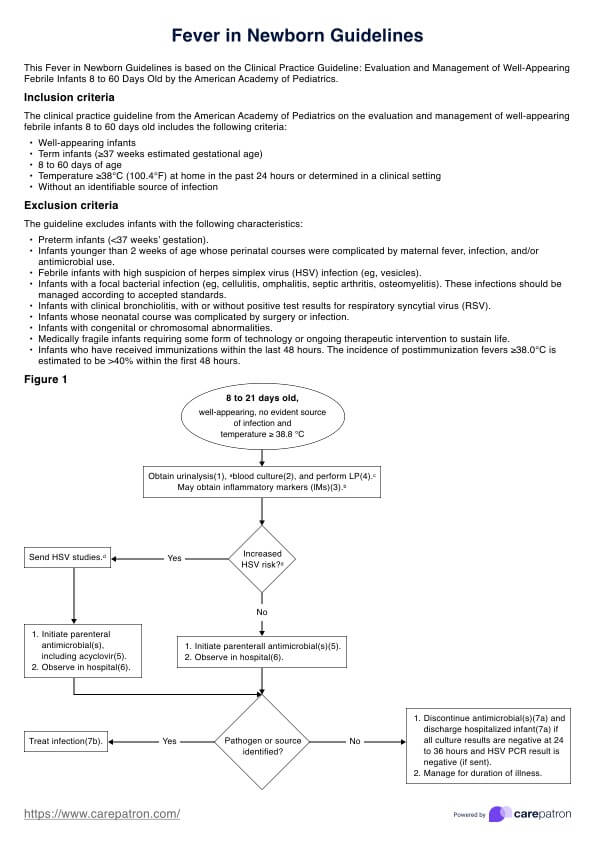
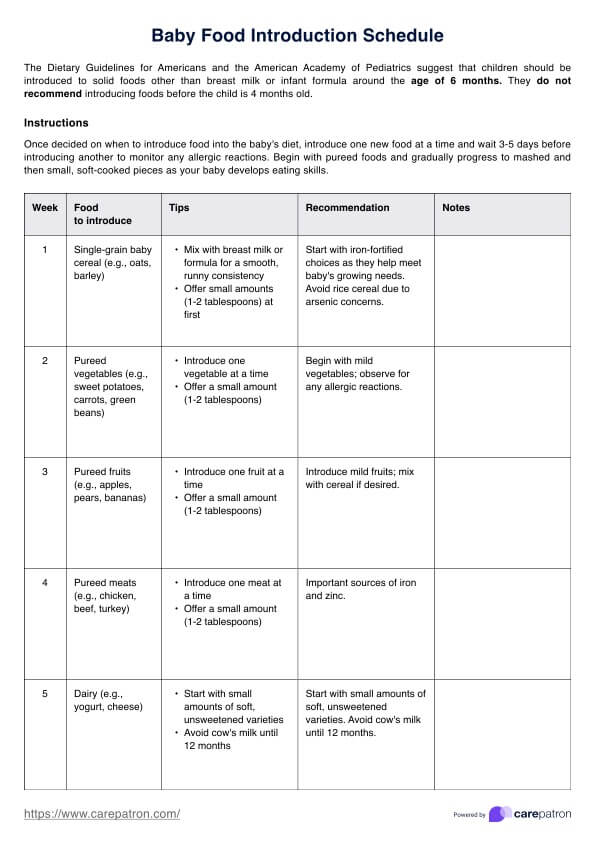
Fluid Volume Deficit Nursing Care Plan
Create a fluid volume deficit nursing care plan with clear steps to assess, monitor, and manage hydration, ensuring patient safety and recovery.


What is a fluid volume deficit?
Fluid volume deficit, also known as hypovolemia, refers to insufficient fluid in the body, specifically within the vascular system. It occurs when there is an excessive loss of fluids or inadequate intake, leading to a decrease in circulating blood volume. This deficit disrupts the balance between the body's fluid input and output, impacting its ability to function optimally. Several causes contribute to fluid volume deficit.
Dehydration resulting from diarrhea, vomiting, excessive sweating, or inadequate fluid intake is common. Additionally, conditions such as bleeding, severe burns, diabetes, and certain medications can lead to significant fluid losses, exacerbating the deficit. This condition may present in very young children or infants and may be evidenced by crying without tears, high fevers, irritability, sunken eyes, and drowsiness.
The consequences of fluid volume deficit can be severe. It affects the body's ability to maintain normal blood pressure, impairing circulation and delivery of oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs. This condition can result in dizziness, rapid heart rate, low blood pressure, decreased urine output, dry mucous membranes, and altered mental status. Left untreated, severe hypovolemia can lead to shock, organ failure, and life-threatening complications.
