This ratio helps in identifying kidney health issues. Abnormal ratios can indicate potential kidney problems such as kidney disease, diabetes-related complications, or high blood pressure.
Protein/Creatinine Ratio Chart
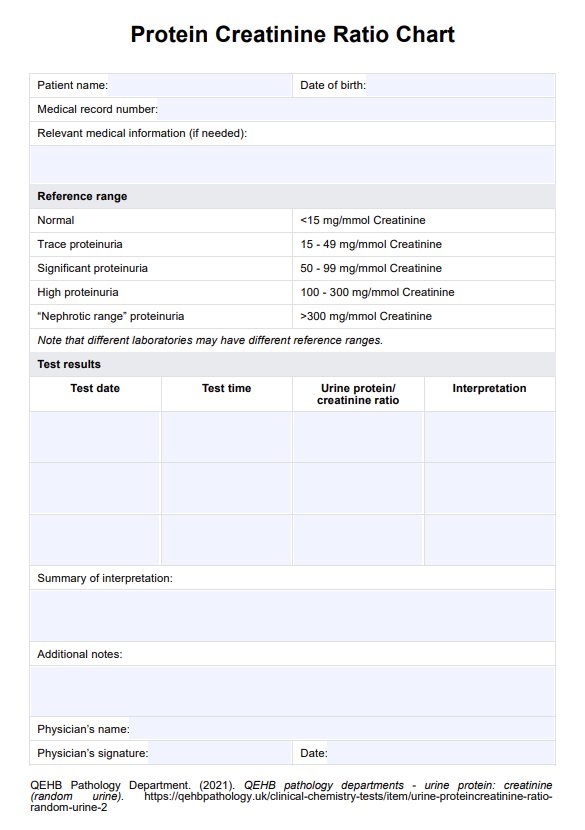
Better assess your patient's kidney function by using our Protein/Creatinine Ratio Chart.
Use Template
Protein/Creatinine Ratio Chart Template
Commonly asked questions
It's calculated by dividing the measured protein concentration in the urine by the measured creatinine concentration. The ratio is expressed as milligrams of protein per milligram of creatinine (mg/mg).
The normal range falls between 0.15 to 0.25 mg/mg. Ratios above this range can indicate proteinuria (excessive protein in urine), suggesting possible kidney issues. Ratios below this range may indicate low protein levels or other kidney-related problems.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











