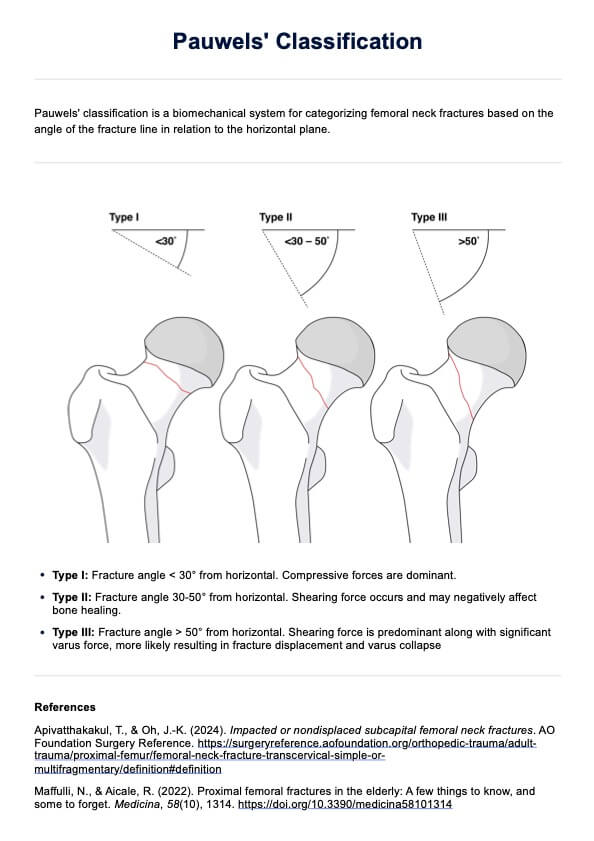
Harvard Step Test
Assess the cardiovascular fitness of your client with the Harvard Step Test! Use our template to check their fitness accurately.


What is the Harvard Step Test?
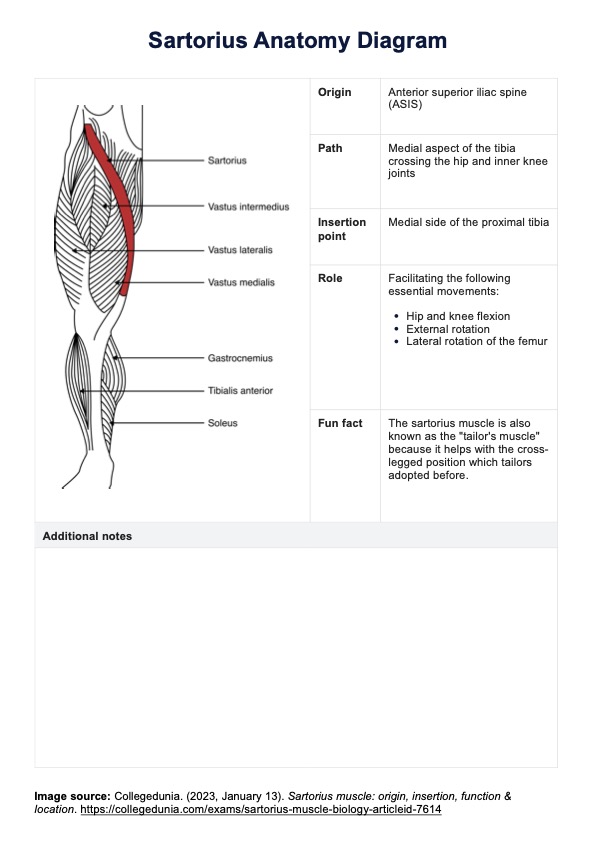
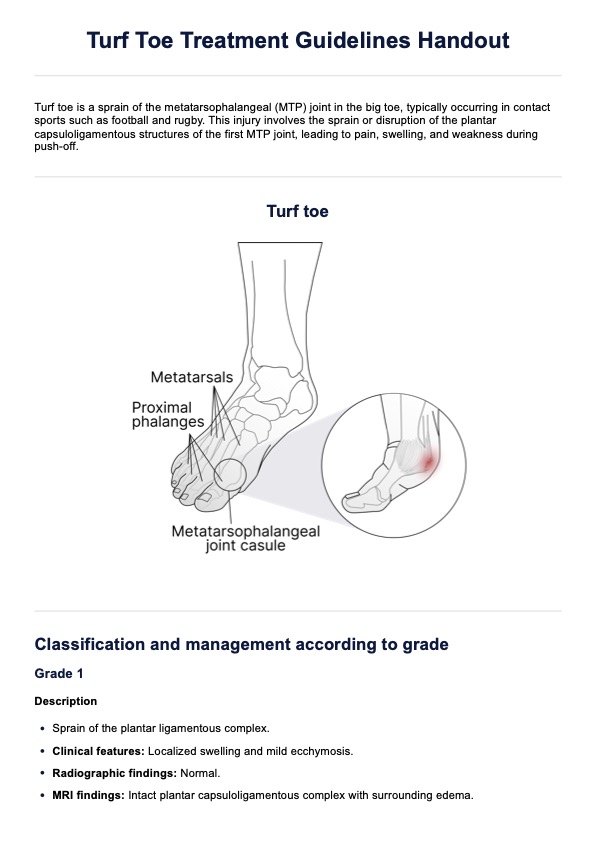
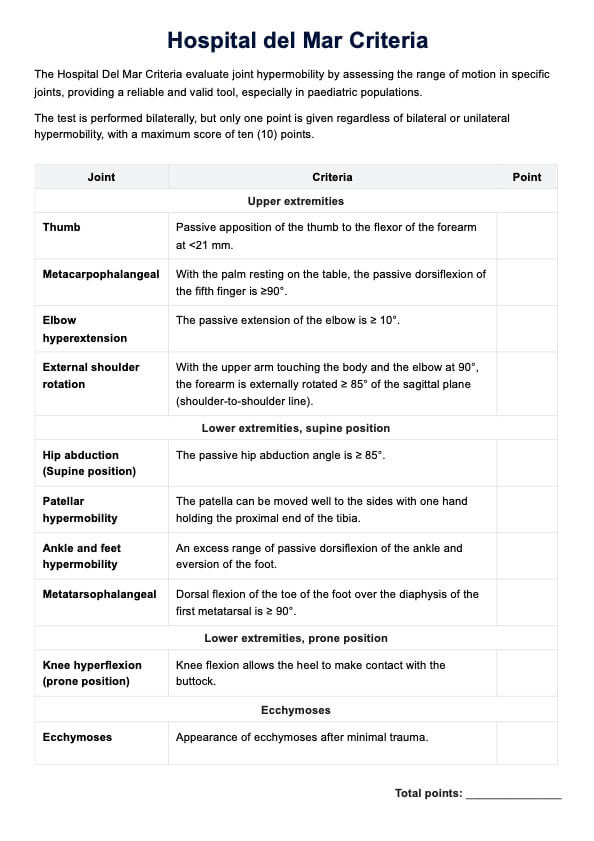
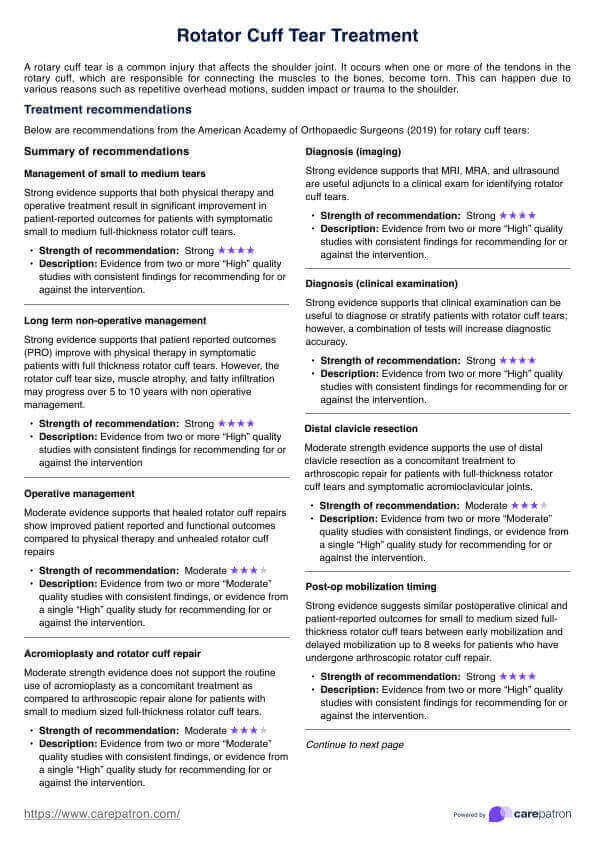
The Harvard Step Test is a widely recognized fitness test designed to measure cardiovascular fitness and endurance by assessing heart rate recovery following exercise. Developed at Harvard University during World War II (Brouha et al., 1943), this test was initially created to evaluate the physical fitness of male college students and adult men enlisted in the military. The test measures a participant's aerobic fitness and heart's ability to recover after physical exertion and then rating fitness index score to determine overall fitness levels. It is often used in physical education, rehabilitation, and exercise physiology studies.
