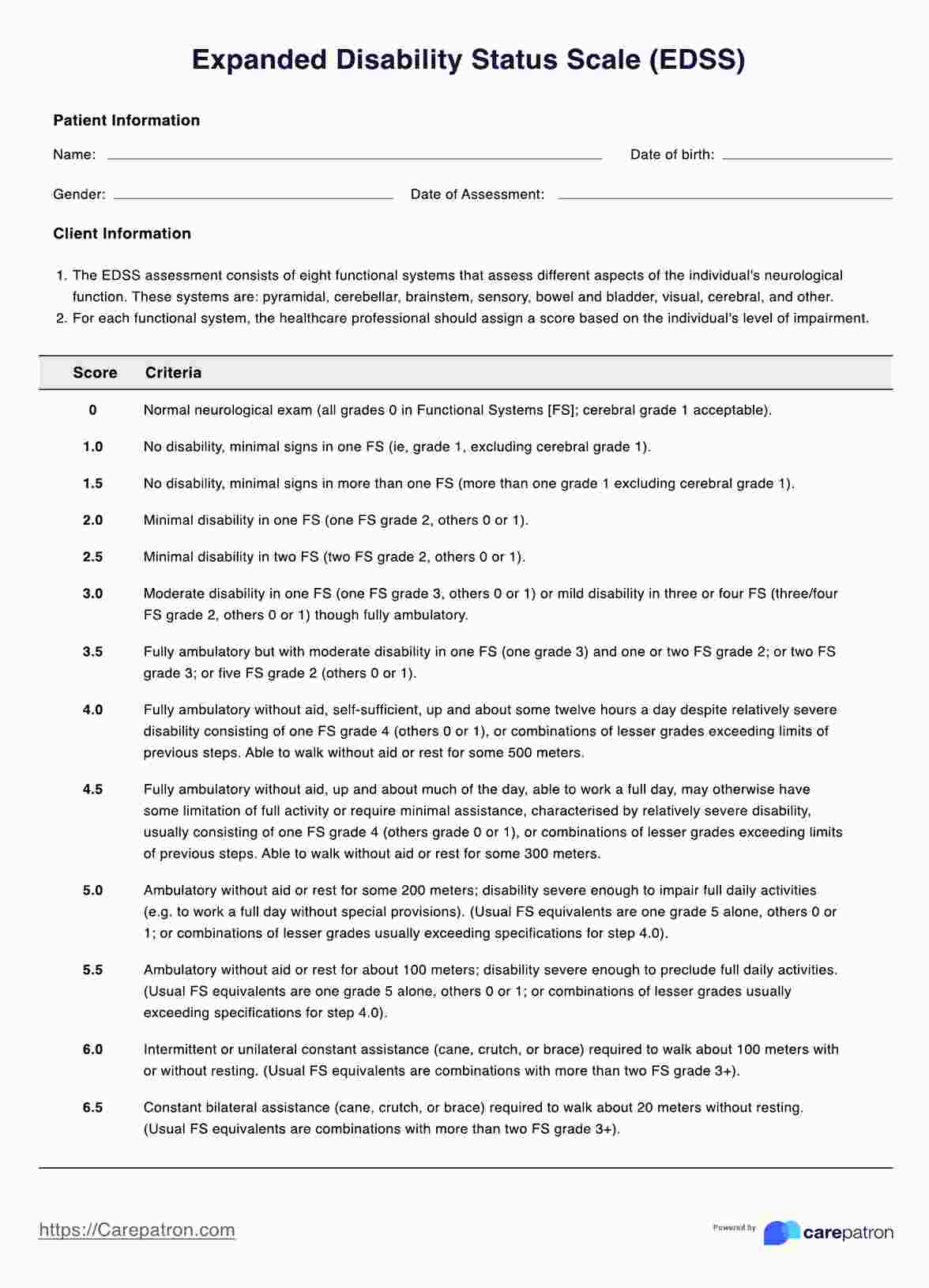
ADL Coding Cheat Sheet
Discover our ADL Coding Cheat Sheet, an essential tool for healthcare professionals to assess and document patients' daily activities efficiently.


What are activities of daily living (ADLs)?
Activities of daily living (ADLs) are routine aspects of daily functioning essential for self-care and independence. Specific ADLs include basic self-care tasks like eating, bathing, dressing, toileting, bed mobility, transferring (moving from a bed to a chair), maintaining personal hygiene, and continence. They are foundational skills typically learned in early childhood.
ADLs are coded in healthcare settings to assess patients' functional status on a spectrum of self-care ability, from complete independence to total dependence on caregivers. This aids in determining the level of assistance a patient requires with daily activities and their specific care needs.
