments, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the patient's health status.
Transition of care
The chart is a tool when patients transition between care settings, such as from hospital to home or vice versa. This promotes continuity of care, allowing different healthcare providers to seamlessly understand and act upon the patient's vital sign trends.
Benefits of using the Nursing Vital Signs Chart
The Nursing Vital Signs Chart offers several benefits that can improve efficiency and accuracy in monitoring patient health. Here's how:
Easy to use
The Nursing Vital Signs Chart is simple to navigate, making it easy for healthcare professionals to record and track patient data quickly.
Saves time
Having a pre-organized template reduces the time spent manually creating charts, allowing for faster monitoring and documentation.
Available in digital and printable formats
The chart can be accessed in digital and printable formats, offering flexibility for different work environments and preferences.
References
Minnesota Department of Health. (2022, March 4). Oxygen levels, pulse oximeters, and COVID-19. https://www.health.state.mn.us/diseases/coronavirus/pulseoximeter.html
Mount Sinai Health System. (2023). Vital signs information. https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/special-topic/vital-signs#
Commonly asked questions
A normal blood pressure reading typically ranges between 90/60 mmHg and 120/80 mmHg. To ensure accuracy, it's important to take multiple blood pressure measurements.
Keeping vital signs in a normal range helps ensure proper functioning and can prevent serious health issues. It allows healthcare providers to spot problems early and respond before they occur.
Systolic pressure is the top number and measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats, while diastolic pressure is the bottom number and measures the pressure when your heart rests between beats.
Yes, the Nursing Vital Signs Chart supports interoperability. It allows for seamless integration and data exchange with other healthcare systems, promoting a cohesive and interconnected approach to patient care across different platforms and settings.
The frequency of use depends on the patient's condition and the care plan. For routine assessments, regular use is recommended to establish baseline measurements. More frequent monitoring may be necessary in dynamic situations, such as postoperative recovery or acute care. Regular assessments ensure a proactive and responsive approach to patient care.