Common challenges when starting a gluten-free or no-grain diet include difficulty finding suitable food options, as many processed foods contain gluten or grains. Individuals may also experience cravings for familiar grain-based foods, which can lead to feelings of deprivation. Additionally, transitioning to a new diet often requires careful meal planning and preparation to ensure nutritional adequacy.
No Grain Diet Food List
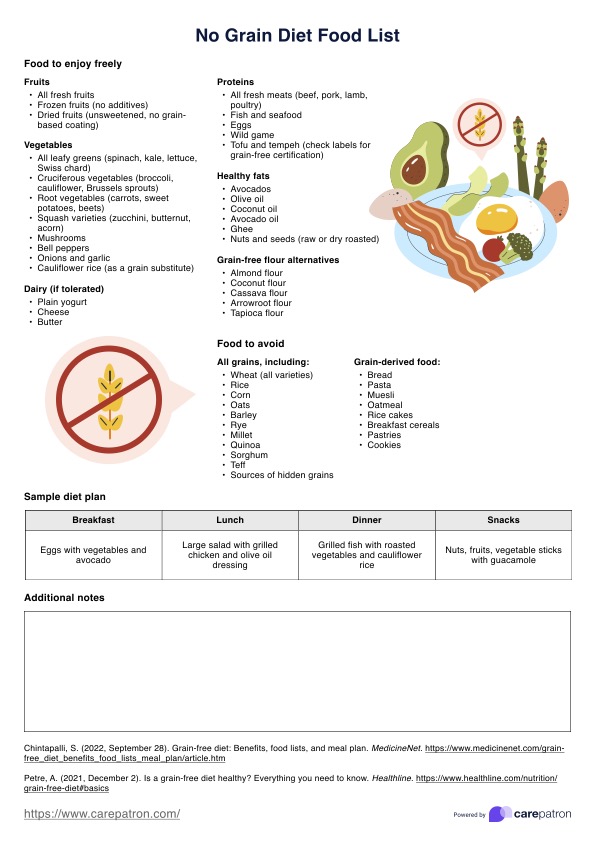
Download a handy No Grain Diet Food List PDF to guide patients in adopting a grain-free diet.
No Grain Diet Food List Template
Commonly asked questions
Individuals can eat various whole foods on a grain-free diet, including fruits, vegetables, lean meats, fish, eggs, nuts, seeds, and healthy fats such as olive oil and avocado. If tolerated, dairy products like cheese and yogurt are also typically included. Legumes and pseudo-grains like quinoa and buckwheat may also be consumed as they do not fall under traditional grains.
A grain-free diet excludes all grains, encompassing wheat, rice, corn, oats, barley, and any products made from these grains, such as bread, pasta, cereals, and baked goods. Additionally, processed foods containing grain-based ingredients or additives are also avoided. This diet focuses on eliminating foods that contain gluten or other grain proteins to reduce potential inflammation or digestive issues.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