ADL coding involves observing and assessing an individual's ability to perform these activities. Healthcare providers use a standardized coding system to document the extent to which each ADL can be done independently, determining the overall ADL score. Accurate ADL documentation is critical for creating effective care plans, ensuring appropriate staffing and resources, and facilitating communication among the healthcare team and family members.
Inaccurate or incomplete ADL coding can lead to inadequate care plans, affecting a patient's recovery and overall well-being. It can also impact billing and reimbursement processes in healthcare facilities. Accurate ADL documentation is a cornerstone of quality healthcare and essential to high-quality care and efficient healthcare operations.
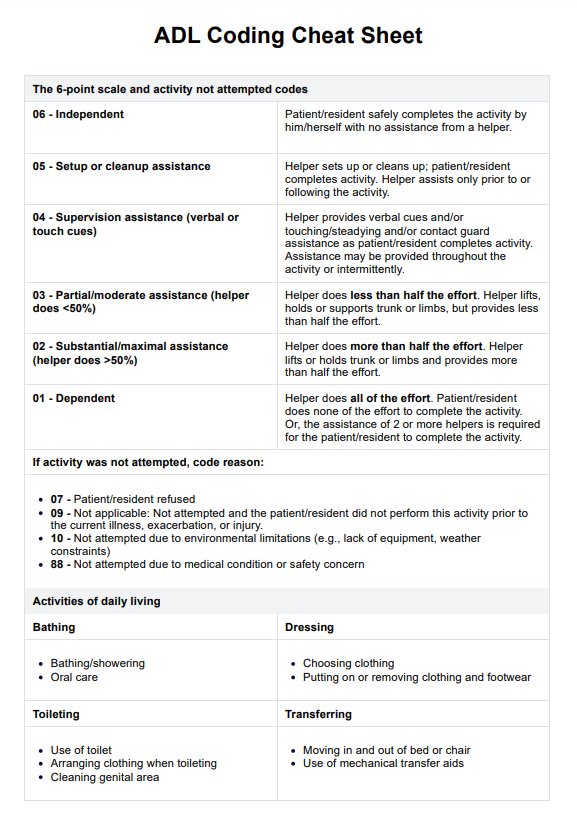
ADL Coding Cheat Sheet Template
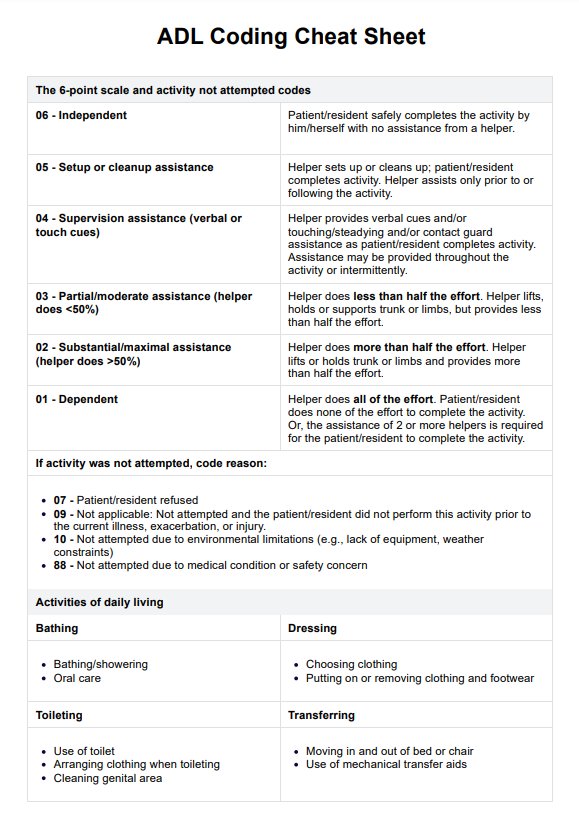
ADL Coding Cheat Sheet Example
How does the ADL Coding Cheat Sheet work?
The ADL Coding Cheat Sheet is a practical tool designed to support healthcare providers in recording and assessing activities of daily living (ADLs). This is based on the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services' (2020) Coding Section GG Self-Care & Mobility Activities. Here's how it works:
Step 1: Access the cheat sheet
Easy access to our printable ADL Coding Cheat Sheet is available via the Carepatron app. This cheat sheet PDF is designed as a quick reference tool, allowing easy note-taking and ADL assessment.
Step 2: Familiarization of ADL categories
Each activity (e.g. bathing, dressing, eating) is documented using its own standard ADL category. For this cheat sheet, we included the categories based on the Katz Index of Independence in Activities of Daily Living.
Step 3: Observe the patient
Observe the patient performing various ADLs under supervision. Pay attention to how independently they can perform each task to determine their individual needs.
Step 4: ADL coding
Refer to the cheat sheet to code each ADL based on the patient's performance. The sheet provides a clear way to assign codes that reflect the level of assistance required for each activity.