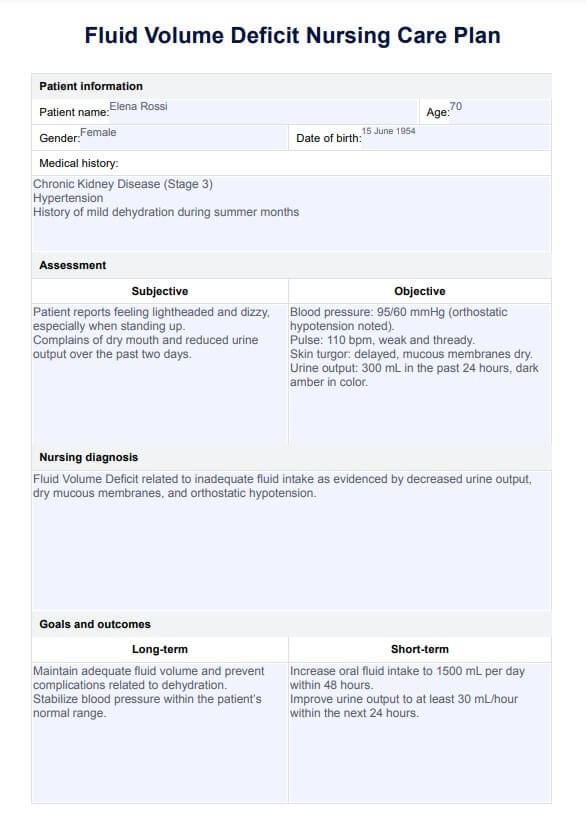
Fluid Volume Deficit Nursing Care Plan Template
Fluid Volume Deficit Nursing Care Plan Example
What is a Fluid Volume Deficit Nursing Care Plan Template?
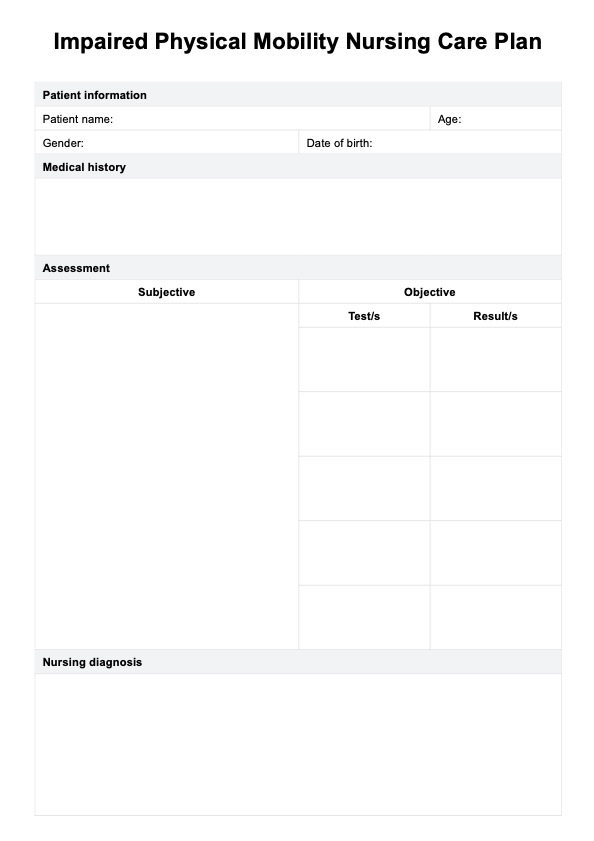
A Fluid Volume Deficit Nursing Care Plan Template is a document where nurses can write pertinent information that can aid in the diagnoses, such as symptoms, a list of medications, assessment guides, rationale, and notes for evaluation, referral, or recommendation. It is often employed when a patient experiences deficient fluid volume, leading to decreased circulating blood volume.
Creating a fluid volume deficit care plan is essential for several reasons. It helps stabilize the patient, guides the assessment and diagnostic process, charts fluid replacement, and mitigates further complications through nursing interventions. Implementing this plan is crucial for ensuring patient well-being and a swift recovery.
How does it differ from a dehydration nursing care plan?
A Dehydration Nursing Care Plan Template is used by nursing and healthcare professionals to provide personalized, effective care for patients who receive a nursing diagnosis for dehydration. This template serves as a guide to ensure all aspects of a patient's condition, including their specific signs and symptoms, underlying causes, and severity of dehydration, are thoroughly assessed and addressed.