A notable adaptation of the original Harvard Step Test is the Modified Harvard Step Test, introduced by A. W. Sloan for female participants (1959). This modified version reduces the step height to 16 inches and reduces the duration from 5 minutes to 3 minutes to account for physiological differences.
The test’s principles are grounded in the relationship between physical exertion, heart rate, and recovery periods, making it a good indicator of cardiovascular and aerobic fitness. It involves participants stepping up and down at a set cadence, followed by pulse count intervals during recovery to determine the fitness index score.
The Harvard Step Test is useful for fitness professionals, physical educators, and healthcare practitioners, especially those involved in physical education, sports science, or rehabilitation programs. It’s particularly valuable for screening and tracking fitness levels in patients and athletes. While effective, it’s essential to ensure participants are well-rested, hydrated, and have avoided substances like caffeine or alcohol that can influence pulse count and aerobic capacity.
Harvard Step Test Template
Harvard Step Test Example
How to use our Harvard Step Test template
Our Harvard Step Test template is designed to guide healthcare professionals through the test procedure with precision. It includes step-by-step instructions, fields for documenting results, the formula for calculating the fitness index score, and normative data for interpreting results.
Follow these steps to make the most of our template:
Step 1: Access the template
Start by obtaining a copy of the template. Click the “Use template” button to edit it digitally on the Carepatron app or click the “Download” button to save a printable version. The template includes all necessary sections, including areas for recording the pulse count, results, and notes.
Step 2: Set up and administer the test
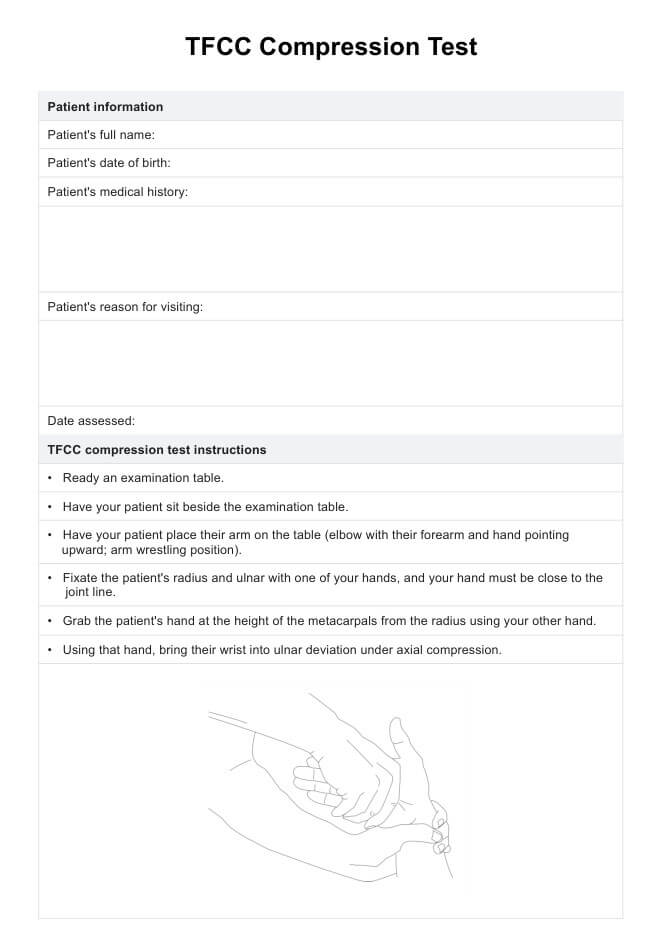
Prepare the testing environment with a sturdy step platform (20 inches for men or 16 inches for women in the modified version), a stopwatch, and a cadence tape or metronome set to 30 steps per minute. Explain the procedure to the participant:
- The participant will step up and down the platform at the given pace for five minutes (or as long as possible).
