Trapezius Tear Test
Learn about trapezius tears and strains, their symptoms, causes, and how to use our Trapezius Tear Test template.


What is a trapezius muscle tear?
A trapezius muscle tear, or strain, occurs when the trapezius muscle is overstretched or torn due to injury, overuse, or sudden forceful movements. This large, triangular muscle extends from the back of the neck and thorax to the shoulder girdle, playing a crucial role in shoulder joint stability, upper body movement, and posture support. Damage to this muscle can lead to trapezius muscle pain, affecting daily activities and overall mobility.
A trapezius tear can result from an acute injury, such as a violent twist, fall, or collision, leading to significant pain and stiffness in the neck, shoulder region, and upper back. Chronic muscle overuse, poor posture, or repetitive motions can also strain the lower trapezius muscle, reducing its ability to stabilize the shoulder joint and leading to discomfort. When the injured muscle is not properly treated, symptoms can worsen, affecting blood flow and delaying recovery.
Symptoms
The severity of symptoms depends on the extent of the muscle damage. Common signs of a trapezius strain or tear include:
- Neck and shoulder pain that worsens with movement.
- Swelling or bruising in the affected area.
- Muscle spasms and a burning sensation in the shoulder region or upper back.
- Stiffness and decreased range of motion in the neck and shoulders.
- Headaches due to referred pain from the trapezius muscle.
- Muscle weakness, making it difficult to perform routine tasks.
Causes
Trapezius muscle pain and strain can result from several factors, including:
- Repetitive motions or muscle overuse from lifting, pulling, or certain sports activities, leading to an upper back muscle strain.
- Lack of warm-up or stretching, which reduces blood flow and increases the risk of a strained trapezius.
- Sudden trauma, such as falls, car accidents, or direct impact, causing an acutely injured muscle.
- Forceful, abrupt movements that overstretch or tear the muscle.
- Poor posture over time, which strains the shoulder girdle and weakens the lower trapezius muscle.
- Occupations or sports involving heavy lifting and repetitive motions, increasing strain on the shoulder region.
Trapezius Tear Test Template
Trapezius Tear Test Example
What is a Trapezius Tear Test?
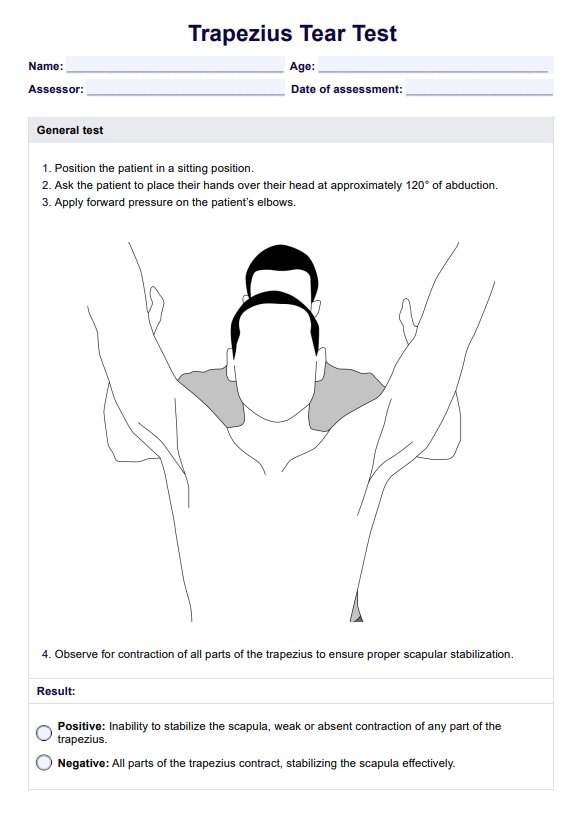
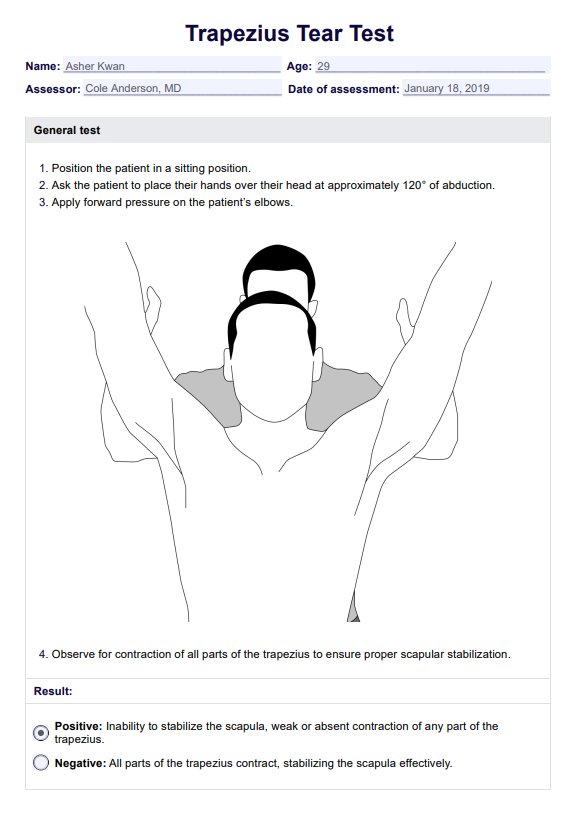
A Trapezius Tear Test is a clinical assessment used to evaluate the integrity and strength of the trapezius muscle. It involves specific movements to determine whether the muscle is functioning properly or if there is a possible tear. The test is divided into assessments for the upper, middle, and lower portions of the trapezius.
