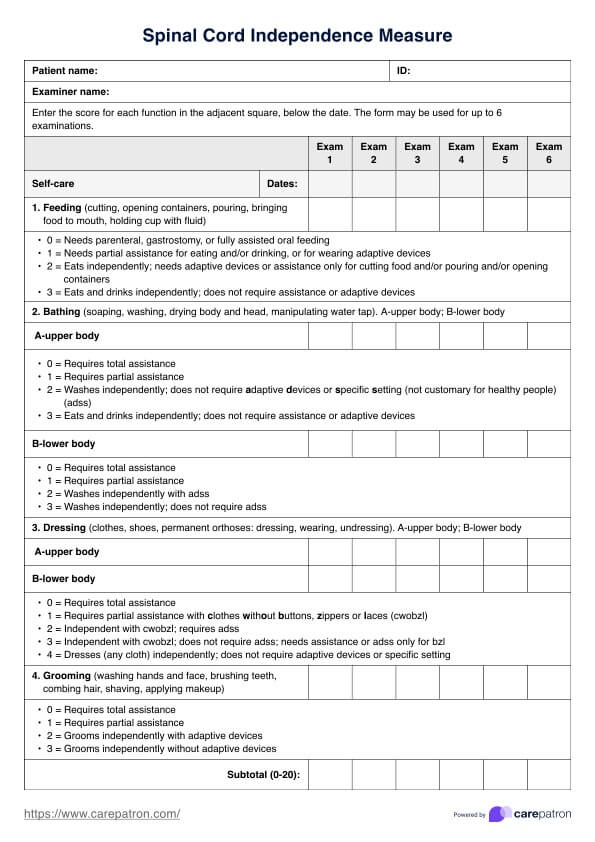
Back Pain Location Charts
Optimize the back pain assessment process with the Back Pain Location Chart. Download now to streamline your evaluation for improved patient care.


Understanding the causes of back pain
Understanding the causes of back pain, from upper back pain to chronic low back pain, is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. These causes can be divided into physical and emotional categories, each influencing the individual uniquely.
Here’s a look at some of the most common physical factors that contribute to back pain:
Physical back pain
Physical causes of back pain are varied and can stem from lifestyle factors and inherent medical conditions. They can result in people suffering from discomfort, stiffness, and limited mobility, thus impacting their daily activities and overall quality of life. Here’s a look at some of the most common physical factors that contribute to back pain:
- Muscle strains and other injuries: Muscle strain and muscle pain can result from heavy lifting, sudden movements, poor posture, and other injuries, such as trauma or falls.
- Spinal cord abnormalities: Conditions like lumbar spine scoliosis (curvature of the spine) and spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal) can lead to back pain.
- Degenerative disc disease: As people age, the discs in their spine can wear down, leading to back pain.
- Bulging or herniated disc: When the soft tissue between spinal vertebrae slips out of place, it can pressure nerves and cause pain.
- Osteoarthritis: This common form of arthritis can also affect the spine and cause back pain.
- Underlying health conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as fibromyalgia or kidney stones, can cause back pain.
Emotional back pain
Back pain isn't always purely physical; emotional factors can also play a significant role. Emotional back pain refers to physical discomfort in the back caused by psychosomatic or psycho-physiological issues, where symptoms stem directly from psychological and emotional factors. This means psychological factors either initiate or exacerbate the back pain.
The International Association for the Study of Pain (2021) notes that depressive symptoms can intensify back pain and increase associated disability. Individuals with back or neck pain are significantly more likely to experience common mental health problems, such as major depressive episodes and anxiety disorders. Despite being recognized as a psychosomatic condition, emotional back pain is not considered a formal medical diagnosis but rather an acknowledgment of the connection between emotional and physical distress.
Psychologists and other health professionals believe that emotional back pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, anxiety, depression, trauma, and unresolved emotional conflicts.