The template includes several key sections: patient information, medical history, assessment, diagnosis, dehydration nursing interventions, rationale, and evaluation. These sections guide healthcare providers through a systematic approach to patient care, starting with an initial assessment, developing and implementing a tailored care plan, and finally evaluating the effectiveness of the interventions.
Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance in patients with dehydration. It prompts the healthcare team to consider all possible causes and contributing factors to the patient's dehydration.
How does our template work?
A nursing care plan for fluid volume deficit is essential for several reasons. It helps implement the patient's stabilization, leads the assessment and diagnostic process, can chart for fluid replacement, and helps mitigate further complications. Implementing this nursing care plan is pivotal in ensuring patient well-being and a swift recovery. Here are the steps for using our template:
Step 1: Gather your resources to monitor fluid intake
Fluid volume deficit nursing care plans are a valuable resource and essential to keep on hand. Make sure that you have a copy of the free printable PDF when the need arises by either clicking the "Download template" or "Use template" button or by searching "fluid volume deficit nursing care plan" on Carepatron's template library's search bar on the website or app.
Step 2: Collate essential information
Once the patient has been diagnosed and assessed for fluid volume deficit, this nursing care plan template will be utilized to ensure all goals of care are met seamlessly.
Assessment, symptom management, interventions, and monitored fluid status and fluid intake can be collated within the single care plan and safely stored in a single database. Monitoring urine-specific gravity can help assess hydration status and fluid balance. All this information is crucial to prevent complications and make it easier to conceptualize individualized treatment options.
Step 3: Store the chart securely
After reviewing the fluid volume deficit nursing care plan and creating a viable and individualized plan for the patient, you need to secure the plan so that access is only granted to relevant parties.
Ensure this through Carepatrons HIPAA-compliant free patient records software. All relevant medical records can be safely stored and collated for ease and security.
Explore our nursing care plan and care plan templates for added support in improving your practice and client results.
What to look out for
After conducting a comprehensive nursing assessment by performing a head-to-toe test and evaluating the patient's fluid intake and output, one may expect the following results and corresponding interpretations if the patient has fluid volume imbalance or deficit:
- Vital signs: Deviations in vital signs, such as tachycardia or hypotension, might indicate dehydration.
- Blood work: Abnormal blood work, including fluid and electrolyte imbalances, fluid volume excess, or renal function irregularities, might signify dehydration.
- Skin elasticity: Diminished skin turgor could signify dehydration.
- Urine color and concentration: Dark, concentrated urine might indicate dehydration. The suggested hourly urine output must be at least 30 mL.
- Cardiac sounds: Severe dehydration may produce abnormal cardiac sounds, potentially leading to dysrhythmias.
- Cardiac rhythm: Severe dehydration and concurrent electrolyte imbalances may contribute to the development of dysrhythmias.
- Mental status: Profound dehydration might lead to alterations in mental status.
Next steps
Nursing care and interventions are pivotal in the fluid balance and facilitating the patient's recovery from fluid volume deficit. Below are some of the key interventions which nurses may take in response to their assessment:
- Encourage or prompt the patient regarding oral fluid intake: Aging can diminish the sensation of thirst; reminders can aid in sustaining oral intake, even when not feeling thirsty.
- Provide intravenous hydration if necessary: Severe dehydration or inability to orally consume fluids may necessitate IV hydration to maintain optimal hydration levels. Administer IV fluids to improve blood flow and address insufficient fluid intake.
- Educate the patient and family on potential dehydration causes: Informing patients enhances comprehension of the diagnosis and empowers them with preventive measures against future dehydration episodes.
- Administer electrolyte replacements as prescribed: Dehydration can result in electrolyte imbalances, warranting vigilant monitoring and supplemental replacements as required.
- Instruct the patient and family on monitoring fluid intake and output: Equipping the patients with this knowledge post-discharge ensures they maintain adequate hydration levels.
- Conduct daily patient weight assessments: Regular weigh-ins enable easy monitoring for potential fluid overload during rehydration.
- Educate the patient on the significance of maintaining proper hydration and nutrition consistently: This instruction promotes patient independence upon discharge and instills awareness about preventing future episodes of dehydration.
Noting the interventions taken and the success of each intervention is critical for a comprehensive care plan.
Commonly asked questions
To create a comprehensive nursing care plan for fluid volume management, customize the plan from the scaffolding provided by Carepatron and cater to the patient's needs through the critical aspects of assessment, diagnosis, intervention, and evaluation.
These valuable plan templates can be used at any point of the treatment journey for a patient with fluid volume deficit to track, monitor, and plan all interventions by healthcare professionals and the patient themselves.
Fluid deficit nursing care plan templates plan efficient and confident care delivery. They are designed to be customized and meet the individual patient's needs.