To assess general trapezius strength, the patient is seated with their hands placed over their head at approximately 120° of abduction. The examiner applies forward pressure on the patient's elbows while observing for proper scapular stabilization. A positive test, indicating a potential tear, is observed if the scapula fails to stabilize or if there is noticeable weakness in any part of the trapezius. A negative test is confirmed if all sections of the muscle contract effectively.
For the upper trapezius, the patient is asked to shrug their shoulder with slight arm abduction to exclude the rhomboids and levator scapulae. Downward resistance is applied to assess strength. A positive result is indicated by difficulty elevating the shoulder, asymmetry, or pain. A negative result is observed when the patient can resist force without discomfort.
The middle trapezius is tested with the patient in a prone position, the arm abducted to 90° and laterally rotated. The patient is asked to extend the arm horizontally against resistance. A positive test is indicated if the scapula fails to retract, suggesting weakness or a tear. A negative test is confirmed if proper retraction occurs with full strength.
To assess the lower trapezius, the patient remains in a prone position with their arms abducted to 120° and the shoulders laterally rotated. The examiner applies resistance to diagonal extension while observing scapular movement. A positive test is observed if the scapula protracts instead of retracting, suggesting a tear or significant weakness. A negative test is indicated if the scapula retracts properly and the patient resists movement effectively.
These tests help identify trapezius muscle dysfunction, allowing for further imaging or clinical intervention if a tear is suspected.
How to use our Trapezius Tear Test template
Our Trapezius Tear Test template is designed to help healthcare professionals accurately assess potential trapezius muscle strains or tears. To use our template effectively, follow these steps:
Step 1: Download the template
First, download the Trapezius Tear Test template from the Carepatron platform. Click the "Use template" button to access the form via the Careptron app, where you can edit it. For a PDF copy, click "Download."
Step 2: Gather patient information
Enter the patient’s name, age, and assessment date, along with your name as the assessor. Using the template, explain how the test works.
Step 3: Conduct the tests indicated in the template
Follow the outlined steps in the template to assess muscle function in the posterior aspect of the neck and shoulder blades. Begin with the general trapezius test to evaluate overall scapular stabilization before moving on to the upper, middle, and lower trapezius tests. Observe for signs of weakness, neck pain, or difficulty maintaining position, which may indicate a pinched nerve or muscle tear.
Step 4: Record and interpret results
Mark each test as positive or negative based on the patient’s response. A positive result suggests muscle weakness, an inability to retract the shoulder blades, or difficulty resisting applied force. Use the Additional Notes section to document compensatory movements or any significant findings that may require further evaluation.
Step 5: Determine next steps
Based on the results, recommend appropriate interventions such as physical therapy, rest, or imaging if a severe trapezius tear or nerve involvement is suspected. Save and share the completed template for documentation and future reference in managing the patient’s recovery.
Benefits of using our template
Our Trapezius Tear Test template is designed to help healthcare professionals accurately and efficiently assess trapezius muscle strains or tears. Here are three key benefits of using our template:
Standardization
Using our template ensures that the Trapezius Tear Test is conducted consistently every time. This standardization reduces variability in test results and improves the reliability of assessments, making it easier to compare results over time or across different patients.
Time efficiency
Our template simplifies documentation, allowing healthcare professionals to quickly and accurately record patient information, test procedures, and results. This efficiency frees up more time for patient care and other critical tasks.
Comprehensive documentation
The template provides a structured format for capturing all relevant details of the Trapezius Tear Test, including patient information, test procedures, and results. Comprehensive documentation is crucial for maintaining accurate medical records and facilitating better communication among healthcare providers.
Treatment for trapezius muscle tear
Managing a trapezius muscle tear involves pain relief strategies and increasing blood flow to the injured muscle to promote healing. Recommended treatments include:
- Rest and ice therapy to reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Physical examination by a healthcare professional to assess muscle strength and injury severity.
- Muscle relaxants or anti-inflammatory medications to ease muscle spasms and discomfort.
- Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises to restore function and improve blood flow.
- Massage therapy or heat application to loosen tight muscles and support healing.
- Correcting posture and using ergonomic support to prevent further strain on the shoulder girdle and neck region.
A proper treatment plan helps restore mobility, improve blood flow, and prevent chronic trapezius muscle pain or neck and shoulder pain from developing. If significant pain persists despite conservative care, further evaluation through imaging and physical examination may be necessary to rule out severe muscle damage.
In addition to these treatments, physical therapy can play a crucial role in long-term recovery by focusing on scapular stabilization, posture correction, and muscle function restoration. A therapist may incorporate manual therapy, resistance exercises, and neuromuscular re-education to enhance strength and flexibility in the posterior aspect of the neck and shoulder blades.
Commonly asked questions
A torn trapezius can heal on its own with proper rest, but recovery depends on the severity of the injury. Mild to moderate tears may improve with ice therapy, gentle stretching, and strengthening exercises to restore muscle function around the posterior aspect of the neck and shoulder blades. However, severe tears may require medical intervention to prevent complications like a pinched nerve or chronic neck pain.
A trapezius strain is a mild overstretching of the muscle, causing neck pain and stiffness. A tear involves actual damage to muscle fibers, leading to more intense pain and possible weakness in the shoulder blades and posterior aspect of the upper back. Strains typically recover faster, whereas tears may take longer and pose a higher risk of affecting muscle function or irritating a pinched nerve.
To test trapezius muscle function, clinicians use a resisted shoulder shrug test to check for weakness or neck pain, and a resisted shoulder abduction test to assess muscle strength near the shoulder blades. Palpation and range of motion tests help identify tenderness in the posterior aspect of the neck. If nerve involvement or a pinched nerve is suspected, imaging or EMG may be required.