Back Pain Location Charts Template
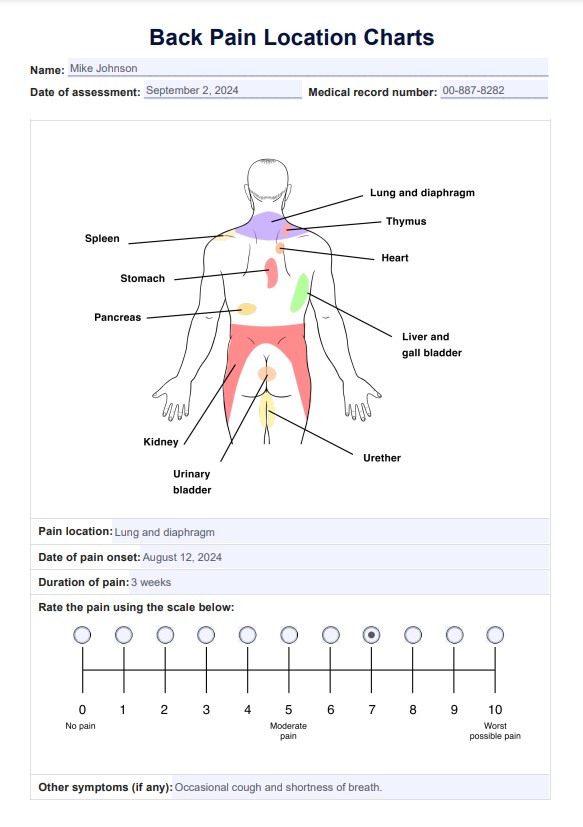
Back Pain Location Charts Example
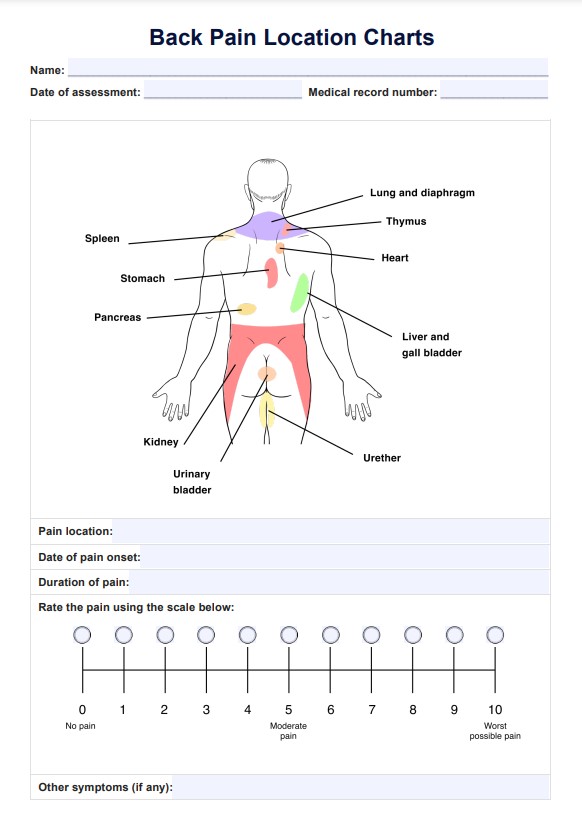
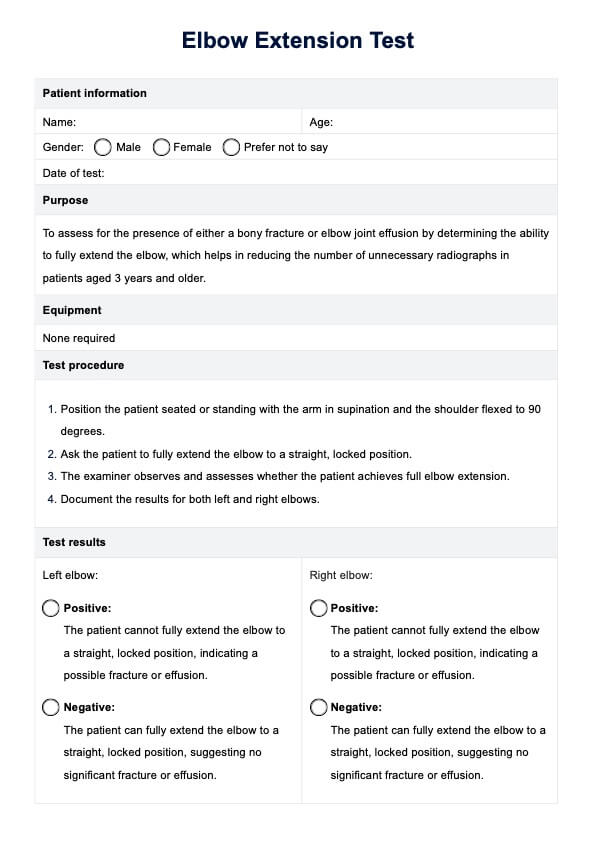
What is a Back Pain Location Chart?