- Encourage them to complete the test but assure them they can stop if needed.
- Begin the test and activate the stopwatch when you say “Go.” Stop the test at the five-minute mark or when the participant is unable to continue.
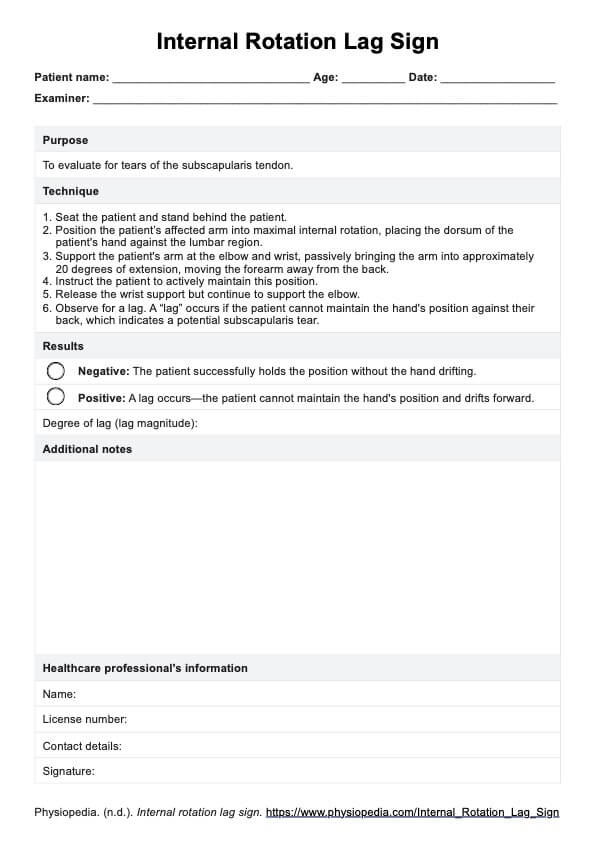
Step 3: Record the participant’s heart beats during recovery
Once the test is complete, have the participant sit on a chair and rest. Using a fitness tracker or heartbeat monitor is easier, but you can also manually count their pulse during the following intervals:
- Between 1 and 1.5 minutes
- Between 2 and 2.5 minutes
- Between 3 and 3.5 minutes
Document these values in the space provided in the template.
Step 4: Calculate the fitness index
Use the formula on the template to determine the fitness index score. Input the total test time (in seconds) and the sum of the pulse counts into the formula provided. This will yield a fitness index that reflects the participant's aerobic fitness.
Step 5: Interpret the results and discuss with the participant
Compare the fitness index score with the normative fitness standards on the template. Discuss the results with the participant, explaining their cardiovascular fitness level. If necessary, provide recommendations for improving fitness or suggest further evaluations.
