The five basic activities of daily living (ADLs) are based on the six functions from the Katz Index. These include bathing, dressing, toileting, transferring, and the ability to feed oneself. These activities reflect a person's ability to manage essential self-care tasks in an assisted living community. The sixth ADL is controlling continence, which some organizations merge with toileting.
Activities Of Daily Living
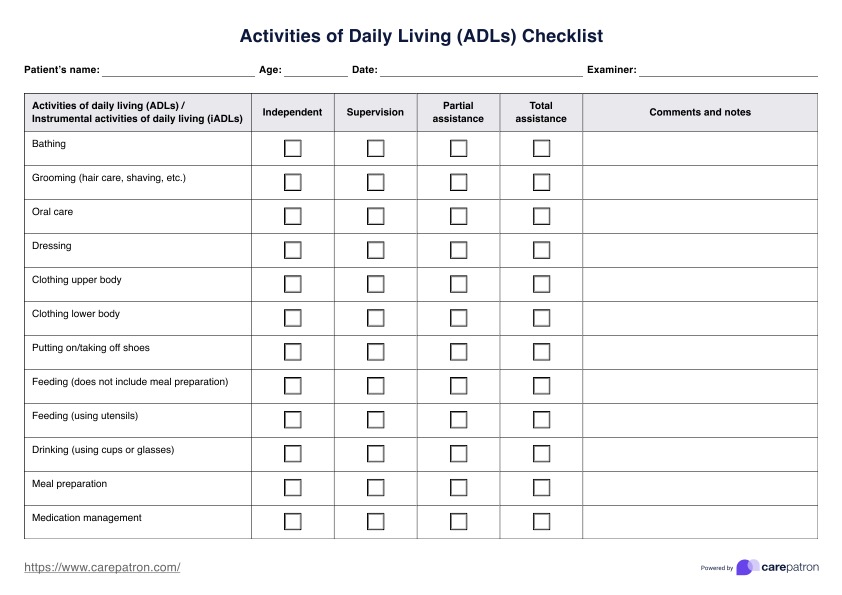
Download our Activities of Daily Living Checklist to better assess your patient's independence. Be better informed when coming up with your care plan.
Activities Of Daily Living Template
Commonly asked questions
The seven instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs) assess a person's ability to live independently and manage everyday life. These IADLs are managing finances, handling transportation, meal preparation, shopping, using communication devices, managing medications, and housekeeping.
The NHS defines 12 activities of daily living as personal care, mobility, eating and drinking, elimination (bladder and bowel function), controlling temperature, keeping safe, communicating, breathing, maintaining relationships, working and playing, expressing sexuality, and selecting appropriate clothes. Additionally, being able to pay bills and manage personal finances is included under IADLs.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