Step 5: Document additional notes
You can also input your observations and insights in the additional notes section. This can be done directly in Carepatron's software, ensuring that all data is stored securely and is easily accessible.
Next steps
After utilizing the ADL Coding Cheat Sheet, healthcare professionals should follow a series of steps to ensure effective and comprehensive patient care. These next steps are critical in translating ADL assessments into meaningful care strategies. Here are some important actions to consider:
Review and analyze ADL data
Once ADL coding is complete, review and analyze the data to gain insights into the patient's functional abilities and limitations. This step is crucial in understanding the patient's overall health and needs.
Develop a personalized care plan
Based on the ADL assessment and coding results, develop a personalized care plan that addresses the patient's specific requirements. This may involve setting goals for better functioning, determining necessary support services, and outlining interventions to improve or maintain the patient's functional abilities.
Collaborate with the care team
Collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as doctors, therapists, and caregivers, to ensure a coordinated approach to the patient's care. Sharing ADL assessment findings can help align the care plan with the patient's treatment objectives.
Monitor and reassess regularly
Regular monitoring and reassessment of the patient's ADL capabilities are vital. Changes in the patient's condition may require adjustments to the care provided, and continuous reassessment ensures that the care remains relevant and effective.
Communicate with the patient and family
Keep the patient and their family informed about the assessment findings and consider their preferences when formulating a care plan. Engaging them in care decisions can improve compliance and satisfaction with treatment processes.
By following these steps, healthcare professionals can translate ADL assessments into actionable care plans, enhancing patient care and outcomes.
Benefits of using this cheat sheet
The ADL Coding Cheat Sheet offers numerous benefits for healthcare professionals, especially in streamlining patient assessments and care planning. Here are some key advantages:
Efficient assessment
The ADL charting cheat sheet simplifies the coding process, allowing quick and efficient evaluations of a patient's functioning. Using this quick reference tool saves valuable time healthcare professionals would otherwise spend looking up coding criteria or guidelines. This efficiency is crucial in fast-paced healthcare environments.
Enhanced accuracy and consistency
Accurate ADL coding is essential for developing appropriate care plans and ensuring patient safety. The cheat sheet provides clear coding criteria, helping reduce assessment errors and ensuring standards are consistent across healthcare providers. Consistent documentation is vital for tracking patient progress and communication among care team members.
Facilitates communication
The cheat sheet allows for standardized communication about care needs between various multidisciplinary healthcare team members. Seamless communication is crucial for coordinating care and making informed decisions.
Educational tool
The cheat sheet serves as an educational resource for new staff or students, providing a clear understanding of ADL coding and its significance in patient care.
Enhanced decision-making
With accurate ADL information, healthcare professionals can make more informed decisions about the level of care and support a patient requires.
Tips for effective ADL documentation
Effective documentation is an essential part of healthcare, crucial for maintaining high-quality patient care and clear communication. Here are comprehensive tips to enhance documentation practices:
Accuracy and timeliness
Ensure ADL documentation is precise and updated promptly. Accurate and timely records reduce errors and provide a reliable account of patient care, which is crucial for ongoing treatment planning or potential insurance claims. Document interactions and assessments immediately after they occur to capture details accurately.
Use standardized tools and objective language
Implement standardized tools to maintain assessment consistency. Use objective language when documenting observations and patient responses. Avoid personal bias or subjective interpretations that might skew the factual representation of patient care.
Legibility and detail-oriented approach
Legibility is key, whether in electronic records or handwritten notes. Use clear formatting and straightforward language. Document all relevant details, including responses to treatments, changes in conditions, and important interactions, to provide a comprehensive picture of the patient's health status.
Privacy and confidentiality compliance
Adhere strictly to privacy laws and regulations. Securely store documentation to protect patient confidentiality. This includes carefully handling electronic records and access controls to ensure only authorized personnel view sensitive patient information.
Implementing these tips can significantly improve the quality of clinical documentation, leading to better patient care and more efficient healthcare services.
Reference
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. (2020). Coding Section GG self-care & mobility activities included on the post-acute care item sets: Key questions to consider when coding. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Quality-Initiatives-Patient-Assessment-Instruments/HomeHealthQualityInits/Downloads/GG-Self-Care-and-Mobility-Activities-Decision-Tree.pdf
Commonly asked questions
ADL coding provides a categorical system for physicians, nurses, and other care providers to assess a patient's ability to perform various essential activities of daily living (ADLs). It helps assess a patient's functional status and need for assistance in basic daily tasks, which is crucial for care planning.
The rule of 3 in ADL coding refers to categorizing ADLs based on the level of assistance needed: independent (no help), some help (up to two times), and dependent (three or more times or total assistance).
ADLs are scored based on the patient's level of independence from 0 to 6. A higher score indicates a greater ability to perform that activity independently. Scoring criteria vary depending on the specific ADL coding system.