Back pain is a common complaint that can manifest in various ways, depending on its location, severity, and the underlying cause. A Back Pain Location Chart assists in understanding where the pain originates and how it might radiate to other body regions. This visual and textual overview helps identify whether your patient is experiencing low back pain, back or neck pain, or pain in the upper back.
Healthcare providers can use this back pain chart or back diagram for pain and guidelines to build a diagnostic plan that may include physical examinations, medical history, and imaging tests. Aside from that it may also aid with creating a comprehensive treatment plan that includes management and prevention techniques designed to alleviate back pain symptoms like back pain radiating to the legs, as this could indicate a more severe issue, such as an intrapelvic mass and improve the patient’s quality of life.
How to use the Back Pain Location Chart
The Printable Back Pain Location Chart can significantly aid in accurately documenting and communicating back pain symptoms. Here are six essential steps to effectively utilize this resource:
Step 1: Download the chart
Begin by downloading this free form from our resources library.
Step 2: Fill out patient information
Start by filling out the patient information section at the top of the chart, including the patient's name, date of birth, and medical record number.
Step 3: Identify the pain location
Study the diagram of the human back provided on the back pain areas chart, which is typically divided into various regions.
Step 4: Document pain details
Specify the date of pain onset and its duration. Use the pain rating scale (ranging from 1 to 10) to rate the intensity of the pain, with 1 representing the slightest discomfort and 10 the most severe.
Step 5: Note additional back pain symptoms
Note any accompanying symptoms or sensations associated with the back pain, such as tingling, numbness, or weakness. This information provides valuable context, as other symptoms may make the pain worse.
Step 6: Include additional comments
Use the provided space for any extra comments or relevant details, such as factors that trigger the pain or previous treatments attempted.
When would you use this Back Pain Location Chart?
The Back Pain Location Chart can be used in various settings and situations. Here are instances when it's appropriate and highly beneficial to use:
- Medical assessment: Healthcare professionals, such as physicians, orthopedists, and physical therapists, use the upper and lower back pain location chart to assess back pain issues accurately. It aids in understanding the exact location and characteristics of the pain, which is vital for determining potential causes and appropriate treatment plans to relieve pain in the back.
- Chiropractic care: Chiropractors can utilize the chart to identify the specific areas of discomfort or misalignment in the spine. This information guides chiropractic adjustments and helps monitor patients' progress in receiving chiropractic care.
- Orthopedic consultations: Orthopedic specialists can use the back pain chart when assessing patients with chronic or complex lower back issues. It aids in localizing the pain and guides decisions about surgical interventions, if necessary.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapists often incorporate body pain charts into patient assessments, helping patients accurately describe pain and its location. It assists in tailoring rehabilitation programs to target the affected area, facilitating a more focused and effective recovery process.
- Pain management clinics: Pain management specialists rely on this form to comprehensively evaluate and manage patients with chronic back pain. It aids in developing personalized pain management strategies.
- Patient communication: Patients themselves can benefit from using the back pain chart or back pain map as a communication tool with their healthcare providers. It allows them to provide detailed information about their pain, aiding in more informed discussions and decisions regarding their care.
Reference
International Association for the Study of Pain. (2021, July 9). Psychology of back pain. https://www.iasp-pain.org/resources/fact-sheets/psychology-of-back-pain/
Commonly asked questions
A Back Pain Locator Chart is a visual tool that helps patients and healthcare providers pinpoint the areas of the back where pain is felt, facilitating accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Anxiety and depression are commonly associated with chronic pain, as ongoing discomfort can significantly impact emotional well-being.
To reduce worry about back pain, engage in regular gentle exercise, practice stress-relief techniques such as mindfulness or meditation, and consult with a healthcare professional to develop a management plan tailored to your specific condition.