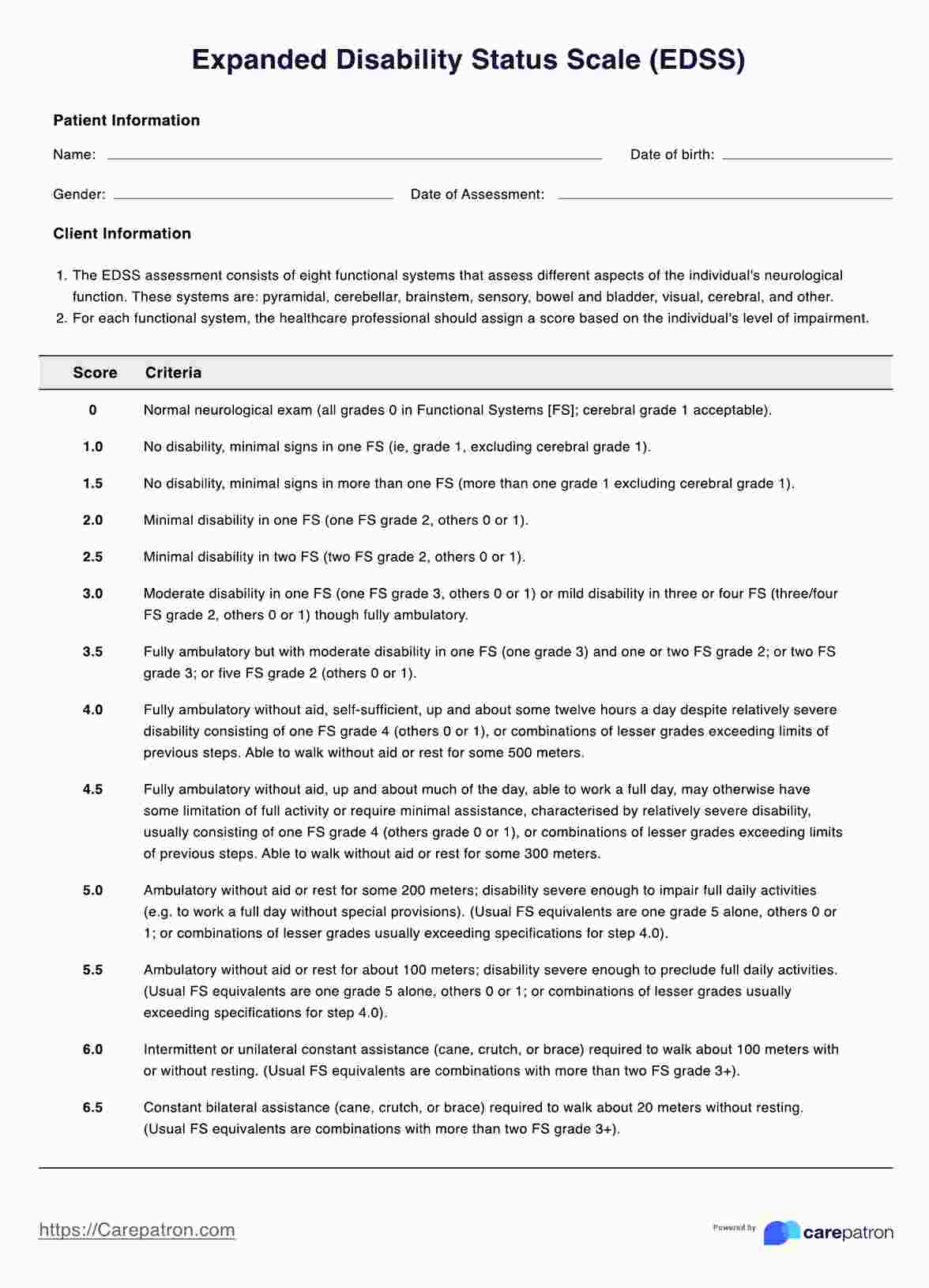
Based on the patient's neurological examination and functional assessment, the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) assigns a score. The exam covers eight functional systems and the person's overall level of disability, and scores range from 0 to 10 in half-point increments. The final score is based on the individual's highest level of disability in any functional system and ranges from 0 (no disability) to 10 (death due to MS).
Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS)
The Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) assesses the degree of disability in patients with multiple sclerosis. Download this PDF to learn more!
Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) Template
Commonly asked questions
The interpretation of the EDSS score involves understanding the individual's level of disability and impairment. The score ranges from 0 to 10, with higher scores indicating a more severe disability. A score of 0 to 3.5 indicates mild to moderate disability, with the individual being able to walk without assistance. A score of 4 to 6.5 indicates significant disability, with the individual needing some form of assistance for walking. A score of 7 to 9.5 indicates severe disability, with the individual using a wheelchair and requiring constant assistance.
Depending on the person's level of disability and the progression of their illness, the frequency of EDSS evaluations may vary. However, giving the test at least once a year is typically advised.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