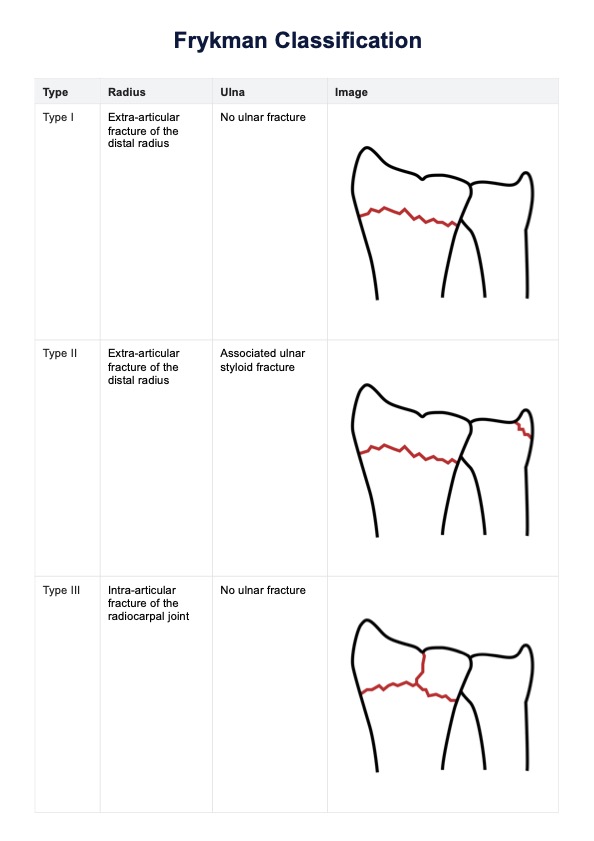
How to score the Harvard Step Test
Scoring the Harvard Step Test involves calculating the participant's fitness index score using a straightforward formula and interpreting the results using normative data. Use the recorded data to calculate the fitness index using the formula:
Fitness index= (100 × test duration in seconds) / (2 × sum of heart rates)
Then, compare the calculated fitness index score to the table in the template for interpretation. Note that the ranges are based on historical data from the test's origin in World War II and may need to be adapted for specific populations. While the table provides useful guidance, creating customized cutoffs tailored to your participant's demographics, such as age, gender, and fitness levels, may yield more accurate insights.
What are the benefits of the Harvard Step Test?
The Harvard Step Test is a valuable tool for healthcare and fitness professionals. It offers multiple benefits, making it an excellent choice for evaluating cardiovascular fitness and overall physical health.
- Requires minimal equipment
The test only needs a sturdy step platform, a stopwatch, and a method to measure pulse, making it accessible and inexpensive to conduct. - Screening for heart disease
By assessing cardiovascular recovery after exercise, the test can help identify individuals at risk of heart-related conditions. - Non-invasive and simple to perform
The test is easy to administer and does not require specialized training or invasive procedures, making it suitable for routine fitness evaluations. - Applicable across various populations
Whether for male college students, general fitness assessments, or screening athletic readiness, the test's versatility allows it to be used with a wide range of participants. - Supports fitness monitoring and improvement
Regular use of the test can help track changes in aerobic fitness and guide personalized fitness or rehabilitation programs.
However, for more accurate insight into a client's fitness (especially athletes), make sure that you also do other fitness tests, such as the Cooper 12-Minute Run Test.
References
Brouha, L., Health, C. W., & Graybiel, A. (1943). The Step Test: A simple method of measuring physical fitness for hard muscular work in adult men. Revue Canadienne de Biologie, 2, 86–92.
Sloan, A. W. (1959). A modified Harvard Step Test for women. Journal of Applied Physiology, 14(6), 985–986. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1959.14.6.985
Commonly asked questions
The Harvard Step Test is simple, cost-effective, and requires minimal equipment, making it accessible for professionals and participants. It is excellent for assessing cardiovascular fitness and tracking progress. However, as stepping up and down can be physically demanding, it may not be suitable for individuals with joint problems, balance issues, or severe cardiovascular conditions.
The formula for the fitness index is "(100 × test duration in seconds) ÷ (2 × sum of heart rates)"
This formula calculates cardiovascular fitness based on exercise duration and heart rate recovery.
Place a sturdy, non-slippery step platform (20 inches high for men, 16 inches for women) in a safe, open area near a chair for resting post-test. Ensure participants wear appropriate attire and have a metronome or audio file for a steady cadence. A stopwatch and a method to measure the pulse are essential for recording results.